Eltham High School
Information Technology
Computer Fundamentals
Facilitators: Mrs. Anderson Simpson
Computer Hardware
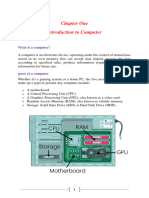
Computer hardware refers to the physical components that make up a computer system. It
encompasses all the tangible parts of a computer that you can see and touch. These components
work together to process data and perform various tasks. Here are some essential hardware
components:
1. Central Processing Unit (CPU): The CPU is often called the brain of the computer. It
performs most of the calculations and executes the instructions of a computer program.
Modern CPUs have multiple cores to handle tasks concurrently, improving performance.
Function: It fetches, decodes, and executes instructions from the computer's memory
2. Random Access Memory (RAM): RAM is the temporary memory that stores data and
instructions that the CPU is currently using. It allows the CPU to access data quickly,
speeding up the computer's overall performance.
Function: Stores information that needs to be used quickly.
3. Storage Devices: Computers use various storage devices to store data permanently or
semi-permanently. Common storage devices include Hard Disk Drives (HDDs) and Solid
State Drives (SSDs).
Function: They provide long-term storage for data and applications. They store data
even
when the computer is turned off and retain it for future use.
4. Motherboard: The motherboard is the computer's main circuit board, connecting all the
other components. It provides the pathways for data and power to flow between different
parts of the computer.
Function: It provides a pathway for data and power to flow between different computer
parts.
5. Graphics Processing Unit (GPU): The GPU is responsible for rendering images, videos,
and animations. It's particularly important for tasks like gaming, video editing, and other
graphics-intensive applications.
Function: For the processing and rendering of images, videos, and graphical content and
games.
�6. Power Supply Unit (PSU): The PSU supplies power to all the components in the
computer, converting the electricity from the outlet into the appropriate voltages needed
by each component.
Function: It ensures a stable and consistent power supply.
7. Cooling System: As computers generate heat while operating, a cooling system (usually
consisting of fans and heat sinks) is required to prevent overheating and maintain optimal
performance.
Function: Scatters heat to prevent overheating and maintain optimal performance.
8. Input Devices: These devices allow users to interact with the computer. Common input
devices include the keyboard and mouse, while touchscreens, stylus pens, and
microphones are also used in certain devices.
Function: To enter data into the computer system.
9. Output Devices: Output devices display or present data processed by the computer.
Monitors and printers are typical output devices, but other examples include speakers and
projectors.
Function: Get information out of a computer system.
10. Expansion Cards: These are optional components that can be added to the motherboard
to enhance the computer's capabilities. Examples include graphics cards, sound cards, and
network interface cards.
Function: To enhance the computer's capabilities.
� Computer Software
Computer systems software refers to the programs and utilities that enable the hardware to
function properly and provide a platform for other software applications to run. These software
components are essential for managing computer resources, providing a user interface, and
facilitating communication between hardware and software. Here are some common types of
computer systems software and their functions:
1. Operating System (OS):
Function: The fundamental software that manages computer hardware and provides an
interface for users and applications to interact with the system.
Examples: Windows, macOS, Linux, Android, iOS.
2. Device Drivers:
Function: Software that enables communication between the operating system and
various hardware devices (e.g., printers, graphics cards, network adapters).
Examples: Printer drivers, graphics drivers, and sound drivers.
3. Firmware:
Function: A type of software embedded in hardware devices to provide low-level control
and facilitate their operation.
Examples: BIOS (Basic Input/Output System), UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware
Interface).
4. System Utilities:
Function: Tools that help manage and optimize computer resources, perform
maintenance tasks, and troubleshoot issues.
Examples: Disk cleanup utilities, antivirus software, system monitoring tools.
5. File Management Software:
Function: Manages files and directories, providing functions for creating, deleting,
copying, and organizing data.
Examples: Windows File Explorer, macOS Finder.
6. Middleware:
Function: Software that acts as an intermediary between different applications or
software components, facilitating communication and data exchange.
Examples: Apache Tomcat, Microsoft .NET framework.
�Computer Software types and functions. Please read the PowerPoint.
� Computer Storage
Computer storage refers to the various methods and technologies used to store and retain data
in a computer system. Understanding computer storage is crucial for students, as such here
are some computer storage.
1. Primary Storage (RAM): Random Access Memory (RAM) is the primary storage in a
computer. It is volatile memory, meaning its contents are lost when the computer is
powered off. RAM is used to temporarily store data and instructions that the CPU needs
to access quickly during program execution.
2. Secondary Storage (Hard Disk Drives - HDDs, Solid State Drives - SSDs): Secondary
storage refers to non-volatile memory used for long-term data storage. Hard Disk Drives
(HDDs) and Solid State Drives (SSDs) are the most common types of secondary storage
devices. Data stored on secondary storage remains even when the computer is turned off.
3. Hard Disk Drives (HDDs): HDDs use magnetic storage to store data on spinning disks
(platters). They offer large storage capacities and are commonly used for storing files,
programs, and the operating system.
4. Solid State Drives (SSDs): SSDs use flash memory to store data. Unlike HDDs, SSDs
have no moving parts, which makes them faster, more durable, and less susceptible to
mechanical failures.
5. Optical Storage (CDs, DVDs, Blu-ray Discs): Optical storage uses lasers to read and
write data on optical discs, such as CDs, DVDs, and Blu-ray discs. These discs are used
for distributing software, media, and data, though they are becoming less common with
the rise of digital distribution.
6. Flash Drives (USB Drives): Flash drives are portable storage devices that use flash
memory to store data. They connect to computers via USB ports and are widely used for
transferring and carrying data between devices.
7. Cloud Storage: Cloud storage involves storing data on remote servers accessed via the
internet. Services like Google Drive, Dropbox, and OneDrive offer cloud storage
solutions, providing users with the ability to access their data from multiple devices with
an internet connection.
8. Magnetic Tape Storage: Magnetic tape storage is an older form of data storage,
primarily used for archival purposes due to its high capacity and relatively low cost per
gigabyte.
�Computer Memory categorized