0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views18 pagesTesting Notes
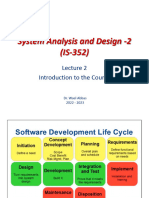
The document provides an overview of software testing, including its definition, methodologies, and the software development lifecycle (SDLC). It discusses the importance of testing in preventing losses and outlines various testing activities, roles, and techniques. Additionally, it covers Agile methodologies, Scrum processes, and different types of testing such as functional and non-functional testing.
Uploaded by
vkarthickkumar25Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views18 pagesTesting Notes
The document provides an overview of software testing, including its definition, methodologies, and the software development lifecycle (SDLC). It discusses the importance of testing in preventing losses and outlines various testing activities, roles, and techniques. Additionally, it covers Agile methodologies, Scrum processes, and different types of testing such as functional and non-functional testing.
Uploaded by
vkarthickkumar25Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 18