0% found this document useful (0 votes)
82 views23 pagesJava Components For Server Development
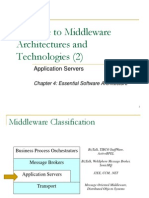
This document provides an overview of Java components for server development, including Java Server Pages (JSP), Servlets, and Enterprise JavaBeans (EJB). It describes how these components can be used to implement middle-tier services that shield clients and developers from complexity while providing features like transactions, security, and resource pooling across remote clients. The document outlines the status and purpose of JSPs, Servlets, and EJBs, and provides examples of how they can be used together in server applications.
Uploaded by
sivakg2000Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
82 views23 pagesJava Components For Server Development
This document provides an overview of Java components for server development, including Java Server Pages (JSP), Servlets, and Enterprise JavaBeans (EJB). It describes how these components can be used to implement middle-tier services that shield clients and developers from complexity while providing features like transactions, security, and resource pooling across remote clients. The document outlines the status and purpose of JSPs, Servlets, and EJBs, and provides examples of how they can be used together in server applications.
Uploaded by
sivakg2000Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 23