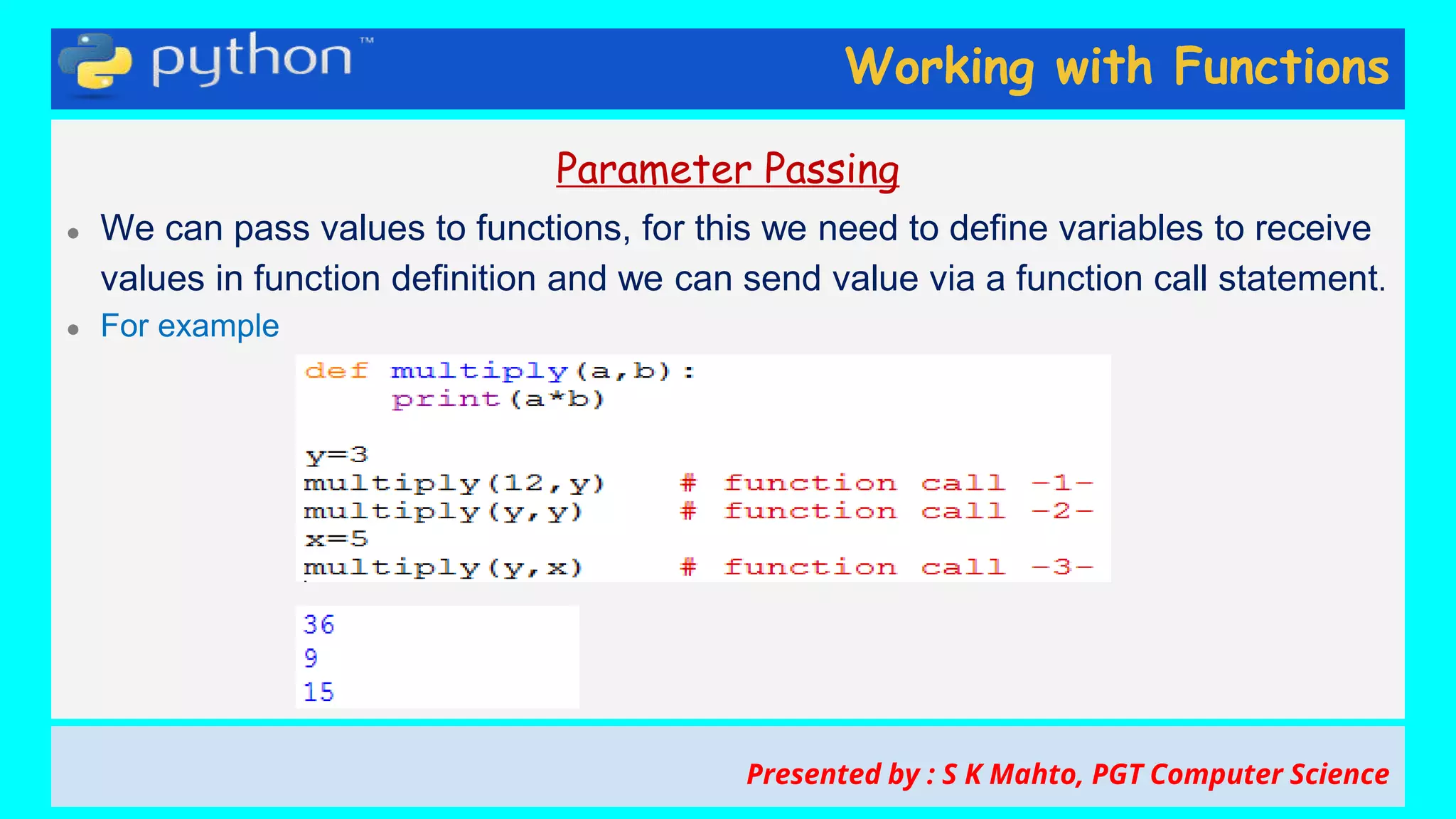
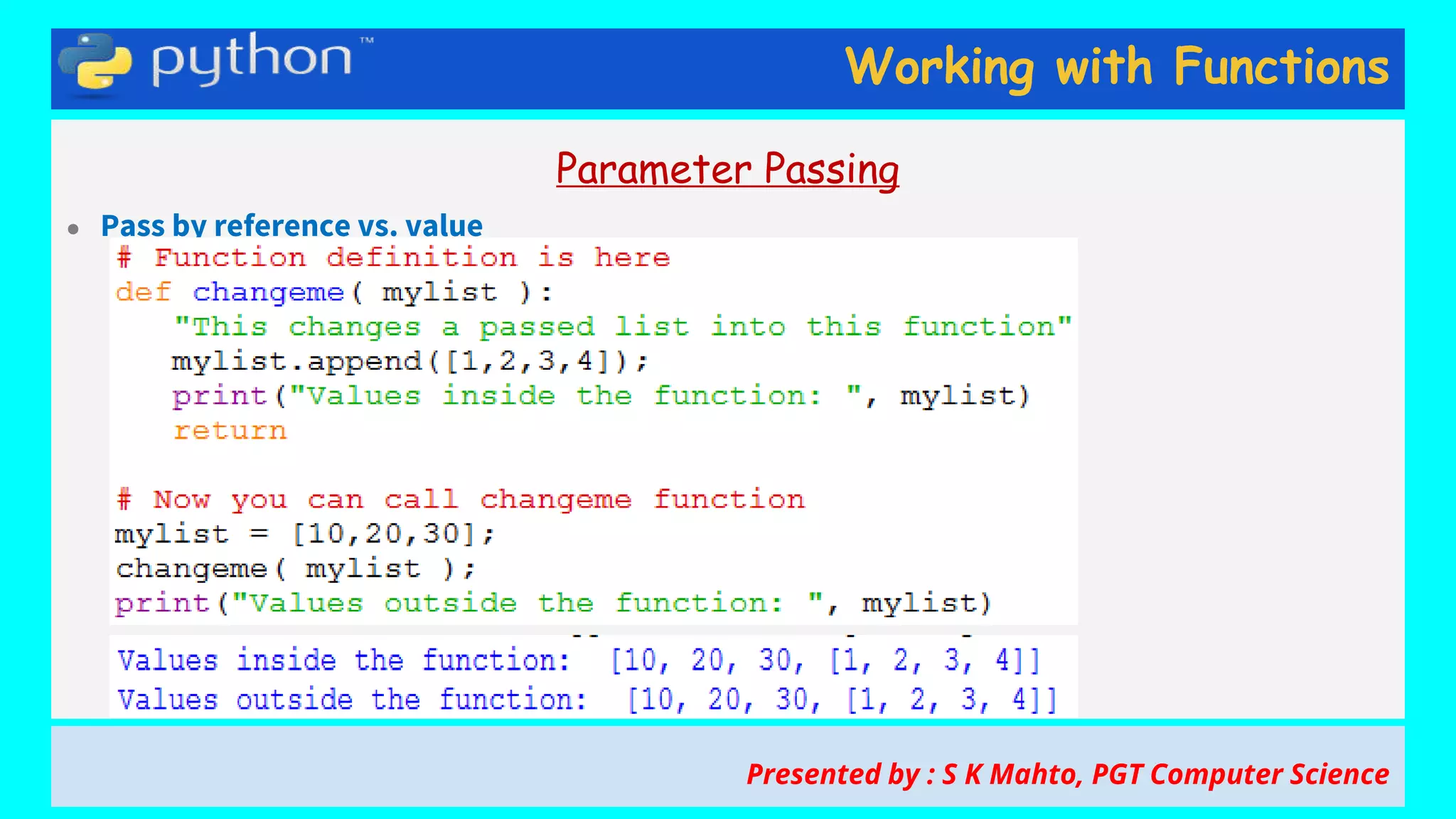
