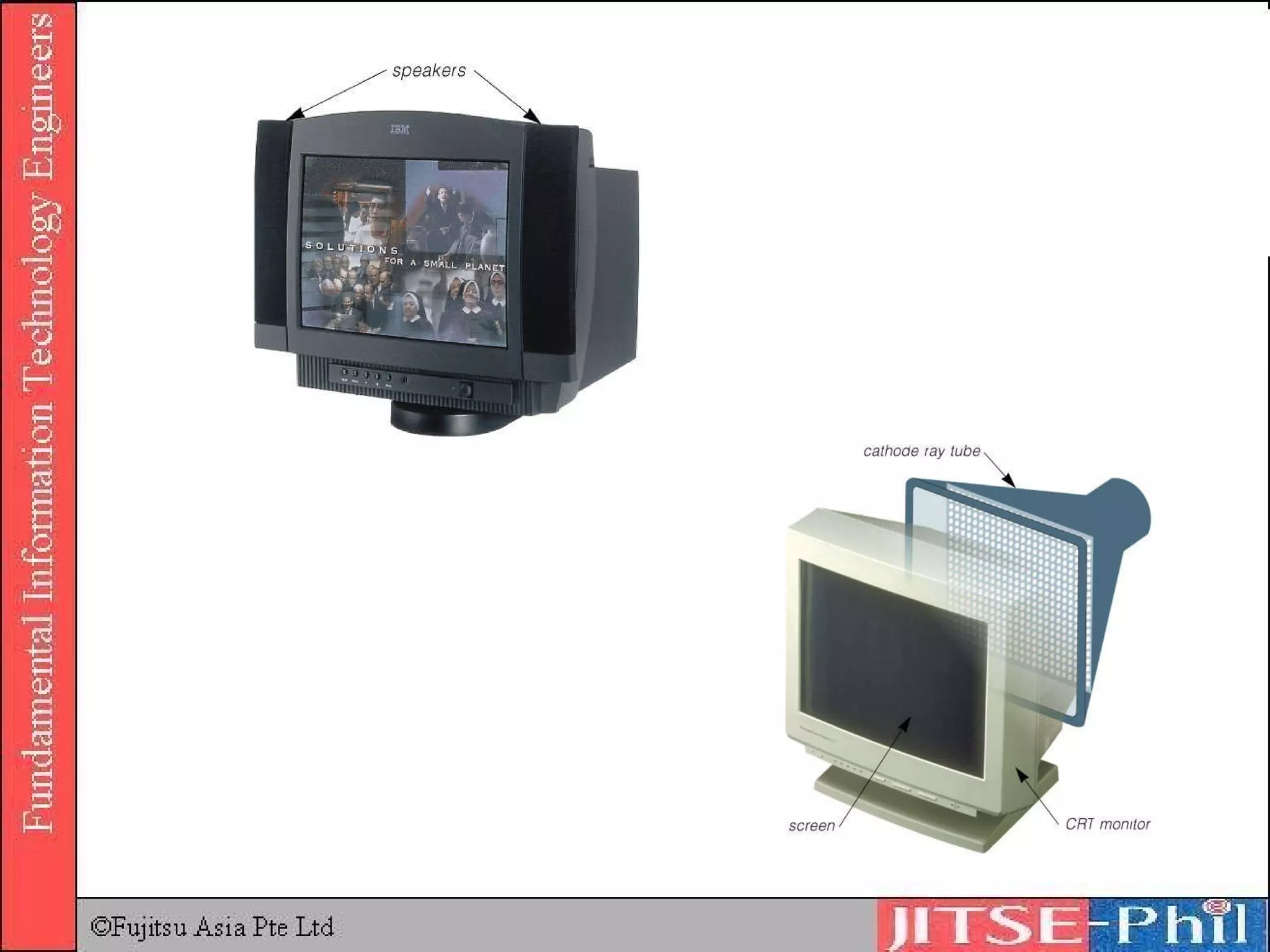
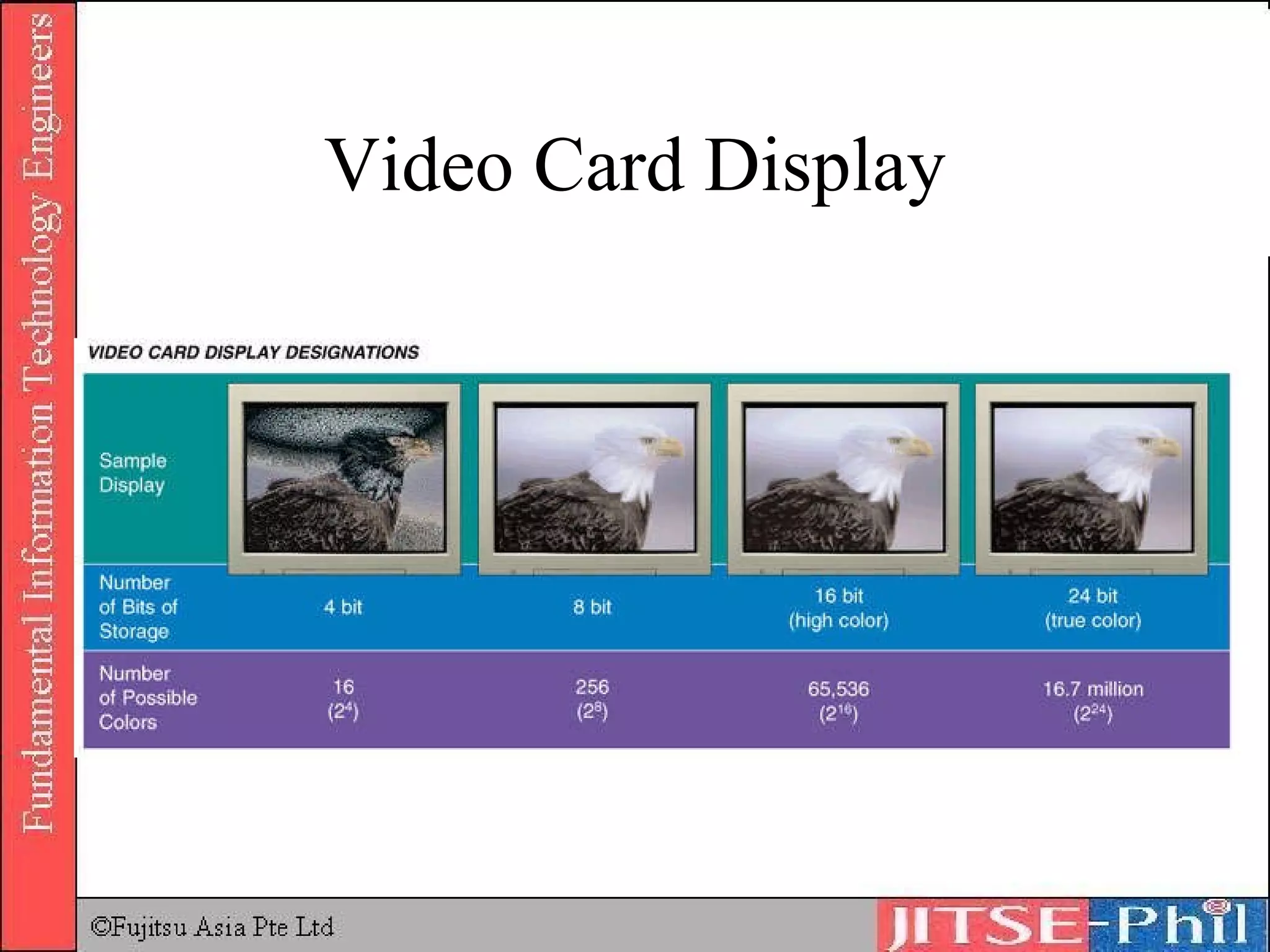
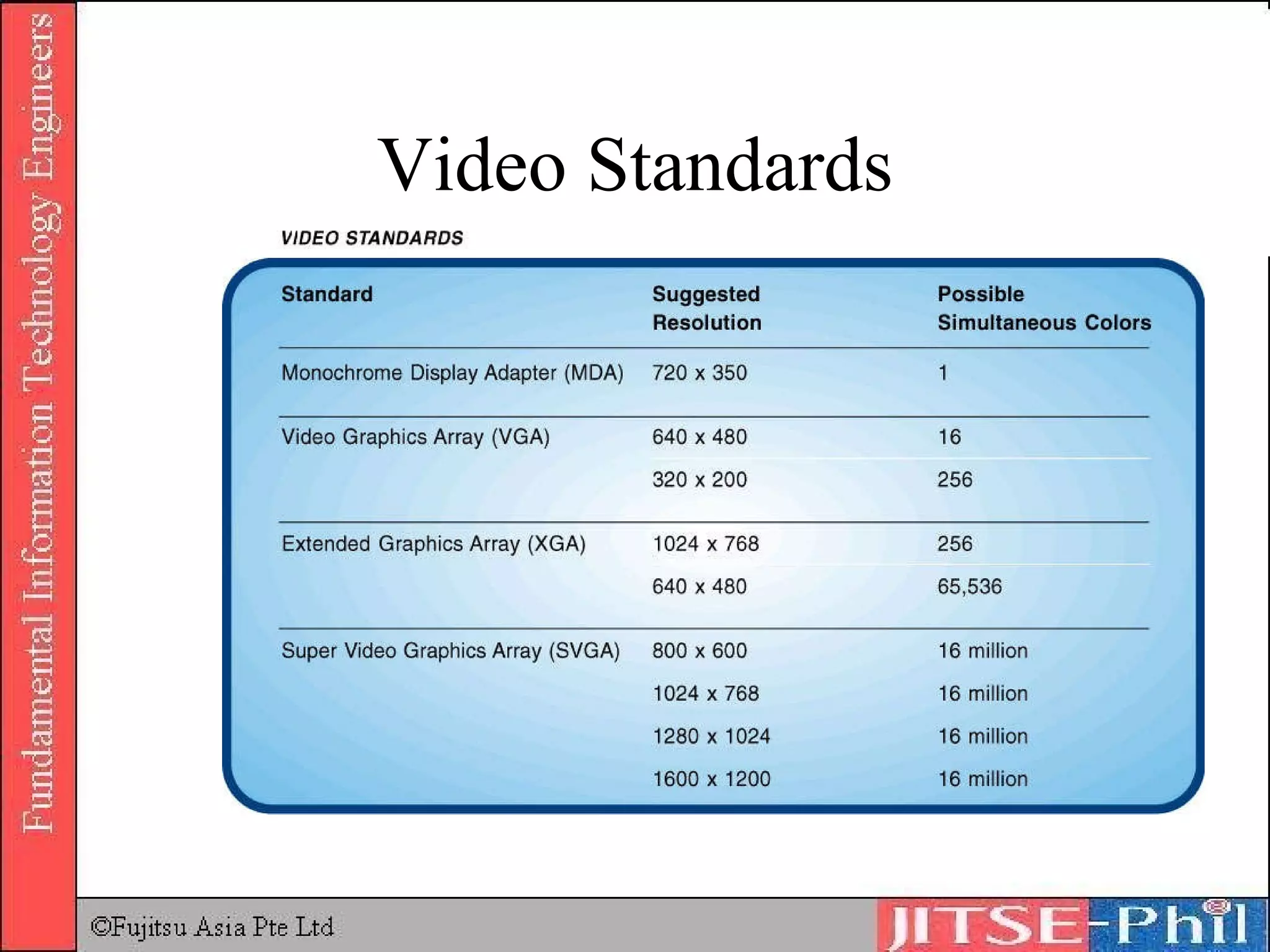
