0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views6 pagesDisplay Counter Project Report Extended
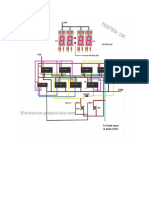
This project report outlines the design and construction of a digital counter circuit that displays numbers from 0 to 9 on a 7-segment display using a 555 timer and a 4026 counter IC. It includes components required, working principles, circuit diagrams, and methods for adjusting delay between number transitions. The project serves as an educational exercise in digital electronics with potential applications in various automation systems.
Uploaded by
Priyanshu JadhavCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views6 pagesDisplay Counter Project Report Extended
This project report outlines the design and construction of a digital counter circuit that displays numbers from 0 to 9 on a 7-segment display using a 555 timer and a 4026 counter IC. It includes components required, working principles, circuit diagrams, and methods for adjusting delay between number transitions. The project serves as an educational exercise in digital electronics with potential applications in various automation systems.
Uploaded by
Priyanshu JadhavCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 6