0% found this document useful (0 votes)
230 views3 pagesResistor Basics: Types, Series, Parallel
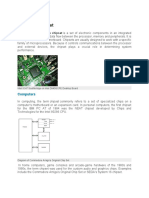
Resistors are used to limit current in electrical circuits. There are different types of resistors like carbon, film, and wirewound. Resistor color codes identify a resistor's resistance and tolerance. Resistors can be connected in series or parallel. In a series circuit, the total resistance is the sum of individual resistances and the current is the same through each resistor. In a parallel circuit, the total resistance is lower than the lowest individual resistance and the voltage is the same across each resistor. Resistors have power ratings that must not be exceeded to avoid overheating.
Uploaded by
raj grdCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
230 views3 pagesResistor Basics: Types, Series, Parallel
Resistors are used to limit current in electrical circuits. There are different types of resistors like carbon, film, and wirewound. Resistor color codes identify a resistor's resistance and tolerance. Resistors can be connected in series or parallel. In a series circuit, the total resistance is the sum of individual resistances and the current is the same through each resistor. In a parallel circuit, the total resistance is lower than the lowest individual resistance and the voltage is the same across each resistor. Resistors have power ratings that must not be exceeded to avoid overheating.
Uploaded by
raj grdCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 3