Project
Work
of
Computer
� Types of
Computers
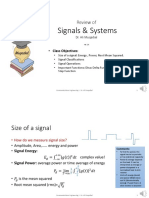
On the basis of On the basis of On the basis of On the basis of
work size brand model
Analog
computers Microcomputers IBM PCs XT computers
Digital
computers Minicomputers IBM compatibles AT computers
Hybrid Mainframe
computers computers Apple/Macintosh PS/2 computers
Super Pentium
computers computers
�On the basis of working principle:
a) Analog Computers
b) Digital Computers
c) Hybrid Computers
� Analog Computers
An analog computer is a computer which is used to process
analog data. Analog computers store data in a continuous form
of physical quantities and perform calculations with the help of
measures. It is quite different from the digital computer, which
makes use of symbolic numbers to represent results.
� Digital Computers
Digital Computer, any of a class of devices capable of solving problems
by processing information in discrete form. It operates on data,
including magnitudes, letters, and symbols, that are expressed in binary
code. By counting, comparing, and manipulating these digits or their
combinations according to a set of instructions held in its memory, a
digital computer can perform such tasks as to control industrial
processes and regulate the operations of machines; analyze and organize
vast amounts of business data; and simulate the behaviour of dynamic
systems in scientific research.
� Hybrid Computers
Hybrid computers are computers that exhibit features of
analog computers and digital computers. The digital
component normally serves as the controller and
provides logical and numerical operations, while the
analog component often serves as a solver of differential
equations and other mathematically complex equations.
� On the basis of size:
a)Microcomputers
b)Minicomputers
c)Mainframe computers
d)Super computers
� Microcomputers
Microcomputer, an electronic device with a
microprocessor as its central processing unit
(CPU). Microcomputer was formerly a commonly
used term for personal computers, particularly
any of a class of small digital computers whose
CPU is contained on a single integrated
semiconductor chip.
� Minicomputer
A minicomputer, or colloquially mini, is a class of smaller
general purpose computers that developed in the mid-1960s and
sold for much less than mainframe and mid-size computers from
IBM and its direct competitors. In a 1970 survey, The New
York Times suggested a consensus definition of a minicomputer
as a machine costing less than US$25,000, with an input-
output device such as a teleprinter and at least four thousand
words of memory, that is capable of running programs in a
higher level language, such as Fortran or BASIC.
� Mainframe Computers
A mainframe computer, informally called a mainframe or big iron, is a
computer used primarily by large organizations for critical applications
like bulk data processing for tasks such as censuses, industry and consumer
statistics, enterprise resource planning, and large-scale transaction
processing. A mainframe computer is large but not as large as a
supercomputer and has more processing power than some other classes of
computers, such as minicomputers, servers, workstations, and personal
computers. Most large-scale computer-system architectures were
established in the 1960s, but they continue to evolve. Mainframe
computers are often used as servers.
� Super Computers
A supercomputer is a computer with a high level of
performance as compared to a general-purpose computer.
The performance of a supercomputer is commonly measured
in floating-point operations per second (FLOPS) instead
of million instructions per second (MIPS). Since 2017,
there are supercomputers which can perform over 1017
FLOPS (a hundred quadrillion FLOPS, 100 petaFLOPS
or 100 PFLOPS).
� On the basis of brand:
a)IBM PCs
b)IBM Compatibles
c)Apple/Macintosh
� IBM PCs
The computers manufactured by IBM company are called
IBM computers. The microcomputers of IBM Company
are called IBM PC. IBM, established by Dr Herman
Hollerith in 1945, is one of the leading companies in
computer manufacturing. These are reliable, strong and
have high processing speed. These are of original types and
quite expensive than others.
� IBM Compatibles
Computers, developed on the principles of IBM
computers are called IBM compatible. They can
perform all the tasks that an IBM computer does.
They are less expensive than originals (IBM)
computers. IBM computers share nearby 80% in the
world and 95% in Nepal.
� Apple/Macintosh
The computers manufactured by the Apple Company
are called Apple computers. These computers are
original and quite expensive than IBM and IBM
Compatible. The operating system and other peripherals
are completely different from IBM and IBM
compatibles.
� On the basis of model:
a)XT computers
b)AT computers
c)PS/2 computers
d)Pentium computers
� XT Computers
XT (Extended Technology) computers are initial personal computer of
IBM company. These computers had 8086 and 8088 processor with 640
KHz – 4.77 to 8 MHz speed. The IBM Personal Computer XT (model
5160, often shortened to PC/XT) is the second computer in the IBM
Personal Computer line, released on March 8, 1983. Except for the
addition of a built-in hard drive and extra expansion slots, it is very
similar to the original IBM PC model 5150 from 1981.
� AT Computers
AT(advanced technology) computers are the successors
of XT personal computers. They had the microprocessors
like 80286 (with speed 1.2 MHz – 10 to 16 MHz),
80386 (with speed 1.2 MHz – 16 to 25 MHz) and
80486 (with speed 4 MHz – 25 to 63 MHz). AT
computers were faster than XT computers.
� PS/2 Computers
PS/2 computers are IBM computers developed in early 1990s. These were
faster and better than previous model of IBM computers. Most of the
computers and laptops were based on PS/2 model. The Personal System/2
or PS/2 is IBM's third generation of personal computers. Released in 1987,
it officially replaced the IBM PC, XT, AT, and PC Convertible in IBM's
lineup. Many of the PS/2's innovations, such as the 16550 UART (serial
port), 1440 KB 3.5-inch floppy disk format, Model M keyboard layout, 72-
pin SIMMs, the PS/2 port, and the VGA video standard, went on to
become standards in the broader PC market.
� Pentium computers
The Pentium are the computers which used the microprocessor
from the Intel Corporation. Earlier Pentium computers had
Pentium I processor with the speed of 16 MHz – up to 200
MHz. Then the processors improved continuously. Pentium
IV computers had the microprocessor with speed of 2.8 GHz.
Besides, Intel Corporation started to upgrade its processor.
Dual core, Core 2 duo, i₃, i₅, i₇ are the succeeding processors
with high speed used in the desktop computers and laptops.
� The End
Made By: Kritagya Dahal
Class: 8
Section: Annapurna
Submitted to: Trivendra Sir