0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views11 pagesPython Programs
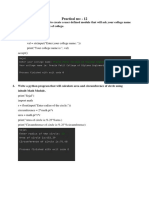
The document contains a collection of Python programs demonstrating various programming concepts such as calculations, data structures (lists, tuples, sets, dictionaries), inheritance, and control flow. Each program includes code snippets with examples for practical understanding. Topics covered range from basic arithmetic operations to object-oriented programming and data manipulation.
Uploaded by
radhikagawali102Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views11 pagesPython Programs
The document contains a collection of Python programs demonstrating various programming concepts such as calculations, data structures (lists, tuples, sets, dictionaries), inheritance, and control flow. Each program includes code snippets with examples for practical understanding. Topics covered range from basic arithmetic operations to object-oriented programming and data manipulation.
Uploaded by
radhikagawali102Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 11