0% found this document useful (0 votes)
31 views5 pagesCloud Computing
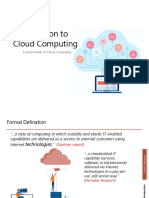
Cloud computing enables users to access and store data and applications over the internet, offering on-demand resources through various service models: IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS. Deployment models include public, private, hybrid, and community clouds, each with distinct advantages and challenges. While cloud adoption provides benefits such as cost efficiency and scalability, it also presents challenges like security risks and compliance issues, with future trends focusing on edge computing, AI integration, and quantum computing.
Uploaded by
rafaelmedina09672734401Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
31 views5 pagesCloud Computing
Cloud computing enables users to access and store data and applications over the internet, offering on-demand resources through various service models: IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS. Deployment models include public, private, hybrid, and community clouds, each with distinct advantages and challenges. While cloud adoption provides benefits such as cost efficiency and scalability, it also presents challenges like security risks and compliance issues, with future trends focusing on edge computing, AI integration, and quantum computing.
Uploaded by
rafaelmedina09672734401Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 5