0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views10 pagesNotes Part 3
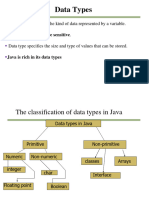
The document discusses character sets and data types in Java. It defines a character set as a set of graphical and textual symbols mapped to positive integers. It states that Java uses Unicode as its character set, which is an international standard capable of representing most world languages. It also discusses the different Java primitive data types like byte, char, short, int, long, float, double, and boolean along with their sizes and value ranges.
Uploaded by
Gunachitra PGTCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views10 pagesNotes Part 3
The document discusses character sets and data types in Java. It defines a character set as a set of graphical and textual symbols mapped to positive integers. It states that Java uses Unicode as its character set, which is an international standard capable of representing most world languages. It also discusses the different Java primitive data types like byte, char, short, int, long, float, double, and boolean along with their sizes and value ranges.
Uploaded by
Gunachitra PGTCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 10