If you
are creating your own Exception that is known as custom exception or user-defined exception. Java custom
exceptions are used to customize the exception according to user need.
By the help of custom exception, you can have your own exception and message. Let's see a simple example
of java custom exception.
class InvalidAgeException extends Exception{ InvalidAgeException(String s){
super(s);
}}
class TestCustomException1{
static void validate(int age)throws InvalidAgeException{
if(age<18)
throw new InvalidAgeException("not valid");
else
System.out.println("welcome to vote");
}
public static void main(String args[]){
try{ validate(13);
}catch(Exception m){System.out.println("Exception occured: "+m);}
System.out.println("rest of the code...");
}}
Output:Exception occured: InvalidAgeException:not valid rest of the code...
exception handled normal flow...
JA VA PROGRAMMING Page 55
Multithreading
Multithreading in java is a process of executing multiple threads simultaneously.
Thread is basically a lightweight sub-process, a smallest unit of processing. Multiprocessing and
multithreading, both are used to achieve multitasking.
But we use multithreading than multiprocessing because threads share a common memory area. They don't
allocate separate memory area so saves memory, and context-switching between the threads takes less time
than process.
Java Multithreading is mostly used in games, animation etc.
Advantages of Java Multithreading
�1) It doesn't block the user because threads are independent and you can performmultiple operations at
sametime.
2) You can perform many operations together so it savestime.
3) Threads are independent so it doesn't affect other threads if exception occur in a singlethread.
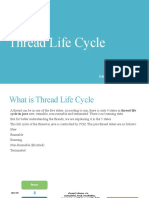
Life cycle of a Thread (Thread States)
A thread can be in one of the five states. According to sun, there is only 4 states in thread life cycle in java
new, runnable, non-runnable and terminated. There is no running state.
But for better understanding the threads, we are explaining it in the 5 states.
The life cycle of the thread in java is controlled by JVM. The java thread states are as follows:
1. New
2. Runnable
3. Running
4. Non-Runnable(Blocked)
5. Terminated
JA VA PROGRAMMING Page 56
How to create thread
There are two ways to create a thread:
1. By extending Threadclass
2. By implementing Runnableinterface.
Thread class:
Thread class provide constructors and methods to create and perform operations on a thread.Thread class
extends Object class and implements Runnable interface.
Commonly used Constructors of Thread class:
oThread() oThread(String name) oThread(Runnable r)
oThread(Runnable r,String name)
JA VA PROGRAMMING Page 57
Commonly used methods of Thread class:
1. public void run(): is used to perform action for athread.
2. public void start(): starts the execution of the thread.JVM calls the run() method onthethread.
3. public void sleep(long miliseconds): Causes the currently executing thread to sleep (temporarily cease
execution) for the specified number ofmilliseconds.
4. public void join(): waits for a thread todie.
5. public void join(long miliseconds): waits for a thread to die for the specifiedmiliseconds.
6. public int getPriority(): returns the priority of thethread.
7. public int setPriority(int priority): changes the priority of thethread.
8. public String getName(): returns the name of thethread.
9. public void setName(String name): changes the name of the thread.
10. public Thread currentThread(): returns the reference of currently executingthread.
11. public int getId(): returns the id of thethread.
12. public Thread.State getState(): returns the state of thethread.
13. public boolean isAlive(): tests if the thread isalive.
14. public void yield(): causes the currently executing thread object to temporarily pause and allow other
threads toexecute.
15. public void suspend(): is used to suspend thethread(depricated).
16. public void resume(): is used to resume the suspendedthread(depricated).
17. public void stop(): is used to stop thethread(depricated).
18. public boolean isDaemon(): tests if the thread is a daemonthread.
19. public void setDaemon(boolean b): marks the thread as daemon or userthread.
20. public void interrupt(): interrupts thethread.
21. public boolean isInterrupted(): tests if the thread has beeninterrupted.
22. public static boolean interrupted(): tests if the current thread has beeninterrupted.
Runnable interface:
The Runnable interface should be implemented by any class whose instances are intended to be executed by
a thread. Runnable interface have only one method named run().
1. public void run(): is used to perform action for athread.
�Starting a thread:
start() method of Thread class is used to start a newly created thread. It performs following tasks:
oA new thread starts(with new callstack).
oThe thread moves from New state to the Runnable state.
oWhen the thread gets a chance to execute, its target run() method will run.
JA