0% found this document useful (0 votes)
72 views4 pagesNull Resource & Dynamic Block
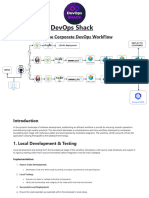
The document explains the use of null_resource and dynamic blocks in Terraform. A null_resource allows for executing scripts and handling external dependencies without managing infrastructure, while a dynamic block enables the generation of multiple nested blocks based on collections, improving resource management. It provides definitions, use cases, examples, and differences between the two features, highlighting their practical applications in real-time scenarios.
Uploaded by
rkandtk1997Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
72 views4 pagesNull Resource & Dynamic Block
The document explains the use of null_resource and dynamic blocks in Terraform. A null_resource allows for executing scripts and handling external dependencies without managing infrastructure, while a dynamic block enables the generation of multiple nested blocks based on collections, improving resource management. It provides definitions, use cases, examples, and differences between the two features, highlighting their practical applications in real-time scenarios.
Uploaded by
rkandtk1997Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 4