0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views5 pagesInstall in Prometheus Stack
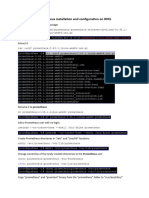
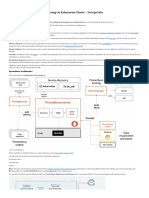
The document provides detailed instructions for installing the Prometheus stack using Helm charts, including prerequisites, installation commands, and post-installation checks. It also covers personalized configuration for Prometheus, Grafana, and Alertmanager, along with commands for testing and accessing the services. Additionally, it includes steps for working with Redis in a Kubernetes environment and verifying the setup through curl commands.
Uploaded by
Alejandro Gonzalez ValenciaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views5 pagesInstall in Prometheus Stack
The document provides detailed instructions for installing the Prometheus stack using Helm charts, including prerequisites, installation commands, and post-installation checks. It also covers personalized configuration for Prometheus, Grafana, and Alertmanager, along with commands for testing and accessing the services. Additionally, it includes steps for working with Redis in a Kubernetes environment and verifying the setup through curl commands.
Uploaded by
Alejandro Gonzalez ValenciaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 5