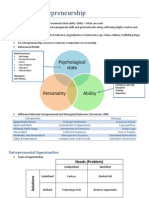
Perils of External Venture Financing- VC is a poor fit for many ventures, require businesses to have a certain growth/size potential;
have a
medium-long term view.• Money comes with strings attached.• False sense of security leading to complacency & lack of control.•
Diminished flexibility to adopt try it- fix it approach in new ventures.• Conflicts between investors & promoter managers |Bootstrapping-
minimize outside debt & equity financing needed from banks & investors. Includes a combination of methods to reduce overall capital
requirements, improve cash flows, take advantage of personal networks & sources of finances. Small and young firms- trouble raising
money as liability of newness & smallness | Thumb rules for Bootstrapping- •Get operational quickly• Look for quick break even & cash
generation• Offer high value products that can sustain personal selling• Keep growth in check• Focus on customer not on VC/external
finance• Focus on cash before profits, market share• Convert fixed costs into variable as much as possible, reducing upfront costs &
allowing business to pay for itself• Leverage social capital | Bootstrapping Methods •Customer-related: are used to improve cash flow from
customers; Advanced payments by creating incentives, Charging interest on overdue invoices, Ceasing relations with late-paying customers•
Owner-related financing- Savings, Loans by owners or from family• Joint utilization of resources with other firms- Sharing employees (CFO),
Assets, Business space (Startup Village), Coordinating purchases with other firms to take advantage of economies of scale •Delaying
payment-Paying late (with permission), Negotiating longer credit periods, Leasing than purchasing | Limits: • Ideal for hustle, niche
ventures• Revolutionary & speculative ventures can’t • Ventures outside promoter’s knowledge domain are difficult • Ventures that require
some critical assets to be deployed even before testing out business concept can’t| • There is a great deal to be gained by making the pie
bigger for everyone rather than fighting over the size of your own piece.
Social Entrepreneurship (SE): Organizations that create new models for provision of products that cater to basic human needs, remain
unsatisfied by current economic or social institutions | TYPES OF ENTREPRENEURSHIP- fig | SE involves: ◦ Recognizing & pursuing opp. to
create social value◦ Crafting innovative approaches to address critical social needs SE is use of start-up companies and other entrepreneurs
to develop, fund, and implement solutions to social, cultural, or environmental issues. Features- Primary goal is adding social value Could
be for-profits, cooperatives, or not-for-profits Look at the poor as consumers and not beneficiaries Focus on ‘triple bottom line’- Planet,
Prosperity, People| Emerging Models for Equitable Growth- Traditional Enterprise-Problem needs to be solved by govt. & NGOs.-> CSR-We
have some responsibility towards society. Let’s look good.-> Social Enterprise-It’s our problem. We need to solve it.-> Shared value-It’s an
opportunity to do well by doing good. | Different Types of Social Businesses- For-profits: surpluses are reinvested for social objectives of
the business Cooperative: “an autonomous association of persons united voluntarily to meet their common economic, social, and cultural
needs and aspirations through a jointly-owned and democratically-controlled enterprise” Producer Organization: legal entity formed by
primary producers which allows to share profits/benefits among members Section 8 Company: Not-for-profit co. that promotes research,
social welfare, protection of environment etc. (Eg- NSRCEL) | Corridor principle: Establishing of a venture enables to see other opp. that
they could not see or take advantage of until they started their initial venture; Enter the corridor to see other doors, One vs. multiple
ventures- Entrepreneurs create multiple ventures to lengthen their entrepreneurial careers, Where to start?- Start one venture at least to
see other venture opportunities | Hybrid social enterprise combine enterprise with embedded social purpose & Pursue dual mission of
financial sustainability & social purpose | Social Entrepreneurs are Change Agents
Sources of competitive advantage- Corporate + Global Strategy: Where should we compete?, Business+ Functional strategy: How should we
compete? | A firm should be Ambidextrous – balance exploration and exploitation – to have sustainable competitive advantage and
growth Corporate Entrepreneurship can aid ambidexterity in firms. CE- Entrepreneurial activity within a mature firm i.e., attempts to
create products, enter markets, or introduce process innovations that are new to firm; To counter the gale of creative destruction & find
new growth opp.| Forms: fig | CE comes with challenges that can be overcome with horizontal structure and incentive alignment.
