CONFIGURATION OF COMPUTER SYSTEM
Hardware: Physical devices of the computer such as keyboard, monitor, printer,
processor and motherboard.
Software: Set of instructions called programs that instructs the computer the
tasks to be performed and how it should be performed.
Data: values or raw facts which are processed by computer to give meaningful
information.
Users: people who write computer programs or interact with the computer.
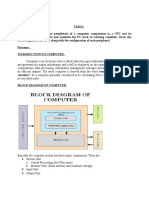
BLOCK DIAGRAM OF COMPUTER SYSTEM
The computer device comprises of four main units:
1. Input unit: The input unit accepts data from the user and converts it into a form
understandable by the computer. The input is given by input devices like keyboard,
mouse etc.
2. CPU (Central Processing Unit): CPU controls, coordinates and supervises the
operations of the computer. It processes the input data. CPU consists of:
a. ALU (Arithmetic and Logic Unit): It performs all arithmetic and logical
operations on input data.
b. CU (Control Unit): It checks the sequence of execution of instructions, controls
and coordinates the overall functioning of the units of computer.
c. Registers: These are high speed storage unit within the CPU. They are used to
temporarily store data, instructions, addresses and intermediate results of
processing.
1
� 3. Storage Unit: Primary memory (main memory) stores the data, instructions,
intermediate results and output temporarily during processing. Secondary
(external) memory stores the data, programs and the output permanently.
4. Output Unit: Output unit provides the processed data in user understandable form.
For Eg. Monitor, printer, speaker etc.
MOTHER BOARD (SYSTEM BOARD)
It is a large Printed Circuit Board (PCB) having many chips, ports, controllers and
other electronic components mounted on it.
It is the main circuit board inside the computer.
It provides a platform for all the components and peripherals to communicate with
each other.
Characteristics of motherboard
The motherboard is characterized by
1. Form factor: This refers to the motherboard‟s geometry, dimensions, arrangement
and electrical requirements. ATX (Advanced Technology Extended) is the most
common design of motherboard for desktop computers.
2. Chipset: Chipset coordinates data transfer between the various components of the
computer. To maximize the computer‟s upgradeability, we need to choose the
motherboard which has a recent chipset.
3. Processor socket: It is a rectangular connector into which the processor is
mounted vertically. It could also be a square shaped connector with many small
connectors into which the processor is directly inserted.
Types of motherboard
1. XT – eXtended Technology: These are old model motherboard.
It has old model processor socket.
RAM slot DIMM and ISA(Industry Standards Architecture) slots.
12 pin power connector and no ports.
Example: Pentium I , Pentium II processors.
2. AT – Advanced Technology:
They have PGA (Pin Grid Array) processor socket.
SDRAM slots.
20 pin power connector PCI slots and ISA slots.
Example: Pentium-III processor.
2
� 3. Baby AT: These have the combination of XT and AT.
These have slot type processor sockets and PGA processor sockets.
SDRAM and DDRRAM slots.
PCI and ISA slots.
12 and 21 pin power connector and have ports.
Example: Pentium-III , Pentium –IV processor.
4. ATX – Advanced Technology eXtended: These are the latest motherboards.
These have MPGA processor sockets.
DDRRAM slots.
PCI and AGP slots.
Primary and secondary IDE interfaces, SATA connectors.
20 and 24 pin ATX power connectors and ports.
Example: Pentium-IV, Dual core, Core 2 Duo, Quad Core, i3,i5,i7 processors.
COMPONENTS OF A MOTHERBOARD
1. Processor (CPU)
Processor or CPU is the main component on the motherboard.
CPU gets data and instructions from the memory, interprets the program
instructions and performs the arithmetic and logical operations required for
the processing of data. The processed data is sent to the memory.
A microprocessor is a tiny integrated circuit(IC) chip that contains the
entire computation engine. INTEL is one of the leading processor
manufacturers.
2. BIOS (Basic Input Output System)
It is a small chip on motherboard that holds the hardware settings required
to activate various devices like keyboard, monitor etc.
The BIOS runs when system is switched ON and performs a Power On Self
Test (POST) that checks if the hardware devices are present and functioning
properly.
The BIOS invokes the bootstrap loader to load the operating system into
memory.
3. CMOS (Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor)
This is a chip which stores the date, time and system setup parameters.
These parameters are loaded every time the computer is started.
4. Slots: A slot is an opening where a PCB can be inserted. It is often called expansion
slot as it allows to expand the capabilities of computer.
