0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views36 pagesChapter 7 - Introduction To Arduino
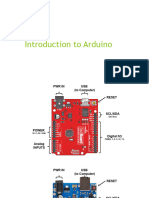
Chapter 7 provides an introduction to the Arduino microcontroller, including its capabilities for reading inputs and controlling outputs. It covers the installation process, first projects, and interfacing with various components like keypads and sensors. The chapter also explains the Arduino IDE, circuit basics, and the concepts of analog and digital signals.
Uploaded by
IZWAN NURLI MAT BISTAMANCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views36 pagesChapter 7 - Introduction To Arduino
Chapter 7 provides an introduction to the Arduino microcontroller, including its capabilities for reading inputs and controlling outputs. It covers the installation process, first projects, and interfacing with various components like keypads and sensors. The chapter also explains the Arduino IDE, circuit basics, and the concepts of analog and digital signals.
Uploaded by
IZWAN NURLI MAT BISTAMANCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 36