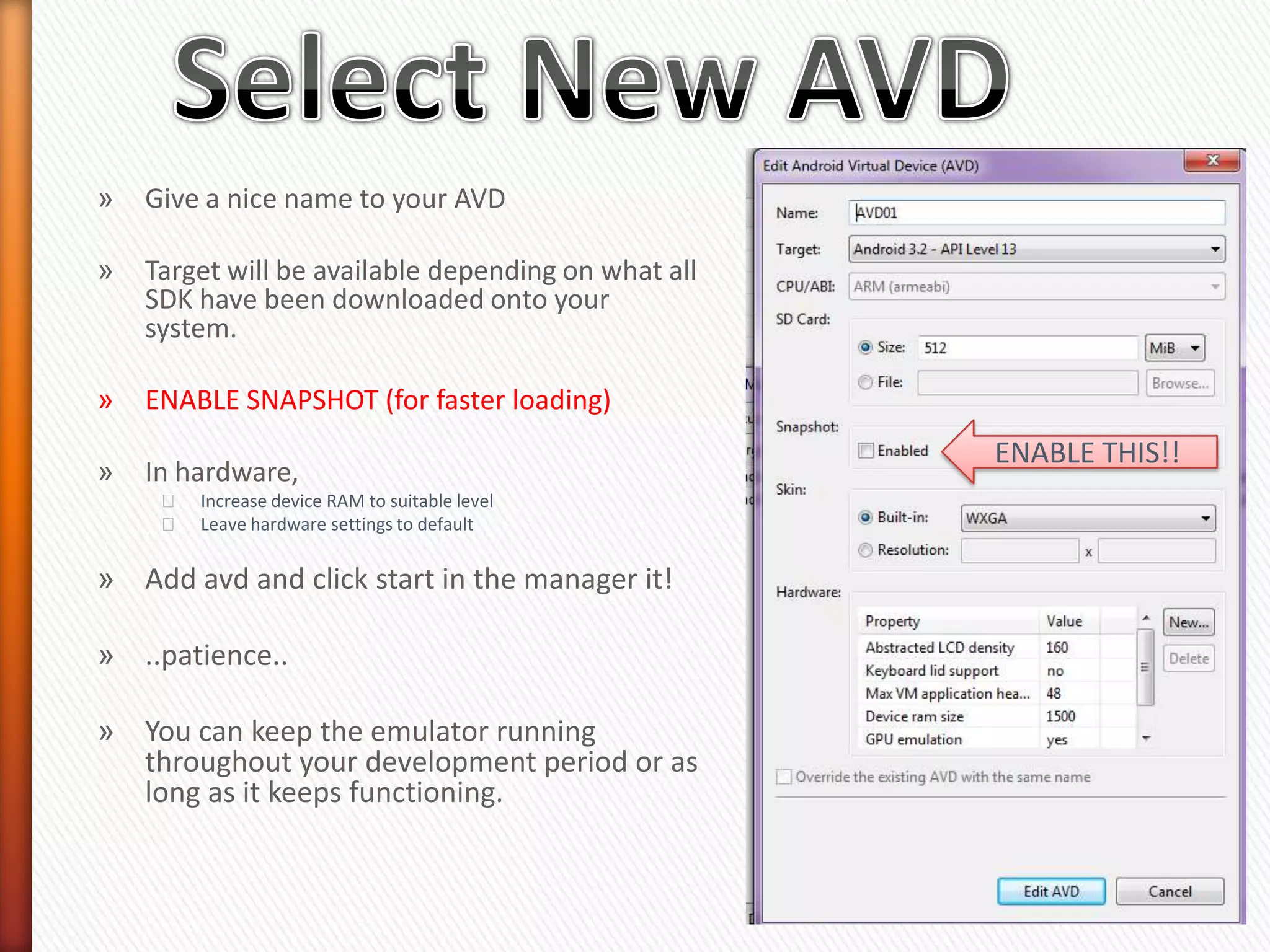
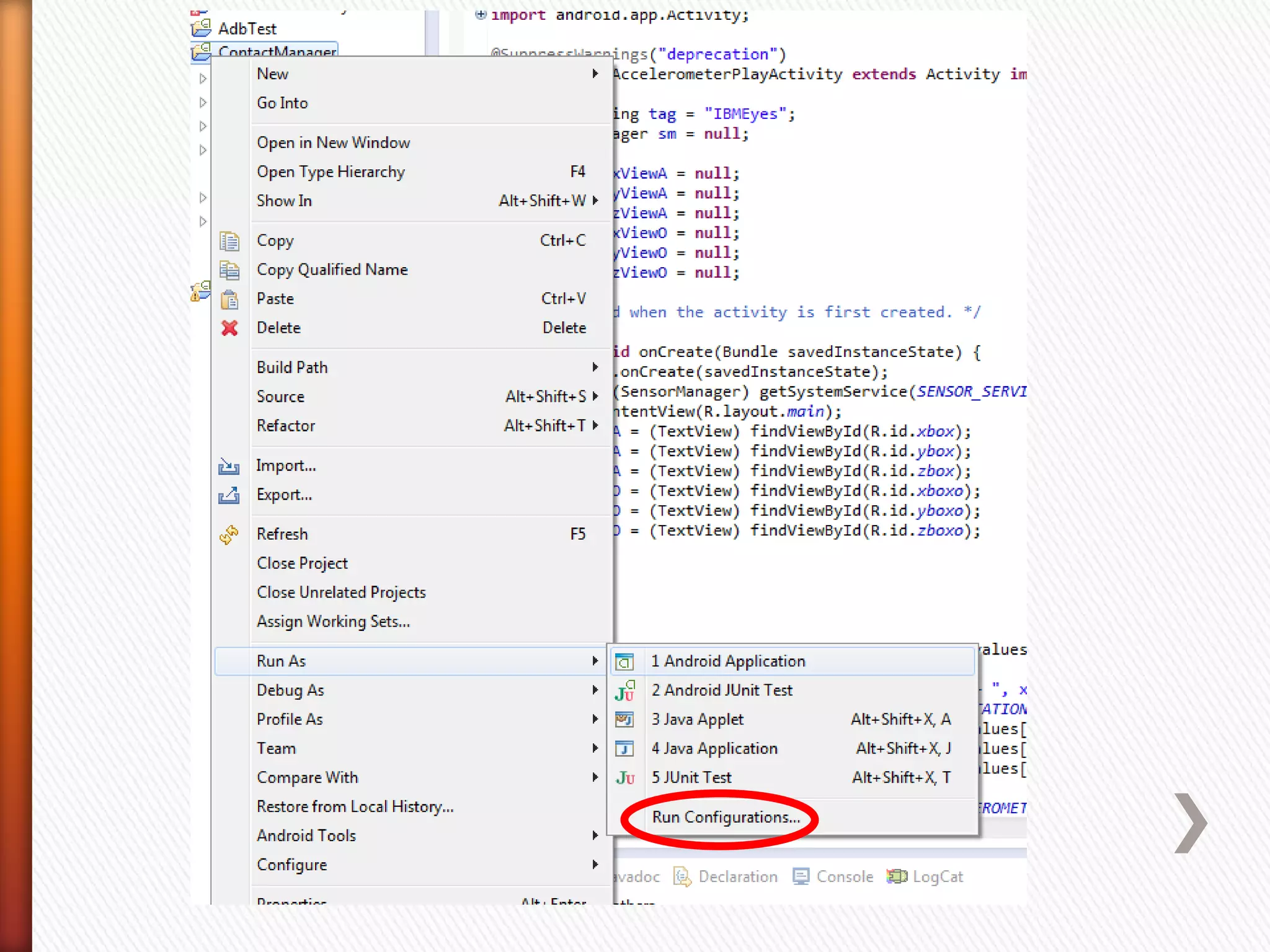
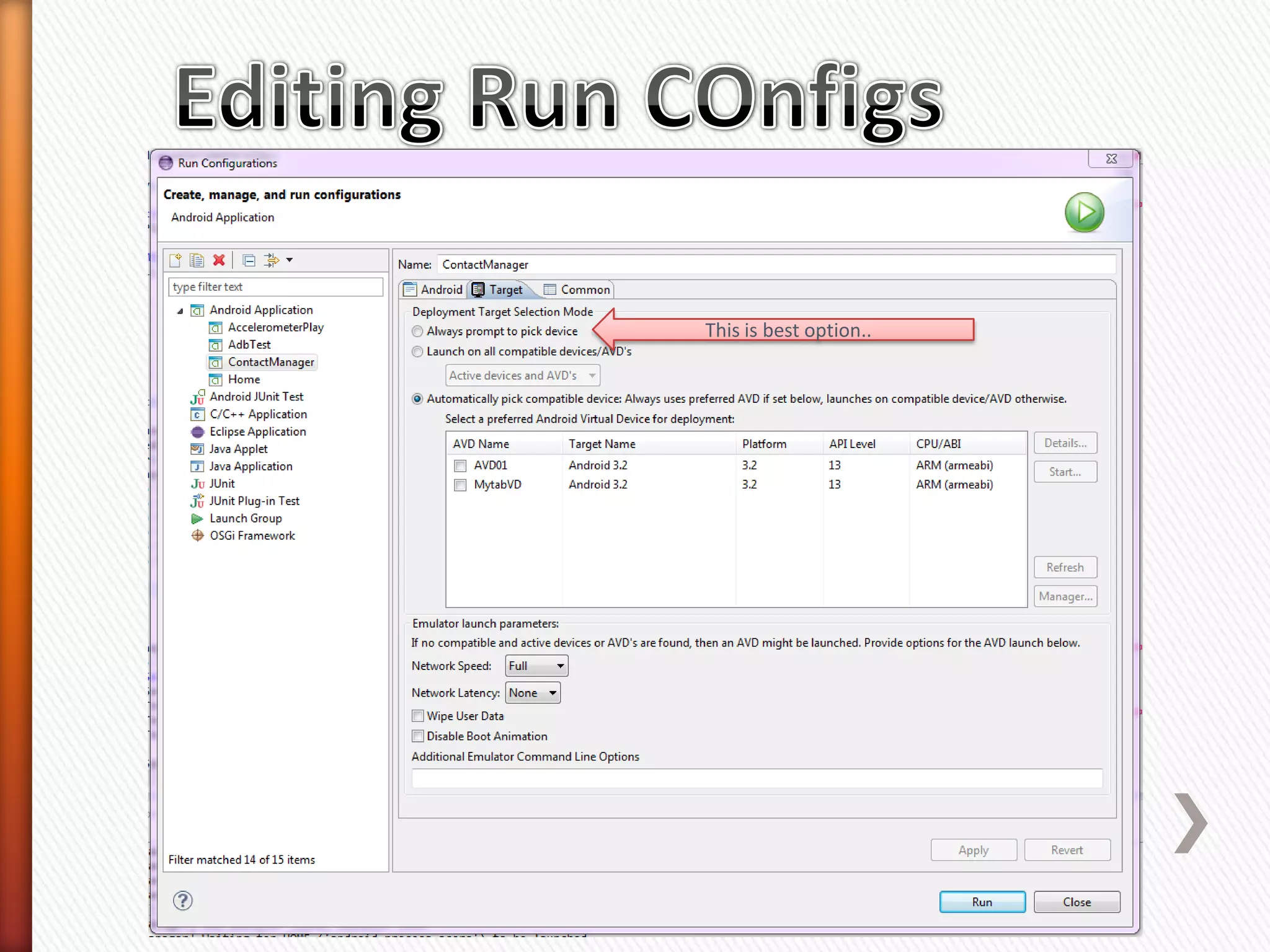
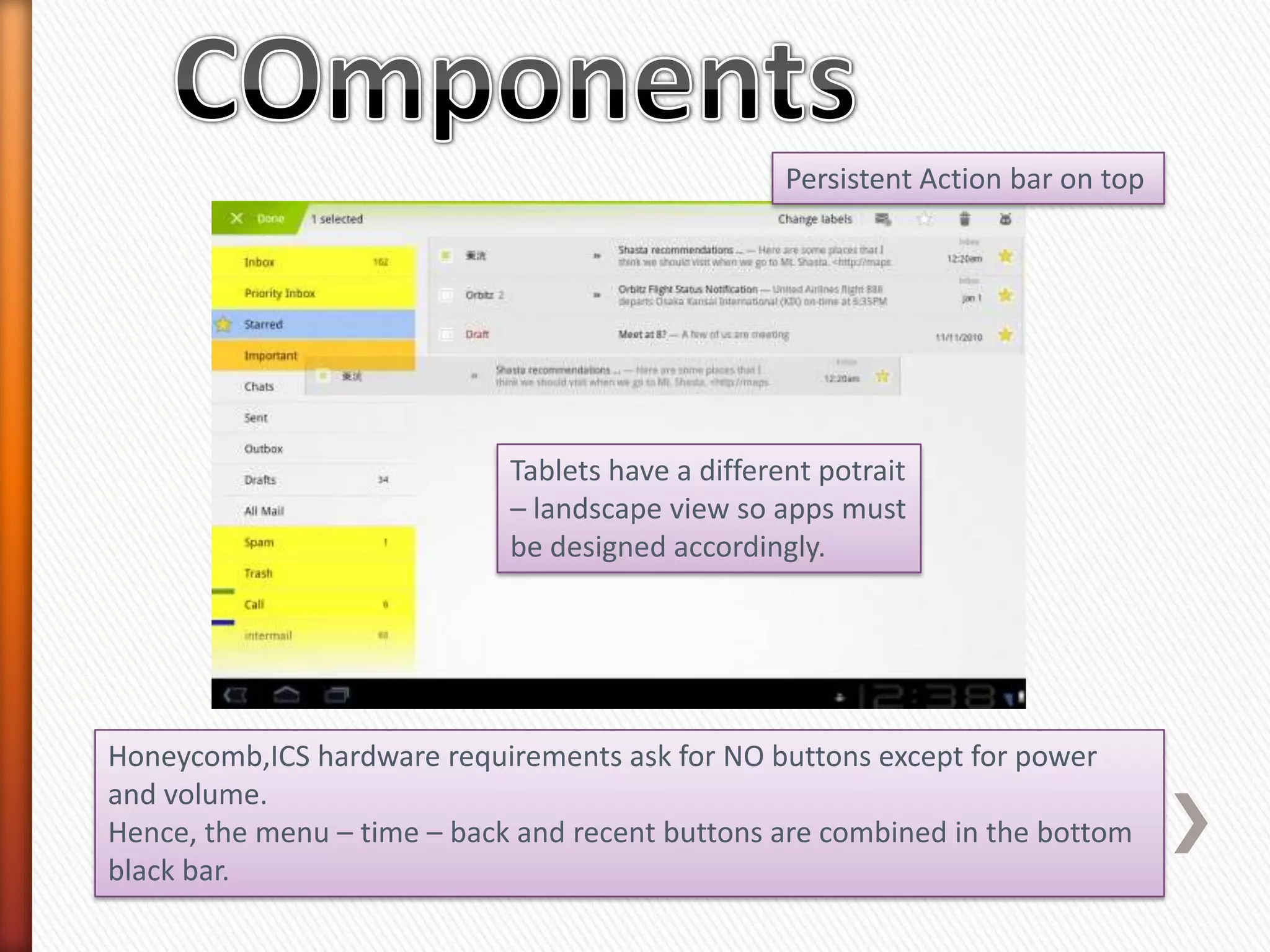
