0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes) 44 views7 pagesTheory - Types of Memory
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content,
claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online on Scribd
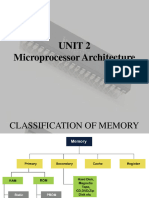
COMPUTER MEMORY
INTRODUCTION
The computer’s memory stores data, instructions required during the
processing of data, and output results. Storage may be required for a
limited period of time, instantly, or, for an extended period of time.
1. Different types of memories, each having its own unique features, are
available for use in a computer. The cache memory, registers, and RAM are
fast memories and store the data and instructions temporarily duy
processing of data and instructions.
2. The secondary memory like magnetic disks and optical
disks has large storage capacities and store the data and
instructions permanently, but aré slow memory devices,
2
Coad
Ru
! |
» snaw Pom woo Le > Lp penbrive
a nom osevose |, ovo Memon
2
fe
Main memory
Disk cache
Magnetic disk
Optical disk
Faster r
Speed Capacity�Internal Memory (Primai
The key features of internal memory are:
1. Limited storage capacity.
2. Temporary storage.
3. Fast access.
4, High cost.
External Memory (Seconda
The key features of external memory storage devices are:
1. Very high storage capacity.
2. Permanent storage (non-volatile), unless erased by user.
3. Relatively slower access.
4, Stores data and instructions that are not currently
being used by CPU but may be required later for processing.
5. Cheapest among all memory.
zw
PRIMARY MEMORY (Main Memory)
Primary memory is the main memory of computer. It is a chip
mounted on the motherboard of computer.
Primary memory is categorized into two main types:
|. Random access memory (RAM)
Il. Read only memory (ROM)
Characteristic of Primary Main Memory
* These are semiconductor memories,
© It is known as main memory.
* Usually volatile memory.
* Data is lost in case power is switched of.
* It is working memory of the computer.
* Faster than secondary memories.
* A computer cannot run without primary memory.
RAM (Random Access Memory) ~
1. The Word “RAM” stands for,“random access memory’ or may also
refer to @hortsterm memory.
. It’s called “random” because you can read store data randomly at any
time and from any physical location.
. Itis a temporal storage memory.
. RAM is volatile that only retains all the data as long as the computer
powered. It is the fastest type of memory.
. RAM stores the currently processed data from the CPU and se
to the graphics unit.�There are generally two broad subcategories of RAM: ne an
(yr
[peewee] seat I eat | YS
Fu Form StaticRendomAcces Memory OyamicRandom Acces Memon J
ROM (Read Only Memory}
. ROM is the l@ngsternnlinteFlalliiennony
2. ROM is “NORBMOLAtIGIVIEHIOnys that retains data without the flow of
electricity.
ROM is an essential chip with permanently written data or programs.
It is similar to the RAM that is accessed by the CPU.
ROM comes with pre-written by the computer manufacturer to hold the
instructions for SOOURESUpIRHEIeOMpULen
Poor
There is generally three broad type of ROM:
1. PROM
2. EPROM
3. EEPROM
Programmable Read-Only Memory (PROM) :
This form of ROM i: . The user or manufacturer can write
data/program on it by using special devices. However, once the program or
data is written in PROM chip, it cannot be changed. If there is an error in
writing instructions or data in PROM, the error cannot be erased. p
chip becomes unusable.�Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory (EPROM
This memory type retains its contents until it exposed to intensegllitaviolet
light that clears its contents, making it possible to reprogram the memory.
Electrically Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory (EEPROM |
EEPROM can be burned (programmed) and erased by first electrical waves
in a millisecond. A single byte of a data or the entire contents of device can
be erased. To write or erase this memory type, you need a device called a
PROM burner.
Urravoiet tant
ive! Rite
iygssisnege.
Fig. 3.72 EPROM ame
Secondary Memory
1. The size of the main memory is @kyssmalpif large data need to be stored in it.
Further, the main memory is volatile in nature i.e. the contents are lost when
power supply is stopped. To overcome these another memory is used in a
computer system called secondary memory or the auxiliary memory.
This is large as well as nonvolatile in nature.
This type of memory is also known as external memory or ponsyolatilé
It is slower than main memory.
These are used for storing Data/Information permanently.
WRwWN
ics of Secondary Memo:
. These are magnetic and optical memories.
. itis known as GaGkupmemonys
. It is non-volatile memory.
. Data is permanently stored even if power is switched off.
. It is used for storage of the data in the computer.
. Computer may run without secondary memory.
. Slower than primary memories.�Main secondary memory are:
1. Magnetic Disk
2. Floppy Disk
3. Hard Disk
4. Optical Disks
Magnetic Disk
The Magnetic Disk is Flat, circular @ISE@B with metallic coating that is rotated
beneath read/write heads. It is a Random access device; read/write head can
be moved to any location on the platter
Floppy Disk
These are small removable disks that are plastic coated with magnetic
recording material. Floppy disks are typically @Q5tiMize (diameter) and can
hold @ggMIBIGRWAtE This portable storage device is a rewritable media and
can be reused a number of times. Floppy disks are commonly used to move
files between different computers. The main disadvantage of floppy disks is
that they can be damaged easily and, therefore, are not very reliable. The
following figure shows an example of the floppy disk
o,�Hard Disk
Another form of auxiliary storage is a hard disk. A hard disk consists of one or
more rigid metal plates coated with a metal oxide material that allows data to
be magnetically recorded on the surface of the platters. Storage capacities of
hard disks for personal computers range from 10 GB to 120 GB (one billion
bytes are called a gigabyte).
Optical Disks
Optical Mass Storage Devices Store bit values as variations in light reflection.
They have higher area density & longer data life than magnetic storage. They
are also Standardized and relatively inexpensive. Their Uses: read-only storage
with low performance requirements, applications with high capacity
requirements & where portability in a standardized format is needed.
Types of Optical Disk
1. CD-ROM (read only)
2. CD-R: (record) to a CD
3. CD-RW: can write and erase CD to reuse it (re-writable)
4, DVD (Digital Video Disk) r
Flash Memory
Flash memory is the most widely used data storage technology in consumer
devices today. It stores our photos, our videos, our music, our documents and
so much more. In fact, flash memory has mostly replaced the magnetic hard
drive disks (HDDs) that used to be common in computers.�MEMORY MANAGEMENT TABLE
Approximate/Actual Values
Abbreviation [Approximate Actual
Bit (common 'b) Oort
Byte B (Capital BY Bites
ilobyies KB O00 Byes Teas bytes
Megabte, MB | All million bytes 1024 KB
werer [Titan bytes 1024 MB
Terabyte tp | “SS Lirillion bytes. 1024 GB
Peubyte m 10" Bytes ToT
Exa Bye EB TO™ Bytes 12
Zeta Bye ZB 10" Bytes 02 E
Yat Byte YB 102470
Bron Byte [BB Tos YB
Gigabyte GB