0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 views43 pagesV.exception Handling
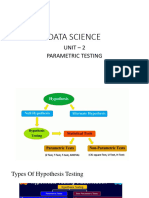
The document discusses exception handling in Java, explaining the concept of exceptions as events that disrupt the normal flow of a program. It differentiates between checked and unchecked exceptions, provides examples of common exceptions, and outlines the use of keywords such as try, catch, finally, throw, and throws in managing exceptions. Additionally, it includes code examples to illustrate exception handling mechanisms and their practical applications.
Uploaded by
Chaitanya Krishna DeepakCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 views43 pagesV.exception Handling
The document discusses exception handling in Java, explaining the concept of exceptions as events that disrupt the normal flow of a program. It differentiates between checked and unchecked exceptions, provides examples of common exceptions, and outlines the use of keywords such as try, catch, finally, throw, and throws in managing exceptions. Additionally, it includes code examples to illustrate exception handling mechanisms and their practical applications.
Uploaded by
Chaitanya Krishna DeepakCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 43