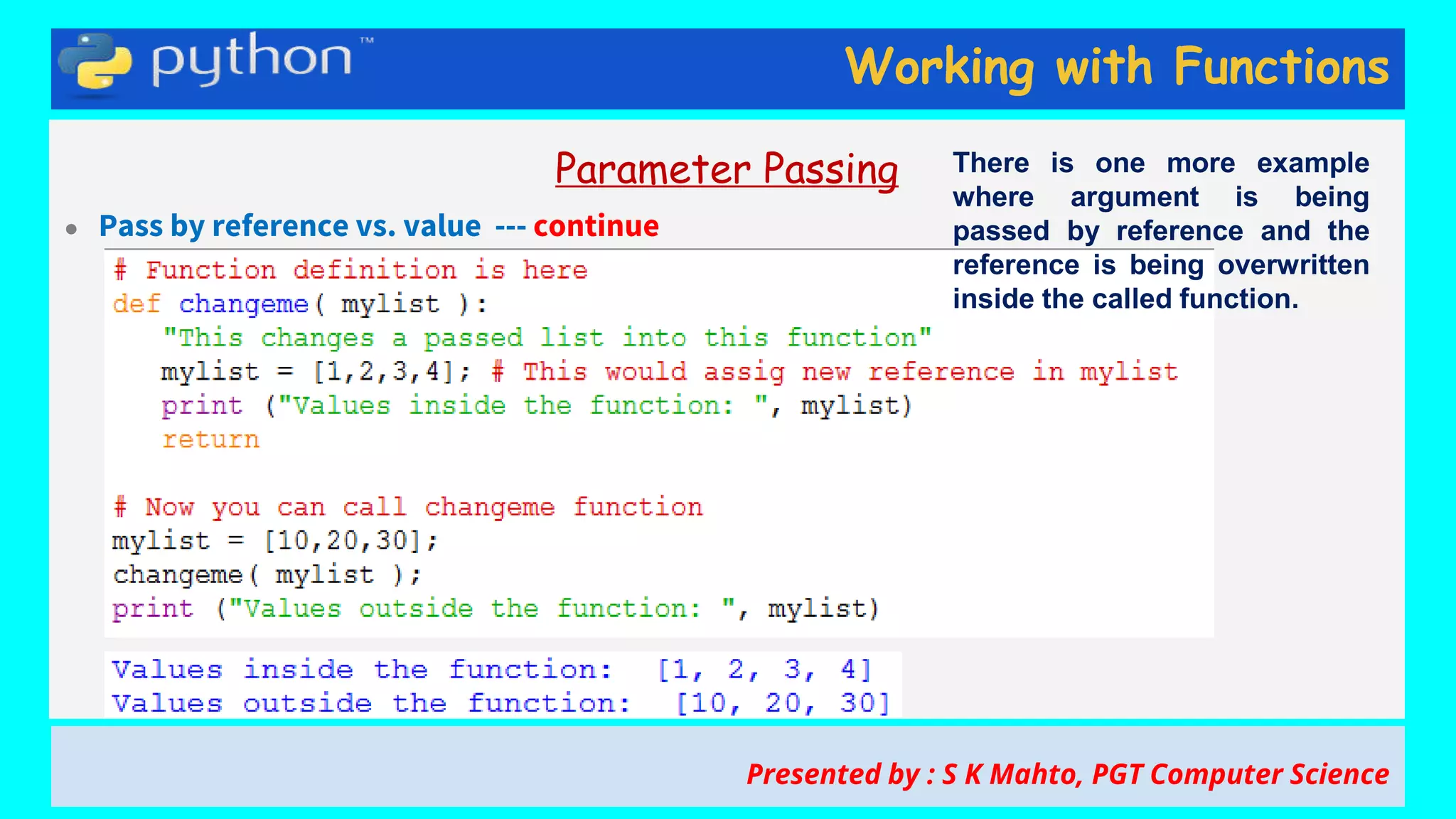
