0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views2 pagesDetailed Networking Basics
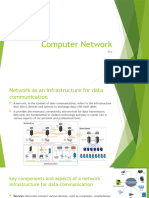
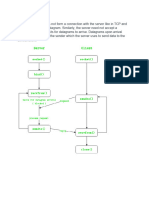
Computer networking enables communication and resource sharing among devices, with Local Area Networks (LANs) and Wide Area Networks (WANs) being the primary types. Key concepts include IP addressing, DNS for domain name translation, and networking devices like routers and switches that manage traffic. Network security is crucial, utilizing measures like firewalls and VPNs to protect data, while understanding these basics is essential for advanced topics in IT.
Uploaded by
barnabas barryCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views2 pagesDetailed Networking Basics
Computer networking enables communication and resource sharing among devices, with Local Area Networks (LANs) and Wide Area Networks (WANs) being the primary types. Key concepts include IP addressing, DNS for domain name translation, and networking devices like routers and switches that manage traffic. Network security is crucial, utilizing measures like firewalls and VPNs to protect data, while understanding these basics is essential for advanced topics in IT.
Uploaded by
barnabas barryCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 2