0% found this document useful (0 votes)
40 views35 pagesBasic Organization of A Computer
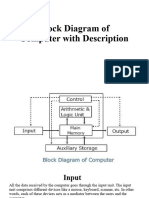
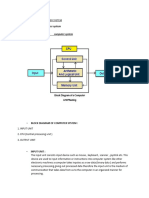
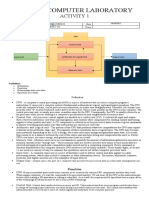
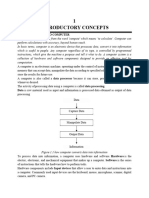
The document outlines the basic organization of a computer system based on Von Neumann architecture, which includes five main components: Input Unit, Output Unit, Storage Unit, Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU), and Control Unit (CU). It explains the functions of each component, detailing how data is input, processed by the CPU, and outputted, along with the roles of primary and secondary memory. Additionally, it discusses the significance of processor speed and its measurement in gigahertz (GHz).
Uploaded by
Ashok KumarCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
40 views35 pagesBasic Organization of A Computer
The document outlines the basic organization of a computer system based on Von Neumann architecture, which includes five main components: Input Unit, Output Unit, Storage Unit, Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU), and Control Unit (CU). It explains the functions of each component, detailing how data is input, processed by the CPU, and outputted, along with the roles of primary and secondary memory. Additionally, it discusses the significance of processor speed and its measurement in gigahertz (GHz).
Uploaded by
Ashok KumarCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 35