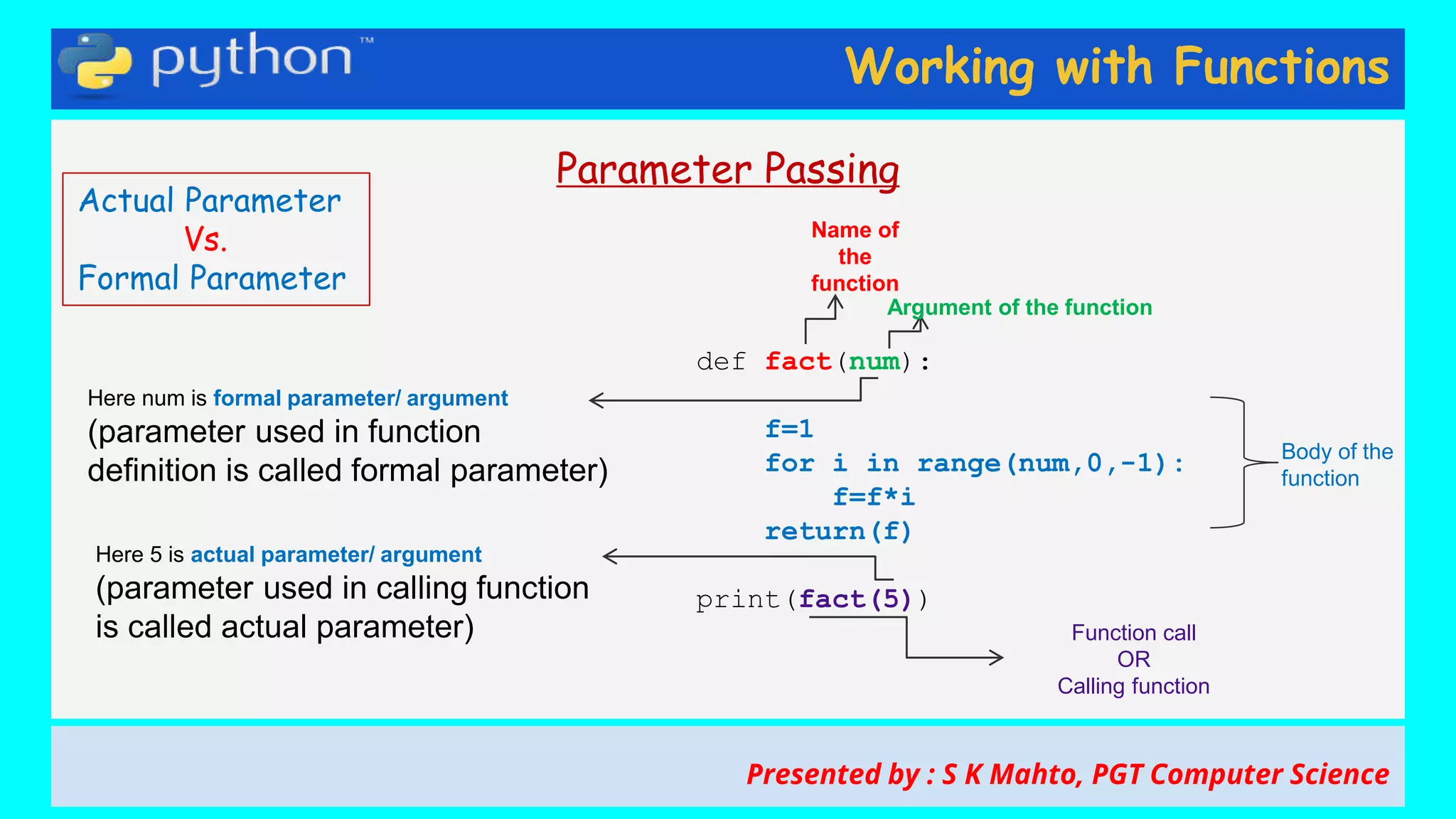
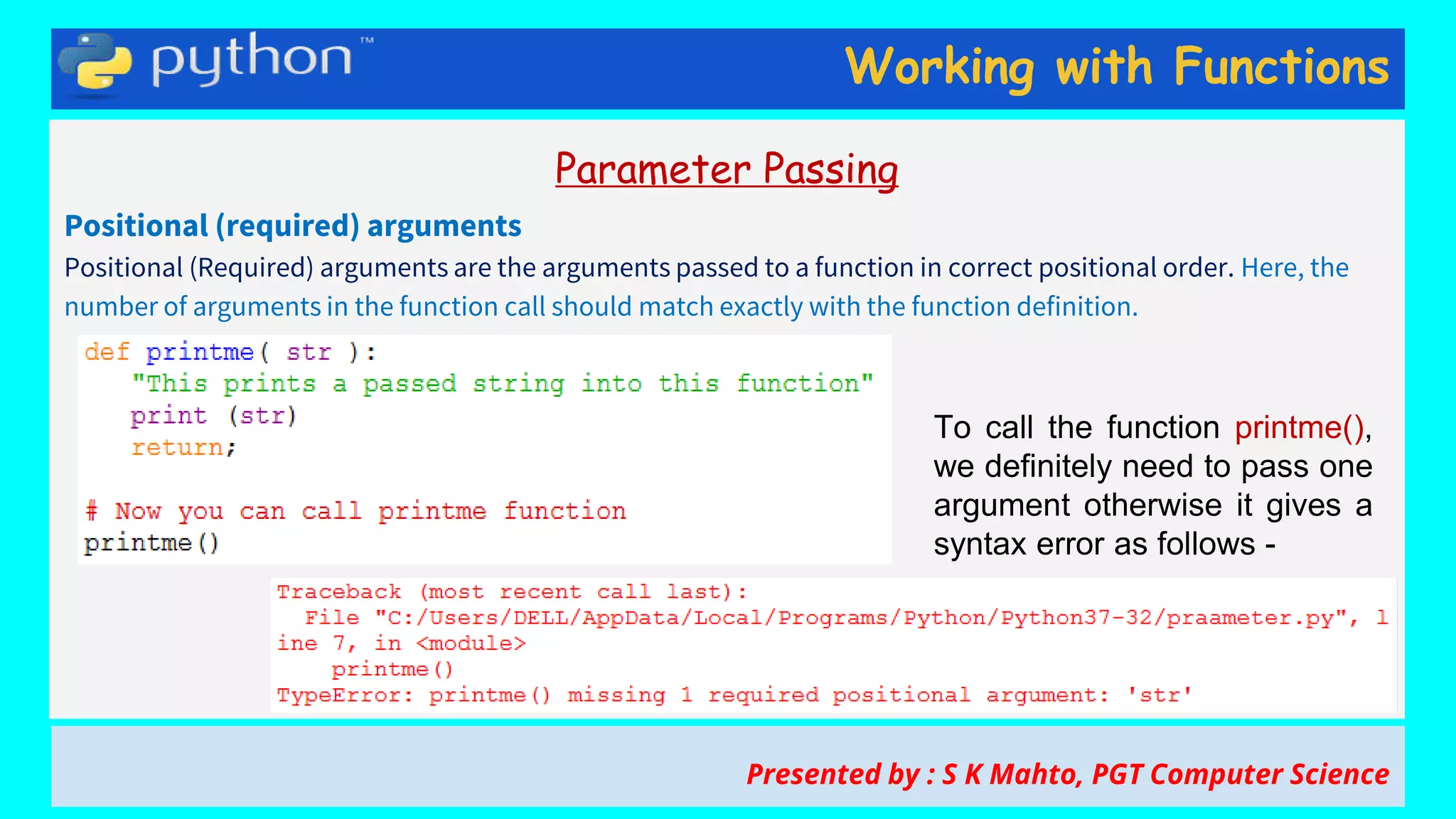
