0% found this document useful (0 votes)
58 views26 pagesC++ Code Assessment
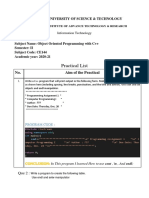
The document contains C++ code snippets for solving various math problems:
1) Solving quadratic equations by taking user input for coefficients a, b, c and calculating the discriminant and roots.
2) Calculating volume and surface area of a hemisphere by taking user input for diameter and calculating radius.
3) Calculating next 50 terms of a sequence by taking user input for first two terms and applying the recurrence relation formula.
4) Performing matrix addition and subtraction of 2x2 matrices by defining the matrices and iterating through them.
5) Evaluating functions like f(x)=xsin(x)-3 and f(x)=cos(x)-sin(x)-x at different points
Uploaded by
SuyashCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
58 views26 pagesC++ Code Assessment
The document contains C++ code snippets for solving various math problems:
1) Solving quadratic equations by taking user input for coefficients a, b, c and calculating the discriminant and roots.
2) Calculating volume and surface area of a hemisphere by taking user input for diameter and calculating radius.
3) Calculating next 50 terms of a sequence by taking user input for first two terms and applying the recurrence relation formula.
4) Performing matrix addition and subtraction of 2x2 matrices by defining the matrices and iterating through them.
5) Evaluating functions like f(x)=xsin(x)-3 and f(x)=cos(x)-sin(x)-x at different points
Uploaded by
SuyashCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 26