100% found this document useful (1 vote)
67 views7 pagesI-O Port Programming in AVR
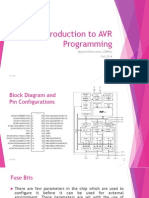
The ATmega32 microcontroller features 40 pins, including three for Vcc and GND, and 23 I/O port pins across four ports (A, B, C, D) with specific pin configurations. The document explains how to configure pin directions and output levels using `DDRx` and `PORTx`, along with example code for setting up and manipulating these ports. Additionally, it provides details on the addresses for the Data Direction Registers for each port.
Uploaded by
Hiếu NguyễnCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (1 vote)
67 views7 pagesI-O Port Programming in AVR
The ATmega32 microcontroller features 40 pins, including three for Vcc and GND, and 23 I/O port pins across four ports (A, B, C, D) with specific pin configurations. The document explains how to configure pin directions and output levels using `DDRx` and `PORTx`, along with example code for setting up and manipulating these ports. Additionally, it provides details on the addresses for the Data Direction Registers for each port.
Uploaded by
Hiếu NguyễnCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 7