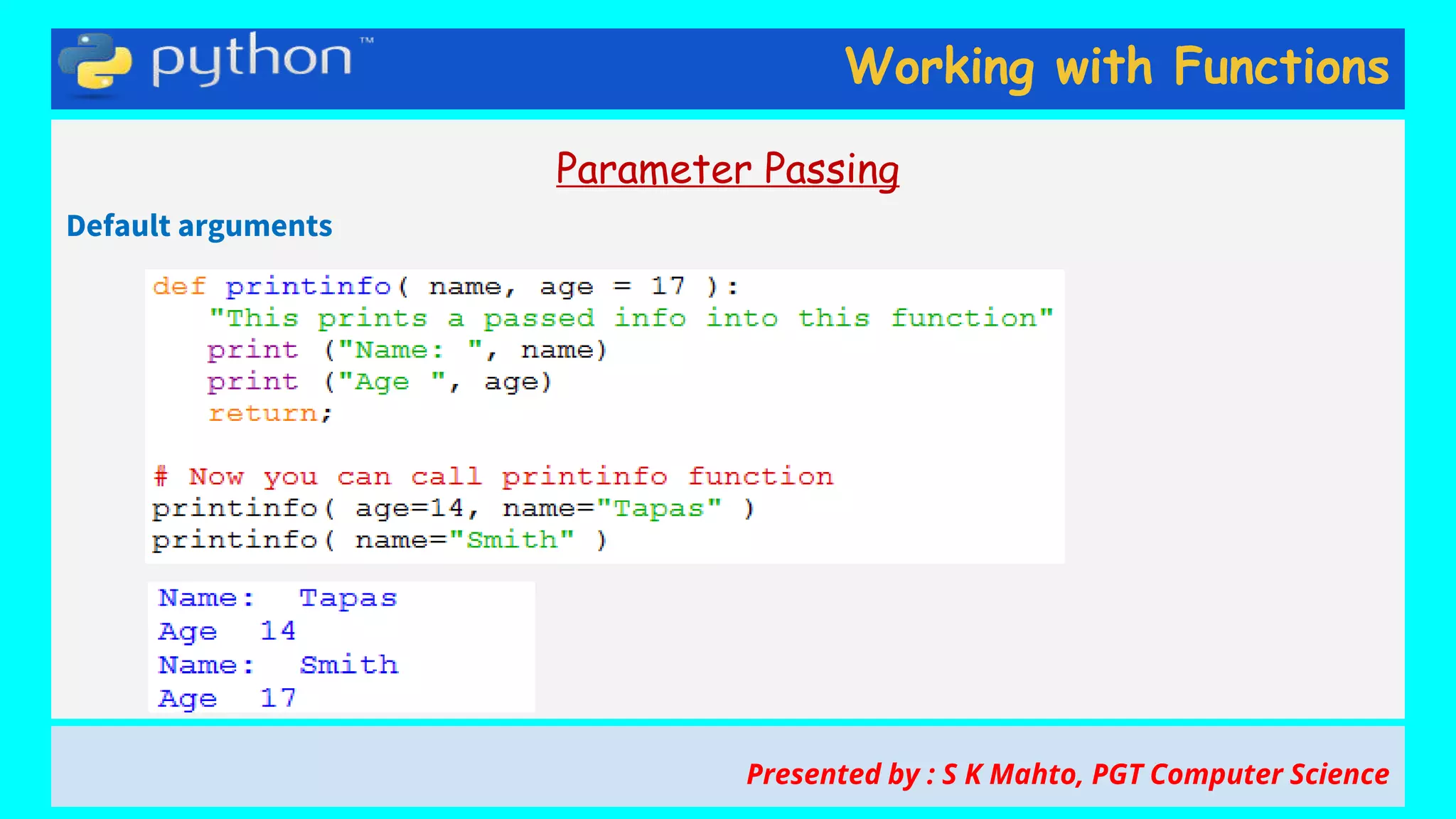
