50% found this document useful (2 votes)
3K views23 pagesTransformer Protection
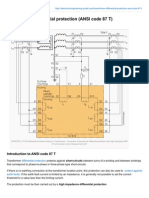
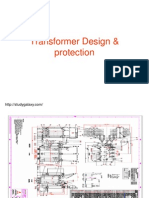
This document discusses transformer protection. It begins with introductions to transformers and relays, explaining their basic workings. It then discusses the need for transformer protection against faults and overloads. Various protection schemes are covered, including short circuit protection, external fault protection, overcurrent protection, du/dt protection, frame leakage protection, overflux protection, winding temperature protection, and protections for specific transformer types. The conclusion emphasizes that transformers require robust protection given their importance in transmission and distribution systems.
Uploaded by
ARVINDCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
50% found this document useful (2 votes)
3K views23 pagesTransformer Protection
This document discusses transformer protection. It begins with introductions to transformers and relays, explaining their basic workings. It then discusses the need for transformer protection against faults and overloads. Various protection schemes are covered, including short circuit protection, external fault protection, overcurrent protection, du/dt protection, frame leakage protection, overflux protection, winding temperature protection, and protections for specific transformer types. The conclusion emphasizes that transformers require robust protection given their importance in transmission and distribution systems.
Uploaded by
ARVINDCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 23