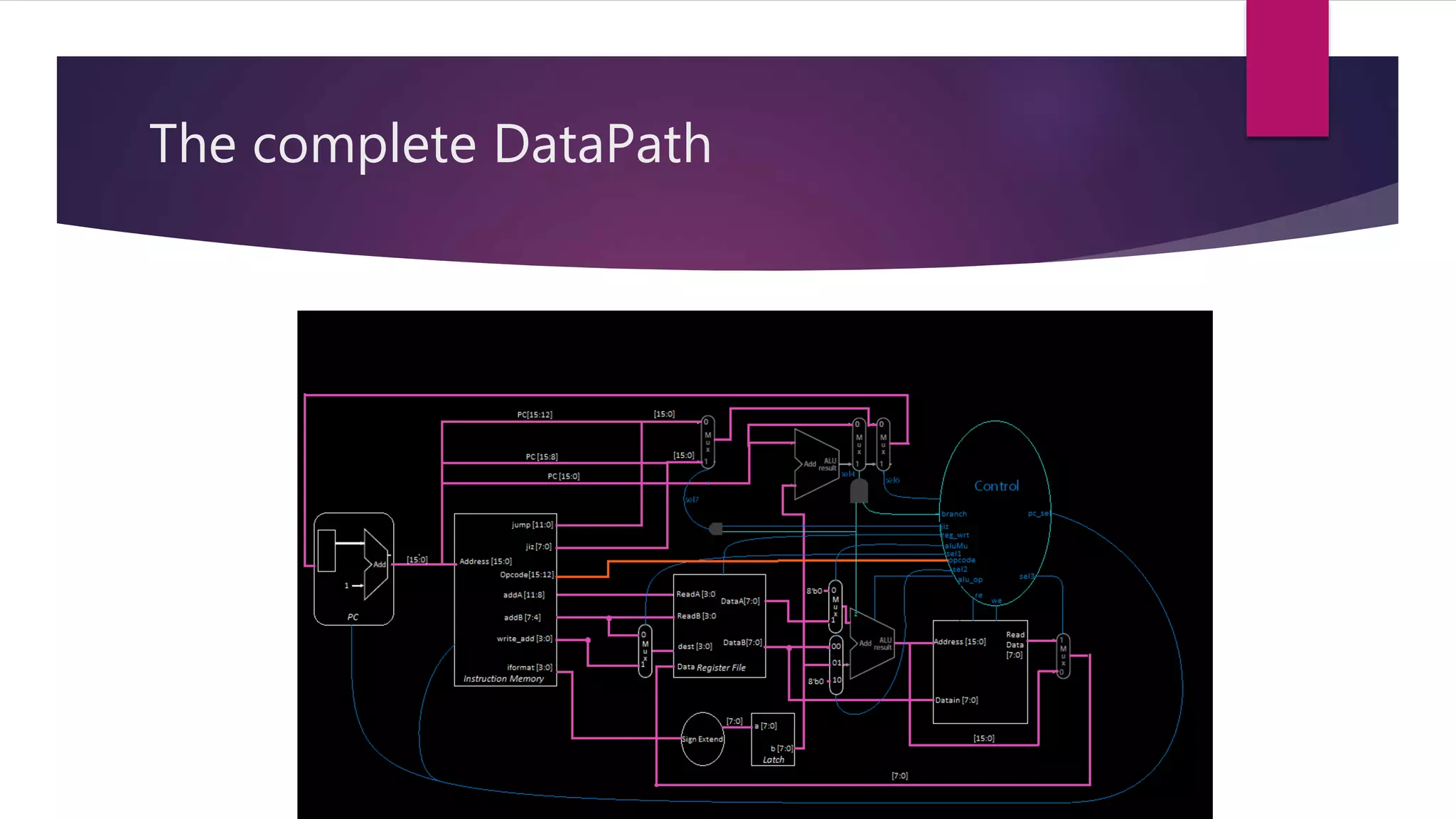
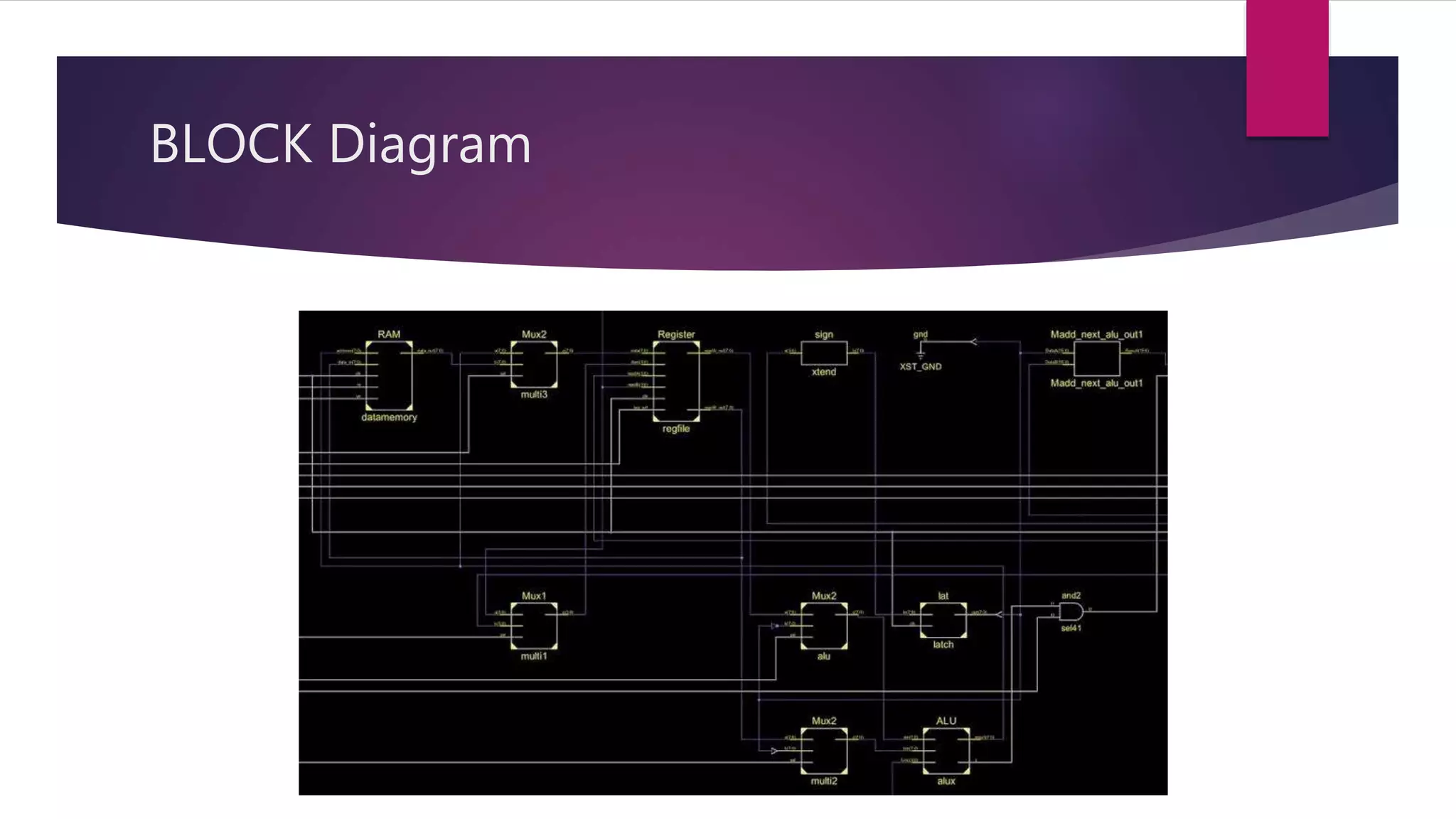
The document details the architecture of a 16-bit RISC processor, emphasizing its components such as the ALU, program counter, instruction memory, data memory, multiplexors, and control unit. It explains why RISC was introduced as a more efficient alternative to CISC, highlighting its faster instruction execution. Additionally, specifications related to the maximum frequencies of registers, instruction, and data memory are provided to illustrate the processor's performance.