0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views6 pagesStudy Notes - Types of Networks
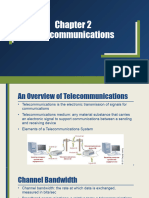
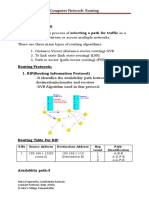
The document provides an overview of computer networks and web technologies, detailing various types of networks such as LAN, MAN, and WAN, along with mobile network evolution from 2G to 5G. It highlights the importance of mobile communication in terms of accessibility, connectivity, and economic impact, as well as its applications in education, commerce, and journalism. Additionally, key web technology concepts like HTML, HTTP, and web browsers are explained.
Uploaded by
richarschelsea030Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views6 pagesStudy Notes - Types of Networks
The document provides an overview of computer networks and web technologies, detailing various types of networks such as LAN, MAN, and WAN, along with mobile network evolution from 2G to 5G. It highlights the importance of mobile communication in terms of accessibility, connectivity, and economic impact, as well as its applications in education, commerce, and journalism. Additionally, key web technology concepts like HTML, HTTP, and web browsers are explained.
Uploaded by
richarschelsea030Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 6