Unit 2: Coding
Learning Objectives
Learners will learn to:
understand and use relational and logical operators
develop text-based programs with conditional (selection) statements
outline the purpose of program libraries
identify and know how to use library functions in text-based programs
Vocabulary
operators
conditions
libraries
Let Us Start
Of course! I have used conditional
Hey! Have you used conditional statements. Conditional statements
statements in Python? I need to are fundamental constructs allowing
understand it to create Python you to make code decisions based on
programs with conditions. specific conditions. They enable your
program to execute different blocks of
code depending on whether certain
conditions are true or false.
1
�Let Us Explore
We have already created an algorithm that uses a condition to check a condition and
then displays a result. To convert an algorithm with conditions into a Python
program, we must learn to use conditional statements in Python.
Write an algorithm that accepts the user's age and determines if he/she is eligible to
vote. The voting age is considered to be 18 years or older.
__________________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________________
Get, Set, Go
2.1 Operators
Operators in Python programming are special symbols or characters that perform
operations on variables and values. Let us look at the relational and logical operators
used to specify conditions by comparing values.
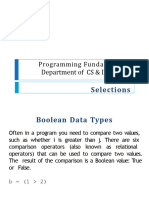
Relational operators
Relational operators are used to create a condition that compares two values. The
output of a relational expression is either ‘True’ or ‘False’ based on the comparison
result.
Operator Name of Description Example
Symbol operator Assuming
x=20 and y=10
== equal to It checks if two values are equal. If the x==y results in
values on both sides of the operator False
2
� are the same, it returns True.
Otherwise, it returns False.
!= not equal to It checks if two values are not equal. If x!=y results in
the values are different, it returns True
True. If they are the same, it returns
False.
> greater than It checks if the value on the left is x>y results in
greater than the value on the right. If True
it is, it returns True; otherwise, it
returns False.
< less than It checks if the value on the left is less x<y results in
than the value on the right. If it is, it False
returns True; otherwise, it returns
False.
>= greater than It checks if the value on the left is x>=y results in
equal to greater than or equal to the value on True OR
the right. If it is, it returns True; y>=x results in
otherwise, it returns False. False
<= less than It checks if the value on the left is less x<=y results in
equal to than or equal to the value on the False OR
right. If it is, it returns True; otherwise, y<=x results in
it returns False. True
Example 1: Program using relational operators
Program
3
�Output
Logical operators
Logical Operators are used to combine multiple conditions and determine the overall
result.
In the expression “marks>37”, you can only check whether the marks are greater than
37. What if you require checking whether it is greater than 37 and less than 18? In such
cases, you can use logical operators to join multiple relational expressions to make a
more complex expression. Logical operators are also known as Boolean operators.
The following logical operators are used in Python:
Logical Description Example
operator assuming x=20 and
y=10
AND The output is True only if all statements (x > 0 and y < 20) results
are true. in True
OR The output is True if any one statement (x > 0 or y < 5) results in
is true. True
NOT The output is True if the statement is (not x > 0) results in False
false.
4
�Example: Program using logical operators
Program
Output
Activity 1
Assuming x=-20, y=20 and z=0, What will be the output of the following statements
in Python?
print (x+y==z)
print( x+y !=0)
print (x> y and z < y)
2.2 Conditional statements
Conditional statements are programming constructs that allow the execution of code
based on certain conditions. They enable the program to make decisions and choose
different paths of execution based on whether a particular condition is true or false.
The most common types of conditional statements are:
5
� Statement Description
if statement The if statement is used to test a specific condition. If the
condition is true, a block of code (if-block) will be
executed.
if - else statement The if-else statement is similar to the if statement except
that it also provides the block of the code for the false
case of the condition to be checked. If the condition
provided in the if statement is false, then the else
statement will be executed.
Nested if statement The nested if statements enable us to use an if-else
statement inside an outer if statement.
Indentation in Python
In Python, indentation is used to declare a block. If two statements are at the same
indentation level, they are part of the same block. Generally, four spaces are given to
indent the statements, a typical amount of indentation in Python. Indentation is the
most used part of the Python language since it declares the block of code. All the
statements of one block are intended at the same level of indentation. If a command
under the ‘if’ statement is not indented, it will give an error.