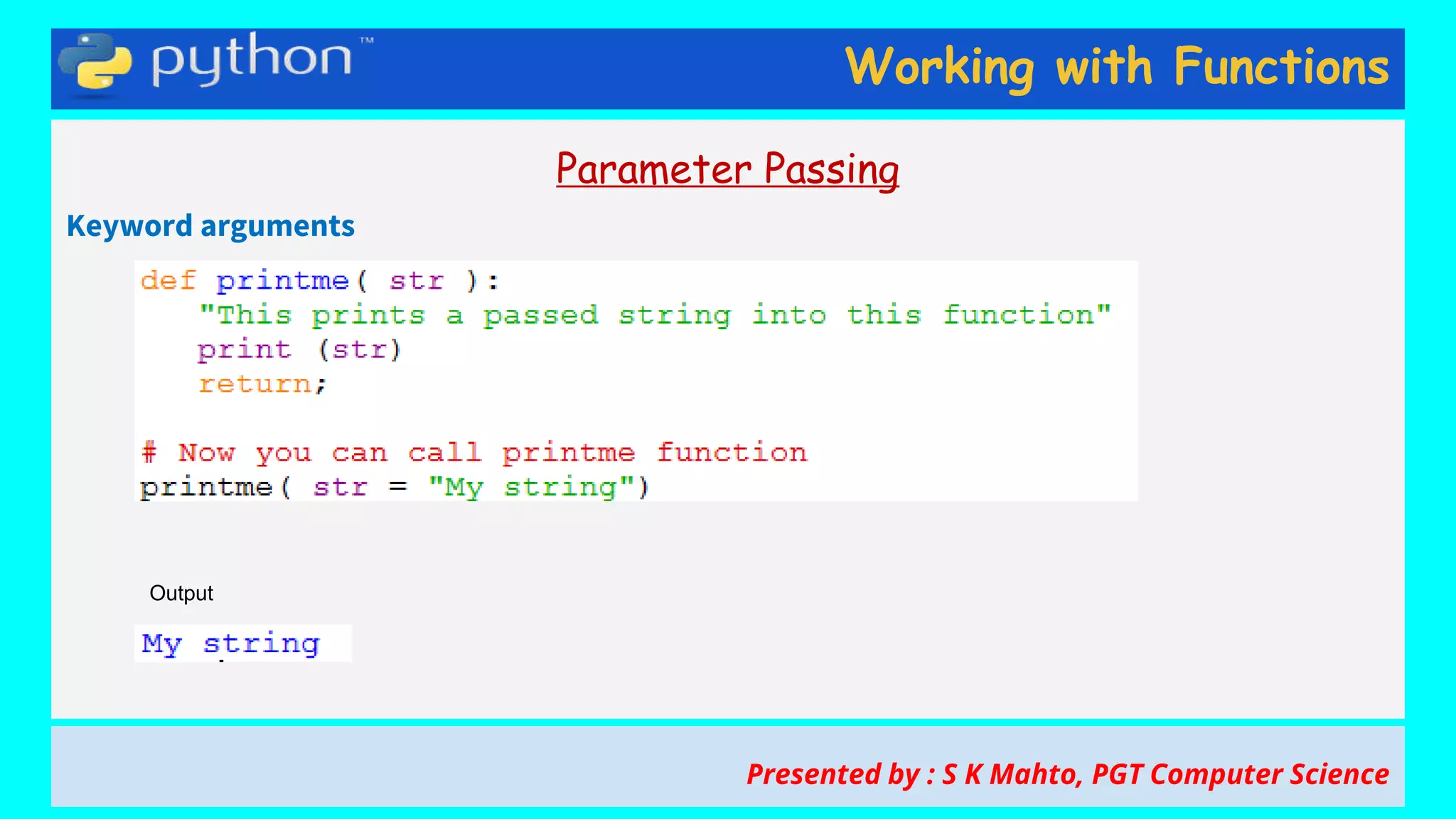
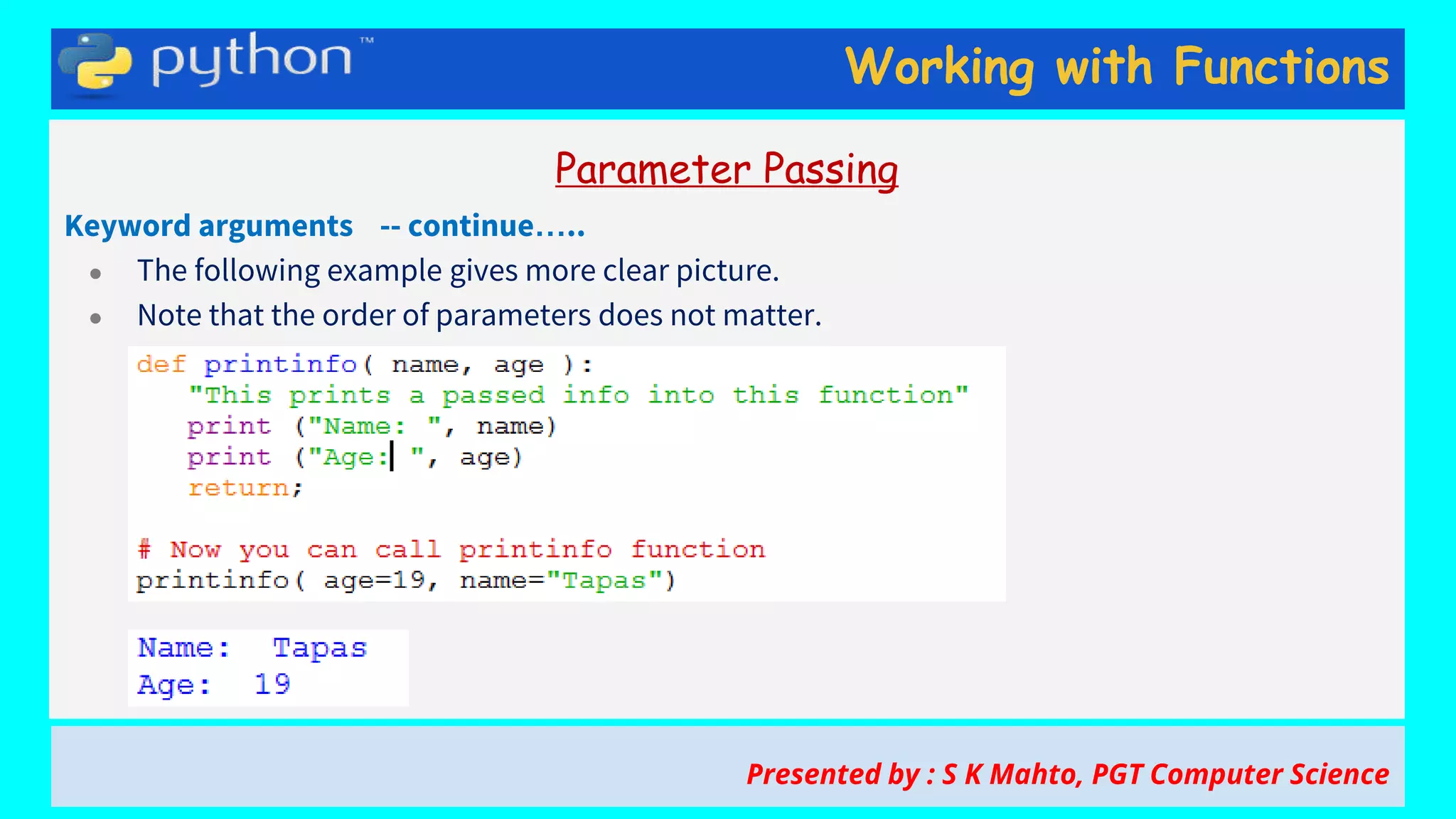
