0% found this document useful (0 votes)
29 views10 pagesTransmission Modes (Data Flow)
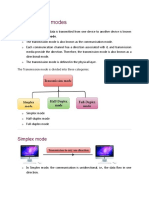
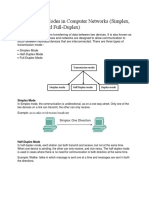
The document explains three transmission modes: simplex, half-duplex, and full-duplex. Simplex allows unidirectional communication, half-duplex enables bidirectional communication but not simultaneously, and full-duplex allows simultaneous transmission and reception. Examples of each mode include TV transmissions for simplex, walkie-talkies for half-duplex, and telephone networks for full-duplex.
Uploaded by
haseebpasha23435Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
29 views10 pagesTransmission Modes (Data Flow)
The document explains three transmission modes: simplex, half-duplex, and full-duplex. Simplex allows unidirectional communication, half-duplex enables bidirectional communication but not simultaneously, and full-duplex allows simultaneous transmission and reception. Examples of each mode include TV transmissions for simplex, walkie-talkies for half-duplex, and telephone networks for full-duplex.
Uploaded by
haseebpasha23435Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 10