0% found this document useful (0 votes)
41 views5 pagesPCB Layout Rules
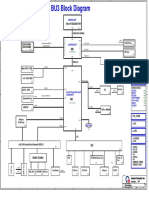
The document outlines essential PCB layout rules, emphasizing the importance of placing core components first and ensuring a balanced, aesthetic design. It highlights the necessity of short wiring, signal separation, and early determination of PCB size and layer number. Additionally, it discusses design for manufacturability (DFM) principles, manual routing before automatic routing, and optimizing routing for efficiency.
Uploaded by
madhumoksha20Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
41 views5 pagesPCB Layout Rules
The document outlines essential PCB layout rules, emphasizing the importance of placing core components first and ensuring a balanced, aesthetic design. It highlights the necessity of short wiring, signal separation, and early determination of PCB size and layer number. Additionally, it discusses design for manufacturability (DFM) principles, manual routing before automatic routing, and optimizing routing for efficiency.
Uploaded by
madhumoksha20Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 5