AS & A LEVEL COMPUTER SCIENCE 9618
TRANSLATION SOFTWARE
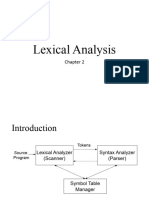
STAGES IN THE COMPLETION OF A PROGRAM
Lexical Analysis
Syntax Analysis
Code Generation
Optimization
1 Davis_Kazibwe@2023KIS
� AS & A LEVEL COMPUTER SCIENCE 9618
STAGES IN THE COMPLETION OF A PROGRAM
STEP1. LEXICAL ANALYSIS
Unnecessary characters ( white space, comments are removed )
Source program is converted to token
TOKENIZATION
Total Number of tokens = 12
Token: Any variable, constant, keyword,
symbol with in the program
2 Davis_Kazibwe@2023KIS
� AS & A LEVEL COMPUTER SCIENCE 9618
LEXICAL ANALYSIS
KEYWORDS TABLE: These include reserved words and operators
3 Davis_Kazibwe@2023KIS
� AS & A LEVEL COMPUTER SCIENCE 9618
LEXICAL ANALYSIS
SYMBOL TABLE:
Identifiers (variable, constant ) names used
Data types
Role ( variable, constant, array , procedure )
Value or location
4 Davis_Kazibwe@2023KIS
� AS & A LEVEL COMPUTER SCIENCE 9618
EXAM STYLE QUESTION
5 Davis_Kazibwe@2023KIS
� AS & A LEVEL COMPUTER SCIENCE 9618
EXAM STYLE QUESTION
6 Davis_Kazibwe@2023KIS
� AS & A LEVEL COMPUTER SCIENCE 9618
EXAM STYLE QUESTION
7 Davis_Kazibwe@2023KIS
� AS & A LEVEL COMPUTER SCIENCE 9618
EXAM STYLE QUESTION
8 Davis_Kazibwe@2023KIS
� AS & A LEVEL COMPUTER SCIENCE 9618
LEXICAL ANALYSIS
How contents of the keyword and symbol used to translate the source code
program ?
1. Keywords / operators are looked up ( in the keyword table )
2. Keywords / operators are represented by the tokens
3. Identifier are loaded up in the ( symbol table )
4. Identifiers are converted to locations or addresses
5. Used to create a sequence of tokens ( for the program )
Additional task completed at the lexical analysis stage that does not involve the of
keyword or symbol table
1. White space removed
2. Redundant characters are removed
3. Removal of comments
9 Davis_Kazibwe@2023KIS
� AS & A LEVEL COMPUTER SCIENCE 9618
STAGE2: SYNTAX ANALYSIS
TASKS PERFORMED IN SYNTAX ANALYSIS
1. Constructing a parse tree ( parsing )
2. Checking the table of tokens to ensure that the rules / syntax / grammar of
the language are obeyed
3. Producing an error report
The process of working out if a
TOKENS
given statement is valid according
to the given BNF production rules is
called parsing
PARSER PARSE TREE
SYNTAX
10 Davis_Kazibwe@2023KIS
� AS & A LEVEL COMPUTER SCIENCE 9618
STAGE2: SYNTAX ANALYSIS
The grammatical rules or syntax for a programming language need to be set out
clearly so a programmer can write code that obeys the rules, and a computer can be
built to check that a program obeys these rules.
The rules can be shown in a “SYNTAX DIAGRAM” or using a meta language such as
BACKUS-NAUR FORM (NBNF ) notation
BACKUS NAUR FORM
Is a mathematical way of defining syntax
On the left we always have a not-terminal symbol meaning it can still be broken
down. Then on the right we have to keep going until we get to a terminal which
ends the rule
11 Davis_Kazibwe@2023KIS
� AS & A LEVEL COMPUTER SCIENCE 9618
STAGE2: BNF SYMBOLS
<> --> Used to enclose a syntactic item
::= --> Used to define something. Means “defined by” or “Consists of”
| --> Used between two or more items to illustrate an “or” or choice between
something
EXAMPLE: Imagine a programmer wants to construct a database. Various authors
will be contributing to the program, therefore everyone needs to know the
grammar rules.
<postal-address> ::= <name> ‘;’ <street-address> ‘;’ <post-code>
Meaning
A postal address consist of or is defined as name, street-address and postal code
with a semi colon separating them
<name> ::= <first-name> “,” <surname>
Note: BNF is more concise than English, that’s why it Is used by the compiler
<>: Always used if something is defined and once everything is defined that’s when
BNF is done. When there is no more further breakdowns
12 Davis_Kazibwe@2023KIS
� AS & A LEVEL COMPUTER SCIENCE 9618
STAGE2: SYNTAX ANALYSIS
This defines only two digits
Incase we have more than 3
digits then we use a recursive
statement. This means
<Number> makes use of itself
13 Davis_Kazibwe@2023KIS
� AS & A LEVEL COMPUTER SCIENCE 9618
STAGE2: SYNTAX ANALYSIS
A word consist of two letters
<word> : : = <letter><letter>
A word consist of any numbers of letter
<word> : : = <letter>|<letter> <word>
Assignment statement
Number = N1 + N2 ;
<Assignment Statement > : : = <Variable > = <Variable> <Operator> <Variable > ;
Note: Variable could be a single letter or letter followed by a single digit
<Variable > : : = <letter> | <letter> <digit>
<operators> : : = + or – or \ or *
14 Davis_Kazibwe@2023KIS
� AS & A LEVEL COMPUTER SCIENCE 9618
STAGE2: SYNTAX ANALYSIS
SYNTAX DIAGRAM Means cannot be
<Digit> : : = 1 broken down
further
<Digit> : : = 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5
15 Davis_Kazibwe@2023KIS
� AS & A LEVEL COMPUTER SCIENCE 9618
STAGE2: SYNTAX ANALYSIS
SYNTAX DIAGRAM
<Assignment Statement > : : = <Variable> = <Variable> <Operator><variable>;
<WORD> : : = <LETTER> | <LETTER> <WORD>
LETTER
16 Davis_Kazibwe@2023KIS
� AS & A LEVEL COMPUTER SCIENCE 9618
STAGE2: SYNTAX ANALYSIS
SYNTAX DIAGRAM
<Word > : : = <Letter> = <Variable> <Letter><Digit>
Word Letter Digit
17 Davis_Kazibwe@2023KIS
� AS & A LEVEL COMPUTER SCIENCE 9618
STAGE3: CODE GENERATION
The code generation stage produces an object code
The program should have correct syntax
The object code is in machine readable form
STAGE 4 : OPTIMIZATION
Qtn: Why code optimization is necessary ?
