100% found this document useful (1 vote)
136 views23 pagesAWS Working Notes
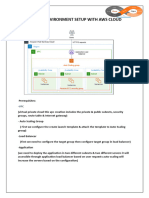
The document provides a comprehensive overview of AWS services and security best practices, emphasizing the importance of managing AWS Organizations, IAM roles, and security groups. It outlines various AWS services such as EC2, RDS, DynamoDB, and EFS, detailing enumeration techniques, potential vulnerabilities, and methods for accessing sensitive information. Additionally, it highlights the significance of proper configuration and monitoring to prevent security breaches within AWS infrastructure.
Uploaded by
doomslayer.1537Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as TXT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (1 vote)
136 views23 pagesAWS Working Notes
The document provides a comprehensive overview of AWS services and security best practices, emphasizing the importance of managing AWS Organizations, IAM roles, and security groups. It outlines various AWS services such as EC2, RDS, DynamoDB, and EFS, detailing enumeration techniques, potential vulnerabilities, and methods for accessing sensitive information. Additionally, it highlights the significance of proper configuration and monitoring to prevent security breaches within AWS infrastructure.
Uploaded by
doomslayer.1537Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as TXT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 23