For mature firms practicing CE, Strategic Challenges: Focus on near-term margins, Size of business, Cyclicality, New businesses but old
lenses| Potential Resolution- Outside hires, Inorganic growth, Three horizon framework (1 Defend the core businesses, 2 Build emerging
businesses, 3 Create viable options) | Incentives and Organizational Challenges: Risk and failure avoidance, Organization design dilemma,
Emphasis on organizational harmony |Potential Resolution- Leeway for ‘well-intentioned failure’, Bottom-up entrepreneurship; Disciplined
empowerment, Differentiated hierarchy, Insulation of entrepreneurial efforts | Decision-making Challenges: Rigid application of financial
metrics and performance measures, Reliance on traditional market research, Linear stage-gate processes| Potential Resolution- Metrics to
align with the horizon of the project, type of innovation, market maturity, ‘Make little, sell little’, Bootstrap, Limited, staged investments |
CE Models- Internal Origin: Integrated Structure- Intrapreneurship, Autonomous Structure- Internal Corporate Ventures (ICV), External
Origin: Integrated: M&A Autonomous- Entrepreneurial Partnerships, CVCs| ICV- process: Combine technologies and markets, (Idea
Generation) Internal Venturing Process (Selection) | CE process- Idea or market opp. -> CE Biz model to make it viable -> Organizational
form/ CE form| Business Model: Conception of how strategies should work together as a whole to enable the company to achieve
competitive advantage | Corporate ventures take time and pivots to arrive at the right business model, just like new ventures.| Exploration
can stop when some new businesses demonstrate high growth potential- become the top priority for managerial attention and resource
allocation| CV: Incubation Process- Choice of model depends on: distance from core biz,capability match, position in three-horizon
framework | CV: Exit Process: Low growth, low margin businesses: pivot/ spin-off/ terminate/franchise, High growth, high margin
businesses with fit: Internalize or keep in incubation | New Age CE: Crowdsourcing: Problem-solving by diverse uncoordinated crowds of
people; is a corporate innovation tool- Diversity in ideas, access resources outside firm boundaries, evaluate and select solutions from
competing ones, Faster time to market| Types: fig | Challenges: Problem identification and decomposition, Problem generalization, Manage
the crowd, Scalability issues, Absorbing solution into existing systems, Consensus in choice of solution | Open innovation is a distributed
innovation process based on purposively managed knowledge flows across organizational boundaries; process for sharing knowledge and
ideas with other org. | Types: Inbound – opening a firm’s innovation processes to external contribution, Outbound – external actors use a
firm’s innovation | Place multiple bets (context of uncertainty) | New age models of CE combine internal and external origins.
Corporate Venture Capital: Equity investments of large corporations (play VC) in startups | Beyond equity investments • Incubation /
Acceleration - structured programs provide space, platforms, mentorship • Corporate accelerator/incubator partnerships – partnership with
�external parties who run accelerator/incubator –NSRCEL • Co-creation / alliances - Strategic partnerships (licensing, marketing, technology)
• Challenges, hackathons | Dual perspective – corporations and startups | Purpose- fig| Structure: •Internal CVC group• Captive funds –
similar to an internal CVC group but operates as a separate legal entity •Third party managed • Multi-corporate funds- Independent of
corporate parent, Allows mid-sized companies to pool in and invest | Blended internal and external ventures-• Spin-along approach-
Integrates elements of spin-in and spin-out strategies|•Innovation Centers- Internal R&D, CVC startups/spin-outs work in close collaboration
| Adv- quicker than in-house R&D (makes quick pivots), team is “asset light with lower operation cost | Challenges- Corp.- Lack of well-
defined or shifting , Missions, Conflicting agenda/priorities of startups and other investors, Inadequate compensation schemes that
motivate managers correctly| For Startups- Risk of imitation of technology/product, Insufficient corporate commitment, Corporations’
processes complex and time-consuming decision making, Not welcome by other VCs | Overcome- Align CVC goals with corporate objectives,
Streamline decision-making processes, Provide CVC executives powerful incentives, not tied to corporate performance, create robust
knowledge transfer channels| Benefits to new ventures: strategic benefits- Access to market, scaling technology, Requirements for large
scale investments, Strong complementarities exist; New ventures’ business model and long-term objectives align with corporate- can learn
and get acquired by corp
Intrapreneurship: use of entrepreneurial mindset and mgmt. techniques within established co.s to foster innovation | Intrapreneur- one
who develops new business/ innovation, leads & guides venture team, answerable to top mgmt., Focal point of entire venture| Challenges:
• Lack of legitimacy and credibility (in the initial stages), Resource consumption rather than resource generation •Resistance and inertia-
Lack of information and significance, • Resource starvation- Comp. for resources from mainstream activities, Pressure to use resources
efficient, Pressure to establish economic viability | Challenges vs Principles: •Resources are available in plenty, but accessing resources is
difficult- Start with available resources (means);redeploy slack resources for pilots •limited incentives to take risks-Build partnerships rather
than top-down incentives to pilot new opportunities •Viability of the venture is necessary, but not sufficient to pursue further- Build your
business case on customer insights; seek approval for affordable loss •Strategic fit, timing, significant and predictable returns are important-
Pilot, Experiment, pivot – Lean Method | Intrapreneur traits- Innovative, Resourceful, Persistence, Persuasiveness -> Tactics- Frequency,
Variety, Individualized consideration -> Champion success | Intrapreneurs bring innovation to firm but also “craft their own jobs” in addition
to achieving high growth