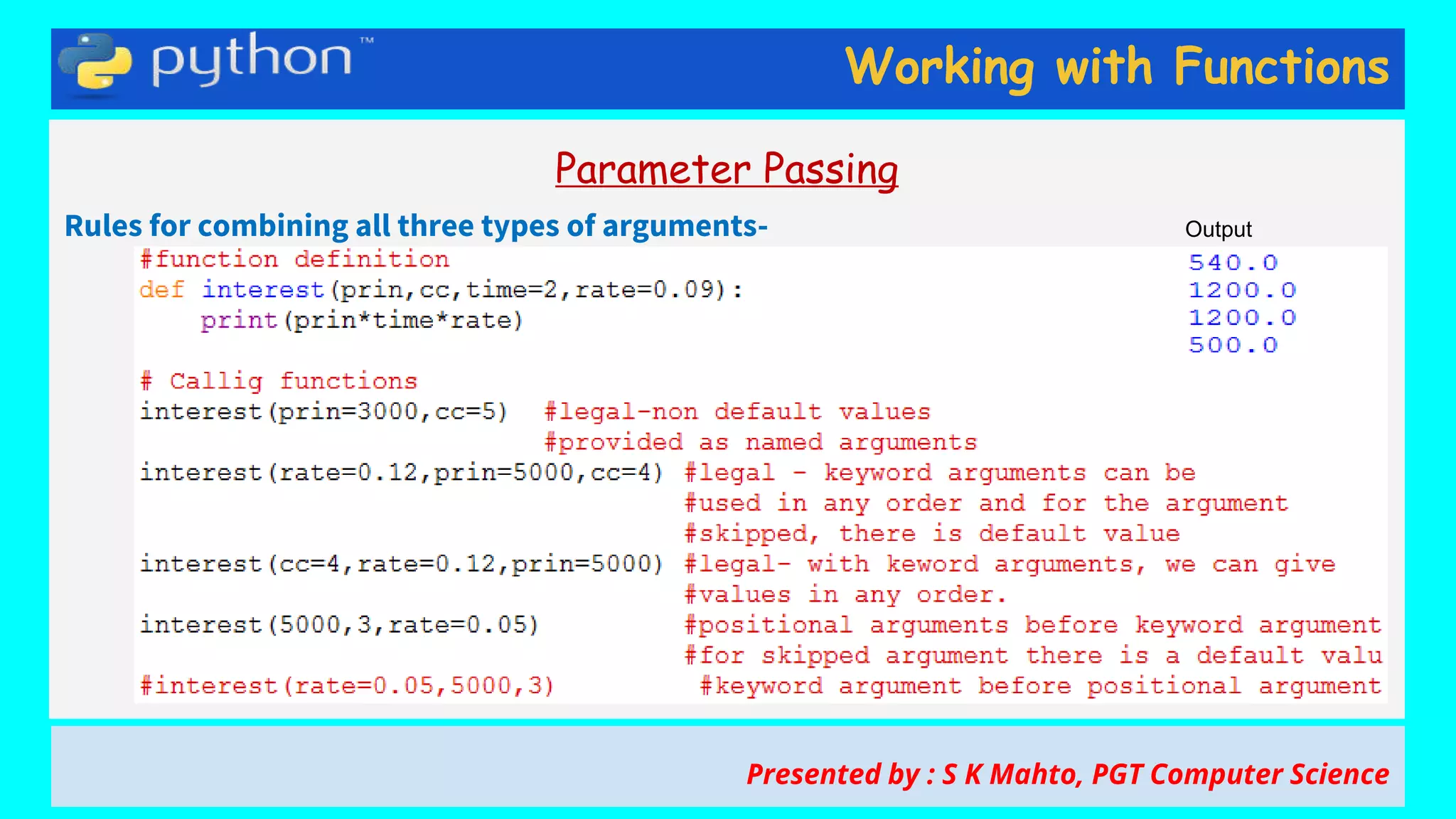
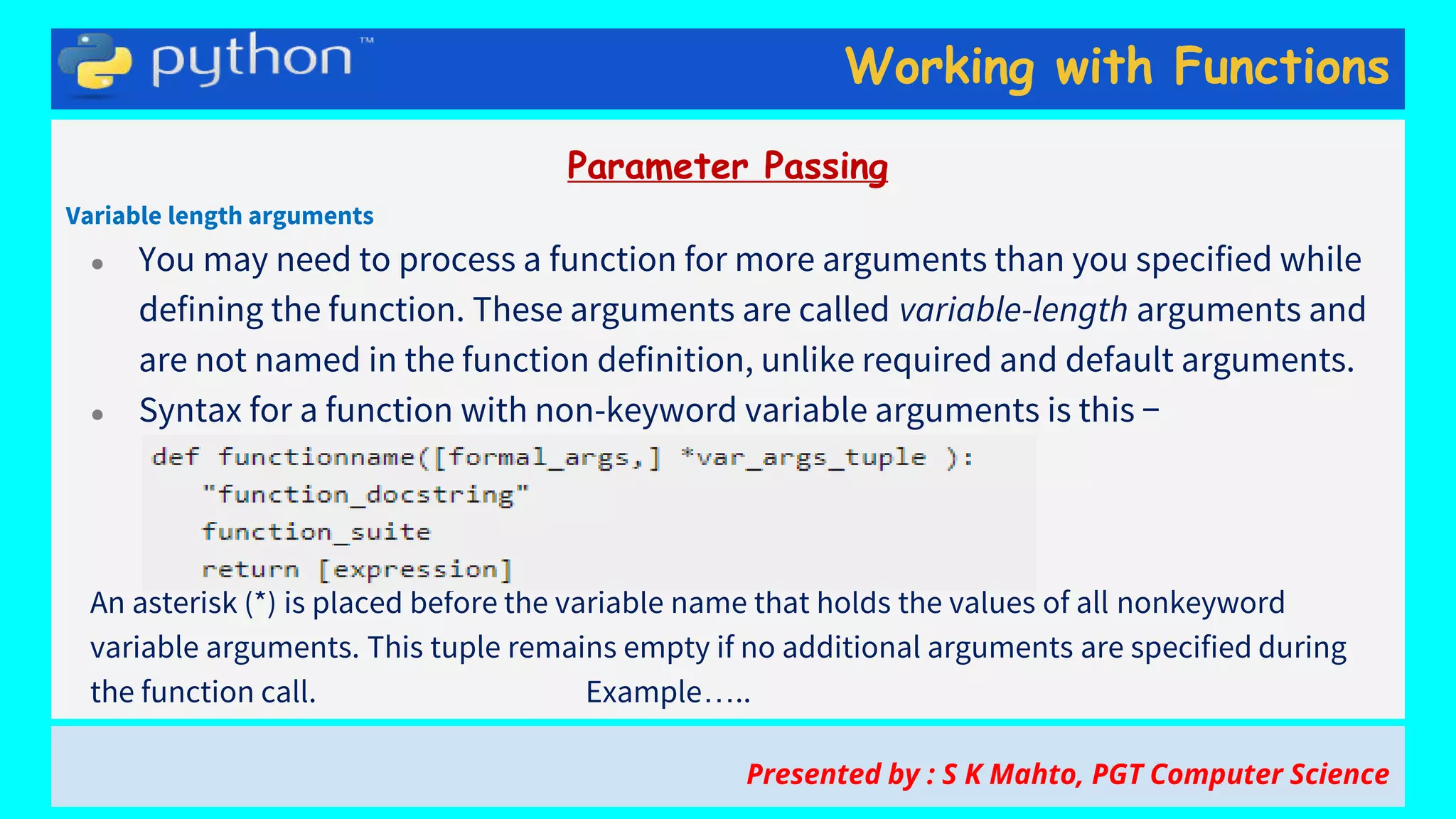