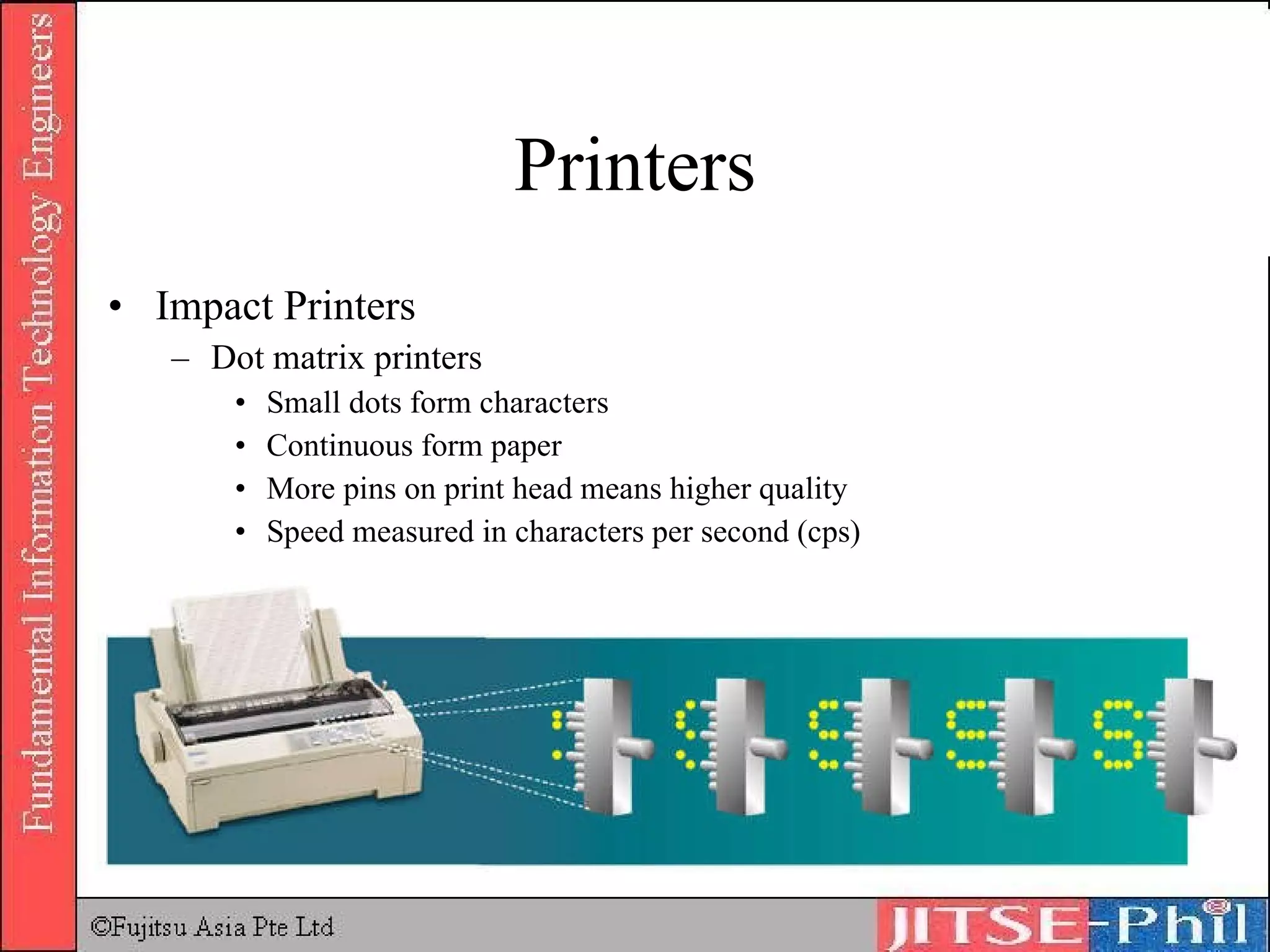
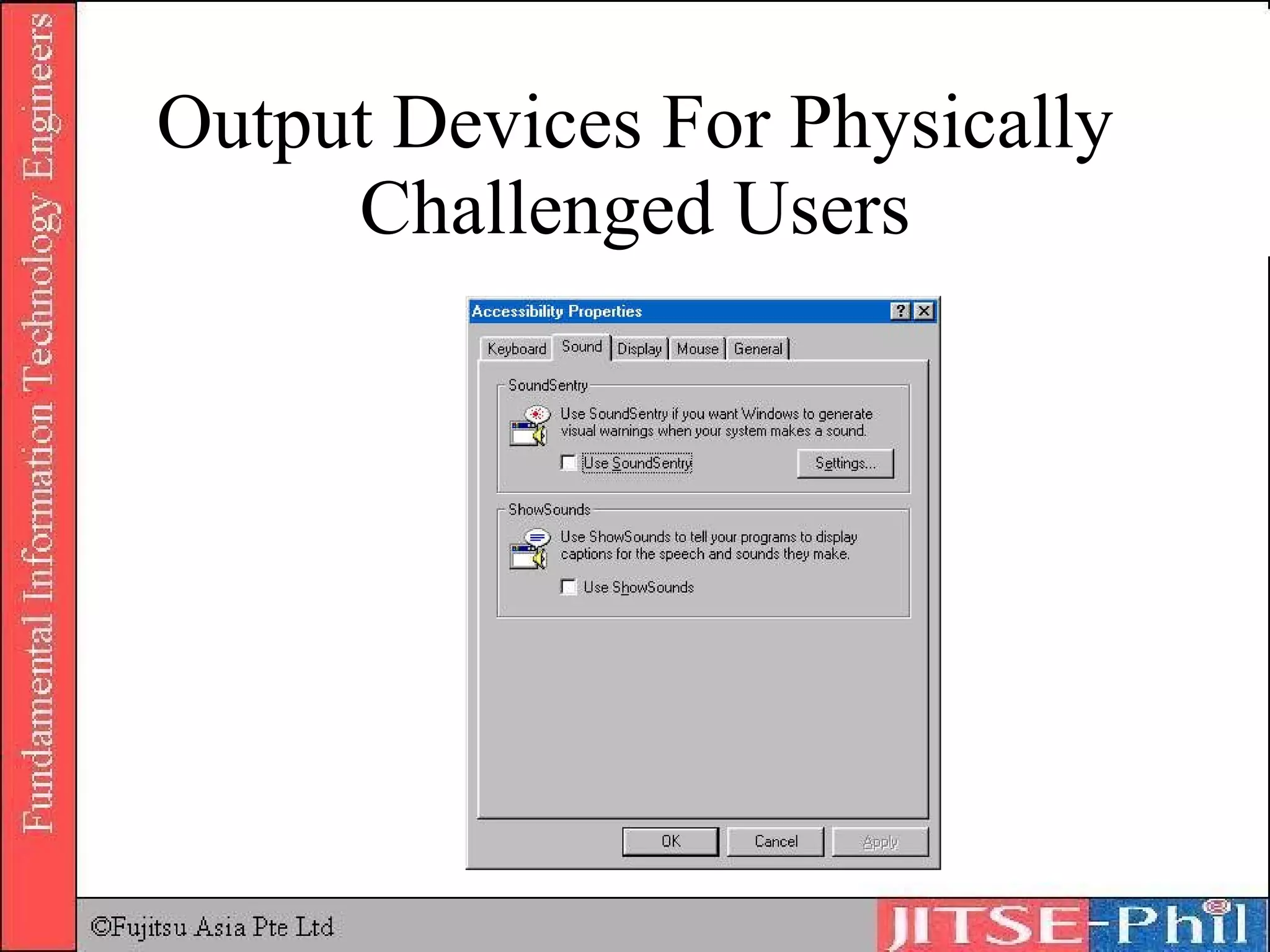
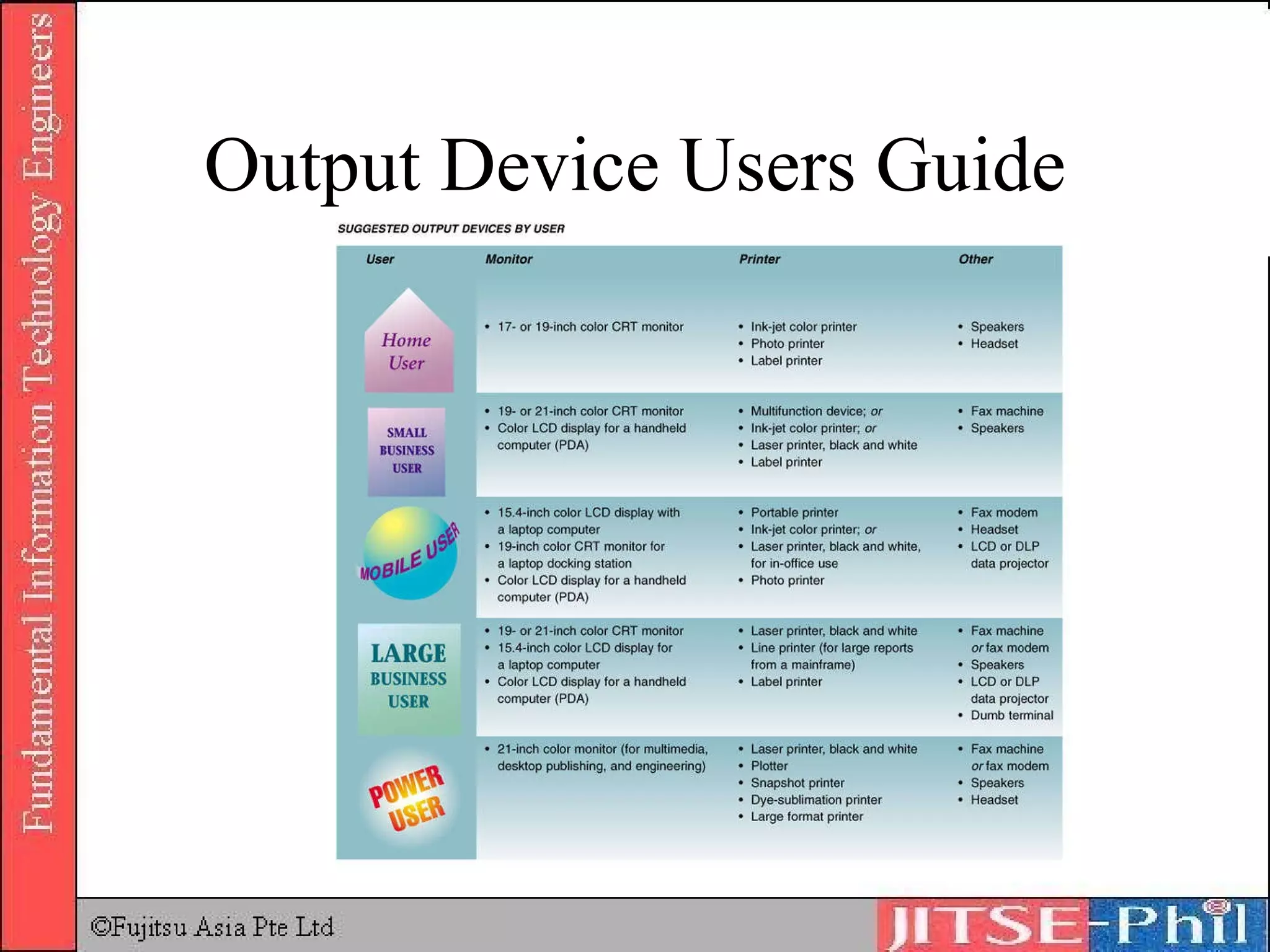
Output devices convey processed data and information to users. Display devices like monitors visually output text, graphics, and video using technologies like CRT, LCD, plasma, and projectors. Printers in turn output hard copies on paper using impact, inkjet, laser, and other technologies. Other output devices include audio speakers, fax machines, and multifunction devices that combine printing, scanning, copying, and faxing functions. Output devices are adapted for physically challenged users through accessibility features and specialized devices like Braille printers.