The different slots are
3
� (1) Expansion slots: Expansion cards are inserted here which give the computer
new features or increased performance. Different expansion slots are:
ISA (Industry Standard Architect): Used to connect modem and input
devices.
PC I (Peripheral Component Inter Connect) slot: Faster than ISA.
Used to connect sound cards, internal modem or SCSI.
AGP (Accelerated Graphic Port) slot: Connects graphics accelerated
card which enhances the visual experience.
(2) RAM slot: Used to install memory. There are two types –SIMM(Single Inline
Memory Module) slot and DIMM(Dual Inline Memory Module) Slot.
(3) Processor Slot: Used to insert the processor chip.
(4) PCI Express slot: Has faster bus architecture than AGP and PCI.
(5) PC Card: Used in laptop computers. Includes Wi-Fi card, network card and
external modem.
5. Disk Controller: It is a circuit that enables the CPU to communicate with a hard
disk, floppy disk or any kind of disk drives. The different disk controllers are:-
(1) HDC (Hard disk controller)
It is a interface that enables the computer to read and write information
to the hard drive.
Advanced Technology Attachment (ATA) was the first HDC. It was
attached to the mother board by 40 wire ribbon cable. This allowed two
drives to connect to motherboard.
Later Enhanced IDE(EIDE) was used which allowed four drives to be
connected to a dual channel controller.
(2) FDC (Floppy Disk Controller)
It is the interface that enables reading from and writing into a floppy
disk drive.
A single FDC board supports a 33 wire ribbon cable and can connect up to
four floppy drives to the motherboard.
6. I/O Ports and interfaces : The ports and interfaces are used to connect external
devices like printers, keyboards or scanners to the computer(motherboard). The
different types of ports are :-
(1) Serial Port
Also called as communication (COM) Port.
They are used to connect communication devices like mouse, modem etc,.
They transfer data serially i.e, one bit at a time.
(2) Parallel Port
Used to connect external input/output devices like printers or scanners.
Here there is parallel transfer of data i.e, one byte at a time.
4
� (3) USB(Universal Serial Bus) port
USB is a plug and play interface between a computer and add-on devices
like printers, scanners, digital cameras, web cameras, speakers etc
A new device can be added without adding an adapter card or even
turning off the computer.
USB supports a data speed of 12 megabits per second.
(4) PS-2 port (Personal System -2 port)
This is also called as mouse port. Developed by IBM to interface
keyboards and pointing devices like keyboards and trackballs
(5) AGP (Accelerated Graphics Port) port
Used to connect graphics card that provides high-speed video
performance required in games applications.
(6) VGA (Visual Graphics Adaptor) port
It connects monitor to the video card. It has 15 Holes.
(7) Ethernet Port
Used to connect Ethernet card which connects to a network and internet.
Data travel at 10 megabits to 1000 megabits per second.
(8) MIDI (Musical Instrument Digital Interface) Port
A MIDI Musical keyboard can be attached .
Transmission between system and electronic musical instrument is done
using this.
(9) Game port Connects a PC to joystick .
(10) IDE (Integrated Digital Electronics) port
Hard disk drives and CD-ROM drives are connected to the motherboard
through IDE port.
(11) SCSI (Small Computer System Interface) port
Used for adding external high speed devices like high speed hard disk,
high – end scanners etc. It does fast data transfer and I-O operations.
These ports are expensive.
7. BUS: A BUS is a collection of parallel wires that form a pathway to carry address,
data and control signals.
Functional features of a BUS:
(1) A Bus is a set of wires and each wire carries one bit of data.
(2) A Bus width is defined by the number of wires in the BUS.
5
� There are two types of BUS:
(1) Internal or System BUS: Connects major components like processor, memory
and I/O.
(2) External or Expansion BUS: Connects different external devices, peripherals,
expansion slots, I/O ports etc. This is slower than System BUS.
System BUS and Expansion BUS are of three kinds:
(1) Data Bus: This provides path to transfer data between CPU and memory. The
Data Bus width affects the speed of the computer. A 16 bit line bus transfer 16
bits of data.
(2) Address Bus: Connects CPU and RAM which carries address to store and
retrieve data.
(3) Control Bus: Is used to control the access and use of data and address line.
MEMORY
A computer memory is an electronic storing space for instructions and data where the
computer‟s processor can reach quickly.
Classification of memory:
(1) Internal memory: This can be directly accessed by the processor.
