0% found this document useful (0 votes)
219 views10 pagesBoolean Logic & Logic Gates Guide
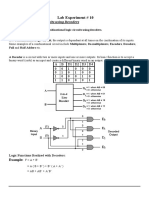
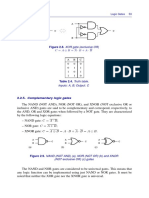
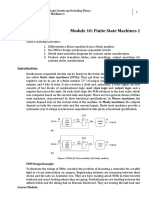
This document discusses binary logic and logic gates. It defines binary logic as using binary variables of 1 and 0 with logical operators like AND, OR, and NOT. Truth tables are used to show the relationship between inputs and outputs. Common logic gates are described, including their symbols and functions. AND returns 1 if both inputs are 1, while OR returns 1 if either input is 1. NOT inverts the input. Combinational logic circuits are built from interconnected gates and their output is determined immediately based on current inputs.
Uploaded by
Ben GwenCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
219 views10 pagesBoolean Logic & Logic Gates Guide
This document discusses binary logic and logic gates. It defines binary logic as using binary variables of 1 and 0 with logical operators like AND, OR, and NOT. Truth tables are used to show the relationship between inputs and outputs. Common logic gates are described, including their symbols and functions. AND returns 1 if both inputs are 1, while OR returns 1 if either input is 1. NOT inverts the input. Combinational logic circuits are built from interconnected gates and their output is determined immediately based on current inputs.
Uploaded by
Ben GwenCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 10