0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views9 pagesCPDS Lab-1
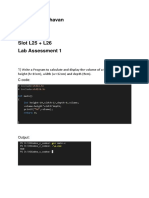
The document contains multiple C programming tasks including generating Fibonacci sequences, finding prime numbers, solving quadratic equations, calculating factorials, finding GCD, solving the Towers of Hanoi problem, performing basic arithmetic operations, finding the largest and smallest numbers in a list, and adding/multiplying matrices. Each task includes a brief description and corresponding C code implementation. The document serves as a comprehensive guide for basic programming exercises in C.
Uploaded by
dudipaladevisheshikumarCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views9 pagesCPDS Lab-1
The document contains multiple C programming tasks including generating Fibonacci sequences, finding prime numbers, solving quadratic equations, calculating factorials, finding GCD, solving the Towers of Hanoi problem, performing basic arithmetic operations, finding the largest and smallest numbers in a list, and adding/multiplying matrices. Each task includes a brief description and corresponding C code implementation. The document serves as a comprehensive guide for basic programming exercises in C.
Uploaded by
dudipaladevisheshikumarCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 9