0% found this document useful (0 votes)
56 views10 pagesCoa 1
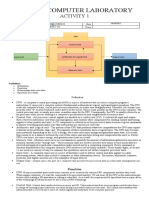
The document outlines the functional units of a digital computer, detailing components such as the input unit, CPU, memory unit, arithmetic and logical unit, control unit, and output unit. It explains how these components interact through a common bus for data transfer and describes the role of each unit in processing input and generating output. Additionally, it introduces concepts related to register transfer language (RTL) and micro-operations, emphasizing their significance in computer architecture.
Uploaded by
Sachin SamriddhCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
56 views10 pagesCoa 1
The document outlines the functional units of a digital computer, detailing components such as the input unit, CPU, memory unit, arithmetic and logical unit, control unit, and output unit. It explains how these components interact through a common bus for data transfer and describes the role of each unit in processing input and generating output. Additionally, it introduces concepts related to register transfer language (RTL) and micro-operations, emphasizing their significance in computer architecture.
Uploaded by
Sachin SamriddhCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 10