0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views6 pagesDocumentation On Arduino UNO
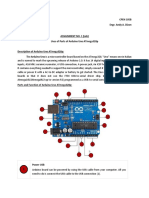
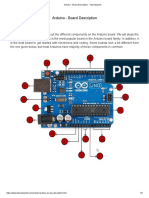
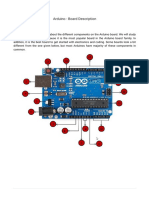
The Arduino UNO is a microcontroller board based on the Atmega328, featuring 20 input/output pins, including 6 analog and 14 digital pins, and is powered via USB or an external supply. It supports Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) for simultaneous data transmission and includes various components like a reset button, voltage regulator, and crystal oscillator. The board allows for digital and analog input/output operations using functions like digitalRead(), digitalWrite(), and analogRead().
Uploaded by
ddhkkabCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views6 pagesDocumentation On Arduino UNO
The Arduino UNO is a microcontroller board based on the Atmega328, featuring 20 input/output pins, including 6 analog and 14 digital pins, and is powered via USB or an external supply. It supports Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) for simultaneous data transmission and includes various components like a reset button, voltage regulator, and crystal oscillator. The board allows for digital and analog input/output operations using functions like digitalRead(), digitalWrite(), and analogRead().
Uploaded by
ddhkkabCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 6