0% found this document useful (0 votes)
52 views5 pagesBiography: LK 1: Lembar Kerja Belajar Mandiri
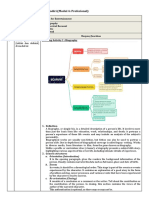
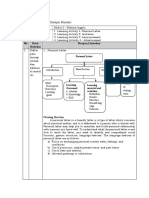
The document discusses different types of texts used in English for entertainment including biography, historical recount, fables, and legends. It provides definitions and characteristics for each genre as well as examples and templates for their common grammatical and structural features.
Uploaded by
DindaCahyaKurniaPutriCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
52 views5 pagesBiography: LK 1: Lembar Kerja Belajar Mandiri
The document discusses different types of texts used in English for entertainment including biography, historical recount, fables, and legends. It provides definitions and characteristics for each genre as well as examples and templates for their common grammatical and structural features.
Uploaded by
DindaCahyaKurniaPutriCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 5