Changeover
Methods
�Direct Changeover
Pilot Running
Parallel Running
Phased Conversation
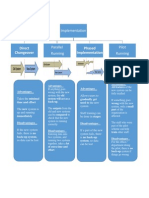
� Direct Changeover
Overview:
Also known as the "big bang" approach.
The old system is immediately replaced by the new system.
The changeover happens on a specified date, and the old system is
completely shut down.
Advantages:
Quick implementation with minimal transition time.
No need to maintain two systems simultaneously, reducing
operational costs.
Disadvantages:
High risk due to no fallback if the new system fails.
Can disrupt operations if issues are encountered after the
switch.
Best Used When:
The new system is fully tested, and the organization can
handle potential downtime.
� Parallel Running Changeover Method
Overview:
Old and new systems run together for a period. Reduced Risk
Data is processed in both systems to ensure accuracy.
Advantages:
Lower risk with the old system as a backup.
Real-Time Comparison
Allows time to fix issues in the new system.
Disadvantages: Gradual Transition
Higher costs and resource demands to run two
systems.
Increased workload for staff managing both systems. Immediate Fallback
Best Used When:
Minimizing risk is a priority, and the organization Thorough Testing
can handle the extra costs.
� Pilot Running
Overview:
The new system is introduced in one department or branch.
Allows real-world testing with a smaller group before full rollout.
Advantages:
Low risk, affecting only a small part of the business initially.
Issues are identified and resolved before full implementation.
Provides valuable user feedback from live operations.
Disadvantages:
Slower implementation, progressing one group at a time.
Can cause temporary inconsistencies across the organization.
Best Used When:
The organization wants to cautiously test the new system.
Ideal for addressing issues before full deployment.
� Phased Conversion
Overview:
The new system is implemented in stages or modules over time.
Each part of the organization or system is transitioned one at a time.
Advantages:
Gradual implementation reduces risk, allowing for smoother
transitions.
Issues can be addressed in smaller phases, reducing the chance of
major disruptions.
Disadvantages:
Extended changeover period can cause inconsistency in operations.
Requires careful planning and coordination to ensure seamless
integration.
Best Used When:
The system is complex, and a gradual approach allows for thorough
testing and adjustments at each stage.
�Thanks for your attention!