0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views7 pagesLab - 8051 C - Assembly Programs
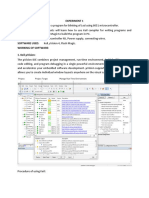
The document outlines a detailed procedure for creating and debugging a project using Keil IDE for the AT89C51 microcontroller. It includes steps for setting up the project, writing code for various experiments such as LED and LCD interfacing, timer operations, DAC interfacing, and handling external hardware interrupts. Additionally, it provides example code snippets for each experiment and notes on peripheral selections required for successful execution.
Uploaded by
aabbash6996Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views7 pagesLab - 8051 C - Assembly Programs
The document outlines a detailed procedure for creating and debugging a project using Keil IDE for the AT89C51 microcontroller. It includes steps for setting up the project, writing code for various experiments such as LED and LCD interfacing, timer operations, DAC interfacing, and handling external hardware interrupts. Additionally, it provides example code snippets for each experiment and notes on peripheral selections required for successful execution.
Uploaded by
aabbash6996Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 7