0% found this document useful (0 votes)
301 views6 pagesPower BI DAX Functions Guide
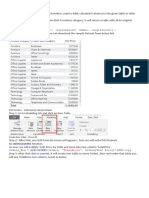
DAX is a formula language used to manipulate and analyze data in Power BI. It allows users to perform calculations on data like finding sums, averages, and other aggregations. DAX formulas create calculated columns and measures. Calculated columns add new fields to existing tables, while calculated measures aggregate data and create new fields. The syntax of DAX formulas includes the formula name, an equals sign, functions, and table and field references. Formulas are evaluated from the inside out.
Uploaded by
Senthil KumarCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
301 views6 pagesPower BI DAX Functions Guide
DAX is a formula language used to manipulate and analyze data in Power BI. It allows users to perform calculations on data like finding sums, averages, and other aggregations. DAX formulas create calculated columns and measures. Calculated columns add new fields to existing tables, while calculated measures aggregate data and create new fields. The syntax of DAX formulas includes the formula name, an equals sign, functions, and table and field references. Formulas are evaluated from the inside out.
Uploaded by
Senthil KumarCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 6