0% found this document useful (0 votes)
102 views4 pagesHW2 Solution
(1) The document is a homework solution for a digital communications course. It contains answers to 4 questions regarding Fourier transforms and filtering of signals.
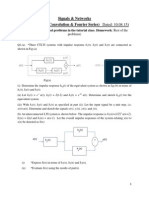
(2) Question 1 involves taking the Fourier transform of two signals - an exponential function and the inverse Fourier transform of two delta functions. Question 2 deals with finding the Fourier transforms of scaled and time-shifted triangular pulses.
(3) Question 3 involves filtering signals with low-pass filters and finding the bandwidth of the output signals. The last question asks the student to use time-shifting properties and a Fourier transform table to determine the Fourier transforms of various signals.
Uploaded by
ThienPhuc TranCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
102 views4 pagesHW2 Solution
(1) The document is a homework solution for a digital communications course. It contains answers to 4 questions regarding Fourier transforms and filtering of signals.
(2) Question 1 involves taking the Fourier transform of two signals - an exponential function and the inverse Fourier transform of two delta functions. Question 2 deals with finding the Fourier transforms of scaled and time-shifted triangular pulses.
(3) Question 3 involves filtering signals with low-pass filters and finding the bandwidth of the output signals. The last question asks the student to use time-shifting properties and a Fourier transform table to determine the Fourier transforms of various signals.
Uploaded by
ThienPhuc TranCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 4