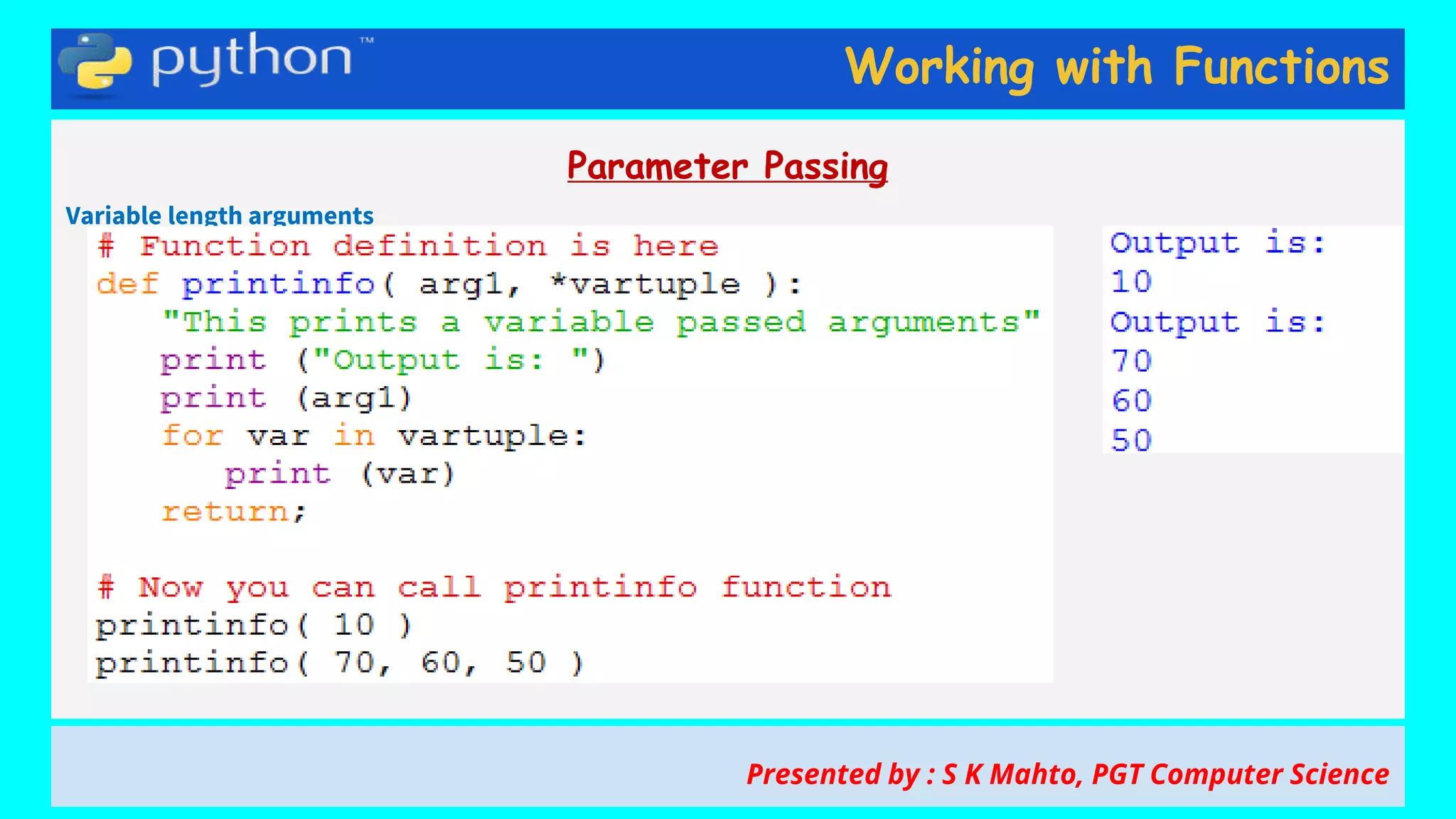