Optimization means that the code will have fewer instructions
Optimized code occupies less space in memory
Fewer instruction reduces the execution time of the program
18 Davis_Kazibwe@2023KIS
� AS & A LEVEL COMPUTER SCIENCE 9618
STAGE4: CODE OPTIMIZATION
19 Davis_Kazibwe@2023KIS
� AS & A LEVEL COMPUTER SCIENCE 9618
STAGE4: CODE OPTIMIZATION
BENEFITS OF OPTIMIZING CODE
1. Code has fewer instructions or occupies less space in memory
2. Time taken to execute whole program decreases
REVERSE POLISH NOTATION
Is a method of representing an arithmetic expression
INFIX FORM : A – B
REVERSE POLISH NOTATION : AB -
20 Davis_Kazibwe@2023KIS
� AS & A LEVEL COMPUTER SCIENCE 9618
CASE 1: USING RPN TO EVALUATE THE EXPRESSION
USING STARTS
21 Davis_Kazibwe@2023KIS
� AS & A LEVEL COMPUTER SCIENCE 9618
CASE 1: USING RPN TO EVALUATE THE EXPRESSION
USING STARTS
Note:
Always solve left to right
Whenever operators enter the stack, use that operator on two values at the top
22 Davis_Kazibwe@2023KIS
� AS & A LEVEL COMPUTER SCIENCE 9618
CASE 1: USING RPN TO EVALUATE THE EXPRESSION
USING STARTS
23 Davis_Kazibwe@2023KIS
� AS & A LEVEL COMPUTER SCIENCE 9618
CASE 2 : INFIX TO RPN CONVERSION
24 Davis_Kazibwe@2023KIS
� AS & A LEVEL COMPUTER SCIENCE 9618
CASE 2 : INFIX TO RPN CONVERSION
25 Davis_Kazibwe@2023KIS
� AS & A LEVEL COMPUTER SCIENCE 9618
CASE 2 : INFIX TO RPN CONVERSION
26 Davis_Kazibwe@2023KIS
� AS & A LEVEL COMPUTER SCIENCE 9618
CASE 3 : RPN TO INFIX CONVERSION
27 Davis_Kazibwe@2023KIS
� AS & A LEVEL COMPUTER SCIENCE 9618
CASE 3 : RPN TO INFIX CONVERSION
28 Davis_Kazibwe@2023KIS
� AS & A LEVEL COMPUTER SCIENCE 9618
THEORETICAL QUESTIONS
Qtn: Explain how RPN is used by an interpreter to evaluate expressions ?
1. Expression are always evaluated left to right
2. Each operator uses the two previous values on the stack ( except unary
minus)
3. If element is a number push that number enter the stack
4. If element is an operator then pop the first two numbers from stack
5. Perform that operation on those numbers
6. PUSH the result back onto stack
7. End once the last item in the expression has been dealt with
Qtn 2: Advantages of using RPN for expression evaluation
1. No need for rules of procedure (BODMAs)
2. No need for brackets
3. In RPN evaluation of operators is always left to right
29 Davis_Kazibwe@2023KIS
� AS & A LEVEL COMPUTER SCIENCE 9618
THEORETICAL QUESTIONS
Qtn3: Identify with reason a data structure that could be used to evaluate an
expression in RPN
STRUCTURE : Stack
REASON : Operands are removed or popped from the stack in the reverse order to
how they were added or pushed
Qtn 4 : What does the statement “ No need for rules of procedure “ mean ?
1. Rules of procedure means different operators have different priorities for
example multiply is done before addition
2. In RPN evaluation of operators is left to right
3. No need for brackets
30 Davis_Kazibwe@2023KIS
� AS & A LEVEL COMPUTER SCIENCE 9618
THEORETICAL QUESTIONS
Qtn5: Explain how an interpreter executes a program without producing a complete
transition version of it.
1. An interpreter examines source code one statement at a time
2. Check each statement for errors
3. If no error is found the statement Is executed
4. If an error is found, this is reported and the interpreter halts
5. Interpretation is repeated for every iteration in repeated sections of code
6. Interpretation has to be repeated every times the program is run
31 Davis_Kazibwe@2023KIS