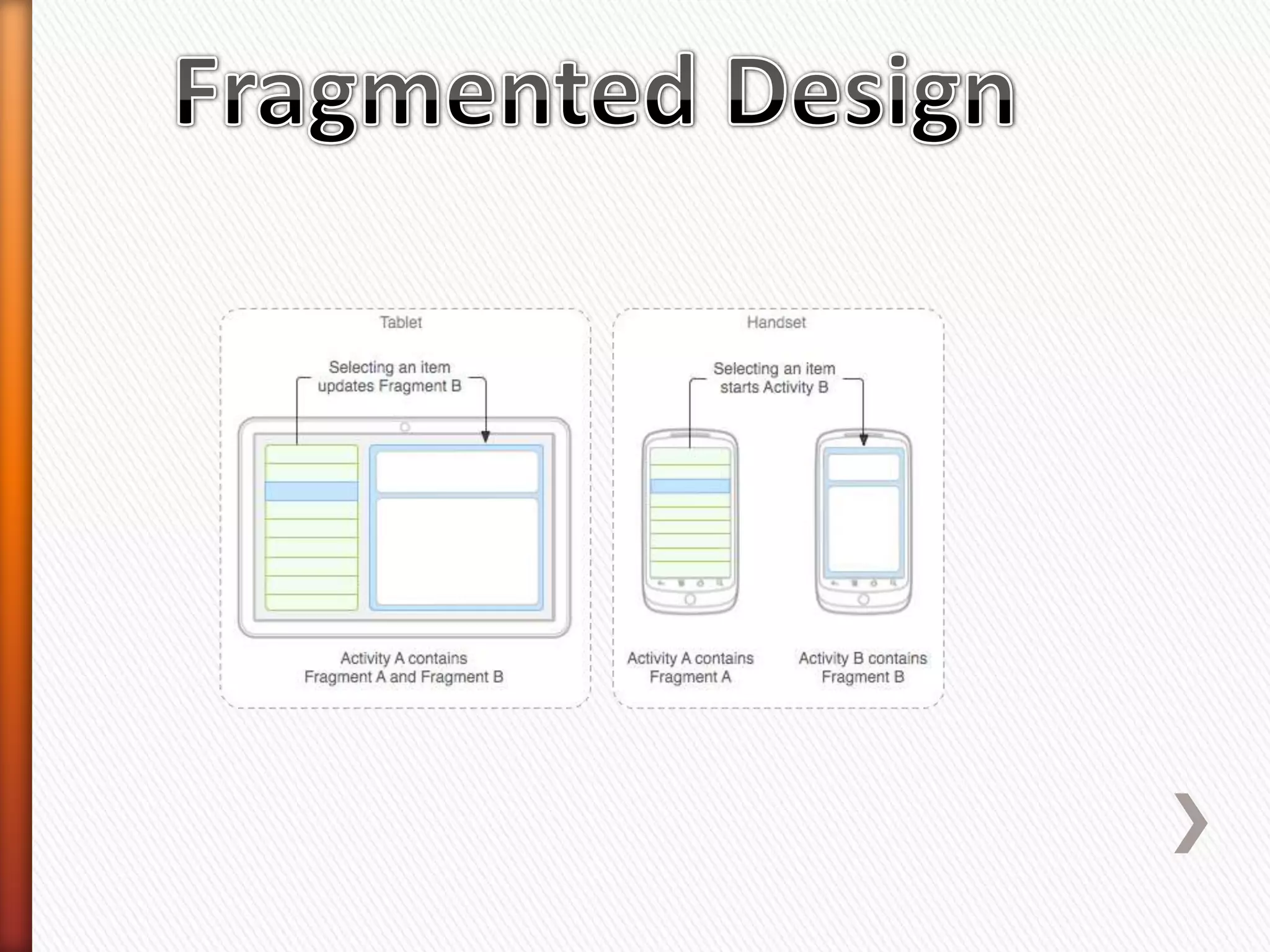
The document provides information about Android operating system. It describes that Android is an open source operating system based on Linux kernel maintained by Google. It allows hardware manufacturers to use it freely on their devices and provides a unified framework for software developers to build and distribute mobile applications. The document then explains Android software stack including Linux kernel, libraries, Dalvik Virtual Machine, application framework and applications layer. It also discusses installing Android SDK, setting up development environment in Eclipse or IntelliJ IDEs, and using emulators or real devices for testing applications.