The if statement
The if statement is used to test a particular condition and if the
condition is true, it executes a block of code known as if-block.
The condition of an if statement can be any valid logical
expression which can be either evaluated to true or false.
Syntax
6
�Example 1: Program to find the number is greater than 5.
Program
Output
Example 2: Program to print the largest of the three numbers.
Program
Output
7
�Activity 2
Write a Python program that accepts a user's age and checks whether he/she is an
adult. The program will display a message if the age entered is more than 18.
The if-else statement
The if-else statement provides an else block combined with the if statement executed
in the false case of the condition. If the condition is true, then the if-block is executed.
Otherwise, the else block is executed.
Syntax
8
�Example: Program to check whether a person is eligible to vote.
Program
Output
Activity 3
Write a Python program that accepts a number from the user and checks whether
the number is even or odd.
The elif statement
The elif statement enables us to check multiple conditions
and execute the specific block of statements depending
upon the true condition among them. Depending upon
our need, we can have any number of elif statements in our
program.
Syntax
9
�Program
Output
2.3 Library Routines
Library routines are pre-written codes that can be used in programs to perform specific
tasks. These are also tested and ready to use. Using library routines saves time by not
having to write code from scratch. It can be included in programs by importing them.
Some of the commonly used library routines are as follows:
MOD
It returns the remainder when one number is divided by another number.
Example: Program that uses MOD.
Program
10
�Output
DIV
It returns the quotient when one number is divided by another number.
Program
output
ROUND
It rounds a number to a specified number of decimal places.
Program
11
�Output
RANDOM
It generates a random number between x and n
Program
Output
Activity 3
Write a Python code for the following:
Input two integers and find DIV and MOD
Generate a random integer between 30 to 50
Unit Review
1. Relational operators are used to create a condition that compares two values.
2. Logical Operators are used to combine multiple conditions and determine the
overall result.
3. Conditional statements are programming constructs that allow the execution
of code based on certain conditions.
12
� 4. Indentation is used to declare a block. If two statements are at the same
indentation level, they are part of the same block.
5. The if statement is used to test a particular condition and if the condition is
true, it executes a block of code known as if-block.
6. The if-else statement provides an else block combined with the if statement executed
in the false case of the condition.
7. The elif statement enables us to check multiple conditions and execute the specific
block of statements depending upon the true condition among them.
8. Library routines are pre-written code that can be used in programs to perform
specific tasks.
9. Some commonly used library routines are MOD, DIV, ROUND and RANDOM.
Check for Understanding
1. Select the correct answer.
a. What will be the output for the following Python code?
i. True
ii. False
iii. Error
b. What of the following in NOT a logical operator?
i. AND
ii. NOT
iii. <=
c. Which conditional statement checks multiple conditions and executes the
specific statement block?
i. if statement
13
� ii. if-else statement
iii. elif statement
d. Which logical operator will give the output True if the statement is false?
i. AND
ii. OR
iii. NOT
2. Answer the following questions.
a. Why is it important to indent the Python code?
___________________________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________________
b. Differentiate between interactive mode and Script mode in Python
Programming.
____________________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________________
14
� c. Explain if - else statement with an example.
___________________________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________________
d. What will be the output of the following Python code?
_______________________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________________
Lab Activity
1. Write a program to accept a character from the user and display whether it is
vowel or a consonant.
2. Create a Python program to develop a remainder machine that takes two
numbers input from the user. It then outputs the remainder after dividing the
first number by the second.
15
� 3. Write a Python program that prompts the user to enter his/her score and
determines the corresponding grade based on the following criteria:
If the score is 90 or above, assign grade A
If the score is between 80 and 89, assign grade B
If the score is between 70 and 79, assign grade C
If the score is between 60 and 69, assign grade D
For any score below 60, assign grade F
After determining the grade, the program should display the result by printing
"Your grade is" followed by the assigned grade.
Resources
https://www.javatpoint.com/python-tutorial
Reference Material
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ft8nK7NSLig
16