0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views70 pagesComputer Software
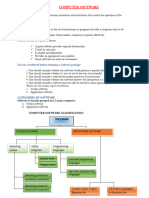
The document provides an overview of computer software, including its definition, classifications, and types such as system and application software. It discusses the advantages and disadvantages of standard versus bespoke software, as well as licensing types like open source and proprietary software. Additionally, it covers operating systems, their functions, and features, along with file management and troubleshooting techniques for common issues.
Uploaded by
rael08079Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views70 pagesComputer Software
The document provides an overview of computer software, including its definition, classifications, and types such as system and application software. It discusses the advantages and disadvantages of standard versus bespoke software, as well as licensing types like open source and proprietary software. Additionally, it covers operating systems, their functions, and features, along with file management and troubleshooting techniques for common issues.
Uploaded by
rael08079Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 70