100% found this document useful (1 vote)
260 views27 pagesLesson 1 - Introduction To System Integration
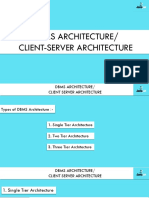
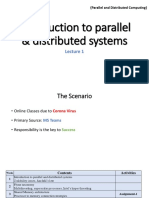
System integration involves connecting different IT subsystems as one large system. It allows for increased productivity, better management of data, and lower costs by avoiding redundant data entry and conversions. Common integration methods include horizontal integration across business units, vertical integration between different levels of an organization, and star or spaghetti integration of multiple subsystems. The goal is to allow data and information to flow freely between applications to make systems more efficient and agile. Challenges can include security issues and complex upgrades when integrating diverse technologies.
Uploaded by
mark daniel beatoCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (1 vote)
260 views27 pagesLesson 1 - Introduction To System Integration
System integration involves connecting different IT subsystems as one large system. It allows for increased productivity, better management of data, and lower costs by avoiding redundant data entry and conversions. Common integration methods include horizontal integration across business units, vertical integration between different levels of an organization, and star or spaghetti integration of multiple subsystems. The goal is to allow data and information to flow freely between applications to make systems more efficient and agile. Challenges can include security issues and complex upgrades when integrating diverse technologies.
Uploaded by
mark daniel beatoCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 27