Features of internal memory
It is used for temporary storage of data and instructions on which the
processor is currently working.
This memory is the fastest.
Is Expensive.
It has limited storage capacity.
The different types of Internal Memory are
Registers: The registers are high speed temporary storage located inside the
CPU.CPU uses registers for the processing of data. The CU(Control Unit )
directs the registers to accept, store and transfer instructions or data ,
perform arithmetic or logical comparisons at high speed.
Cache memory: This is a high speed memory available inside CPU to speed up
access of data and instructions stored in RAM memory.
6
� Types of Cache memory:
L1 Cache: This is built into the processor.
L2 Cache: This is located next to processor on a separate chip between CPU
and RAM.L1 cache is faster than L2
L3 Cache: Separate cache chip on the motherboard.
CPUs have cache size varying from 256KB (L1), 6MB (L2), to 12MB (L3).
Primary memory: It is also known as main memory. The two types of Primary
memory are:-
RAM (Random Access Memory): RAM is faster memory and volatile in
nature. This temporarily stores operating system, application programs and
current data.
ROM (Read Only Memory): ROM is small , non volatile memory. It stores the
Boot Firmware called BIOS.
Types of RAM:
(1) DRAM (Dynamic RAM):Mostly used as main memory. It is small and cheap. It
uses transistors and capacitors. DRAM must be refreshed continually to store
information. It is slow because the refreshing takes time. Speed ranges from 50
to 150 ns (nano second).
(2)SRAM (Static RAM): Mostly used in cache memory due to its high speed.
Uses multiple transistors ( 4 to 6) for each memory cell. It does not need
constant refreshing and hence is faster. SRAM is more expensive and needs
more space. Speed ranges from 2 to 10 ns.
(3)SDRAM (Synchronous Dynamic RAM):Is a special type of DRAM. It is
synchronized to the system clock and so knows when the next cycle is coming
and keeps the data ready. This increases the efficiency by reducing CPU waiting
time.
(4)DDR-SDRAM (Double Data Rate SDRAM): Data transfer rate is double
when compared to SDRAM.
7
�POWER SUPPLY
Continuous power supply is essential for the computer to prevent it from breakdown,
failure or shutdown.
Two types of power supply are
(1) SMPS (Switched Mode Power Supply): SMPS converts 230 volts of AC power
from the electrical outlet to 5 to 12 volts DC power needed by the system
components. SMPS contains the power card plug and a fan for cooling.
(2) UPS (Uninterrupted Power Supply): An UPS is a power supply that has battery to
maintain power in the event of a power failure. UPS keeps the computer running for
several minutes to few hours after power failure and lets us save data that is in
RAM before shutting the computer.
Two types of UPS:
(i) Online UPS: An online UPS avoids power lapses by continuously providing
power from its own inverter, even when the power line is functioning
properly. Online UPS are more expensive than the standby UPS.
(ii) Standby UPS (Off-line UPS): This UPS monitors the power line and
switches to battery power as soon as it detects a problem. The switch over
takes several milliseconds during which time, the computer does not receive
any power.
8
� ABBREVIATIONS
1. PCB - Printed Circuit Board
2. XT - Extended Technology
3. AT - Advanced Technology
4. DIMM - Dual-In-Line Memory Module
5. ISA - Industry Standard Architecture
6. PCI - Peripheral Component Interconnect
7. SRAM - Static Random Access Memory
8. SDRAM - Synchronous Dynamic Random Access Memory
9. DDR RAM - Double Data Rate Random Access Memory
10. SIMM - Single In Line Memory Module
11. AGP - Accelerated Graphics Port
12. IDE - Integrated Digital Electronics
13. SATA - Serial Advanced Technology Attachment
14. USB - Universal Serial Bus
15. MIPS - Millions Of Instructions Per Second
16. IC - Integrated Chip
17. POST - Power On Self Test
18. HDC - Hard Disk Controller
19. FDC - Floppy Disk Controller
20. DMA - Direct Memory Access Mode
21. EIDE - Enhanced Integrated Digital Electronics
22. PS-2 – Personal System-2
23. SCSI - Small Computer System Interface
24. VGA - Visual Graphics Adaptor
25. MIDI - Musical Instrument Digital Interface
26. DRAM - Dynamic Random Access Memory
27. SMPS - Switched Mode Power Supply
28. UPS - Uninterrupted Power Supply
29. BIOS - Basic Input Output System
30. CMOS - Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor