0% found this document useful (0 votes)
84 views23 pagesClass 16 - Factor Formulae and Solving Equations
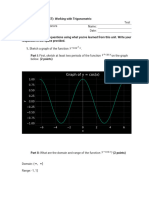
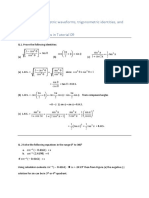
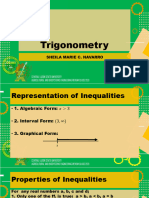
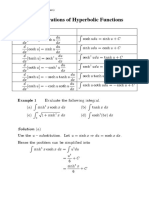
The document covers trigonometric identities and factor formulae, providing examples of solving equations involving sine and cosine functions. It includes detailed solutions for finding general solutions in radians for various trigonometric equations. Additionally, it demonstrates proofs using factor formulae and introduces the form of expressions involving sine and cosine.
Uploaded by
Indar SoochitCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
84 views23 pagesClass 16 - Factor Formulae and Solving Equations
The document covers trigonometric identities and factor formulae, providing examples of solving equations involving sine and cosine functions. It includes detailed solutions for finding general solutions in radians for various trigonometric equations. Additionally, it demonstrates proofs using factor formulae and introduces the form of expressions involving sine and cosine.
Uploaded by
Indar SoochitCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 23