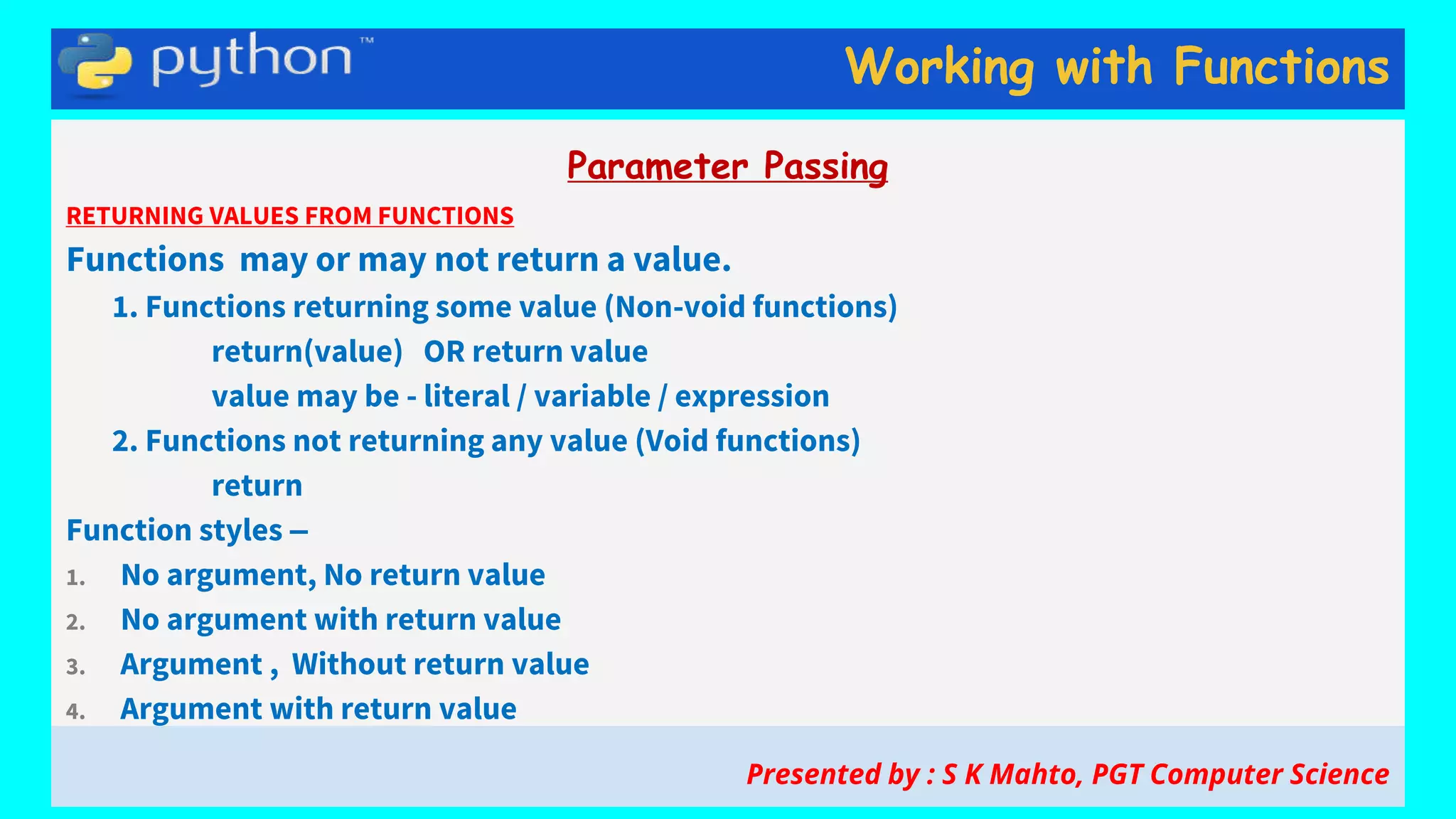
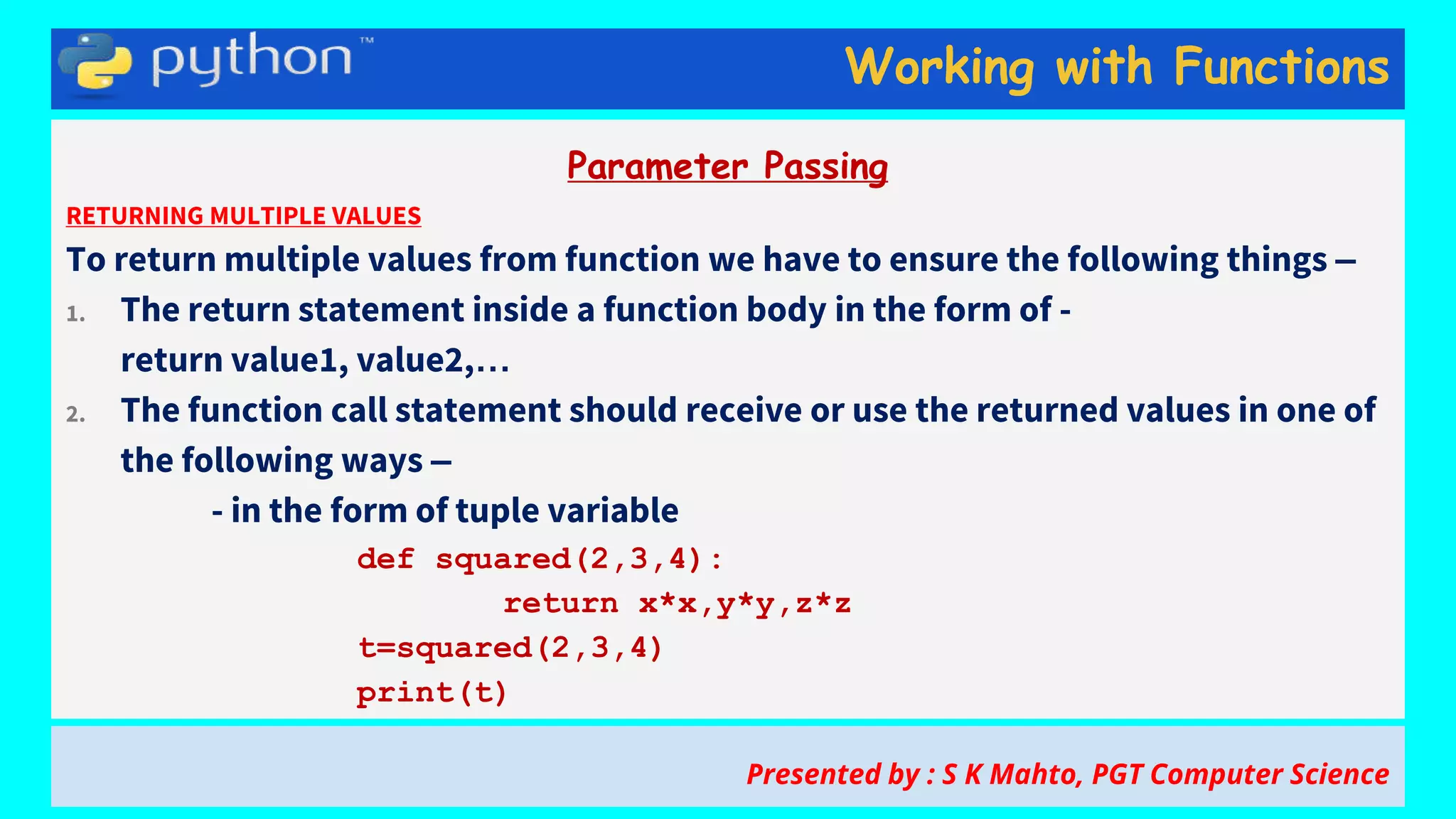
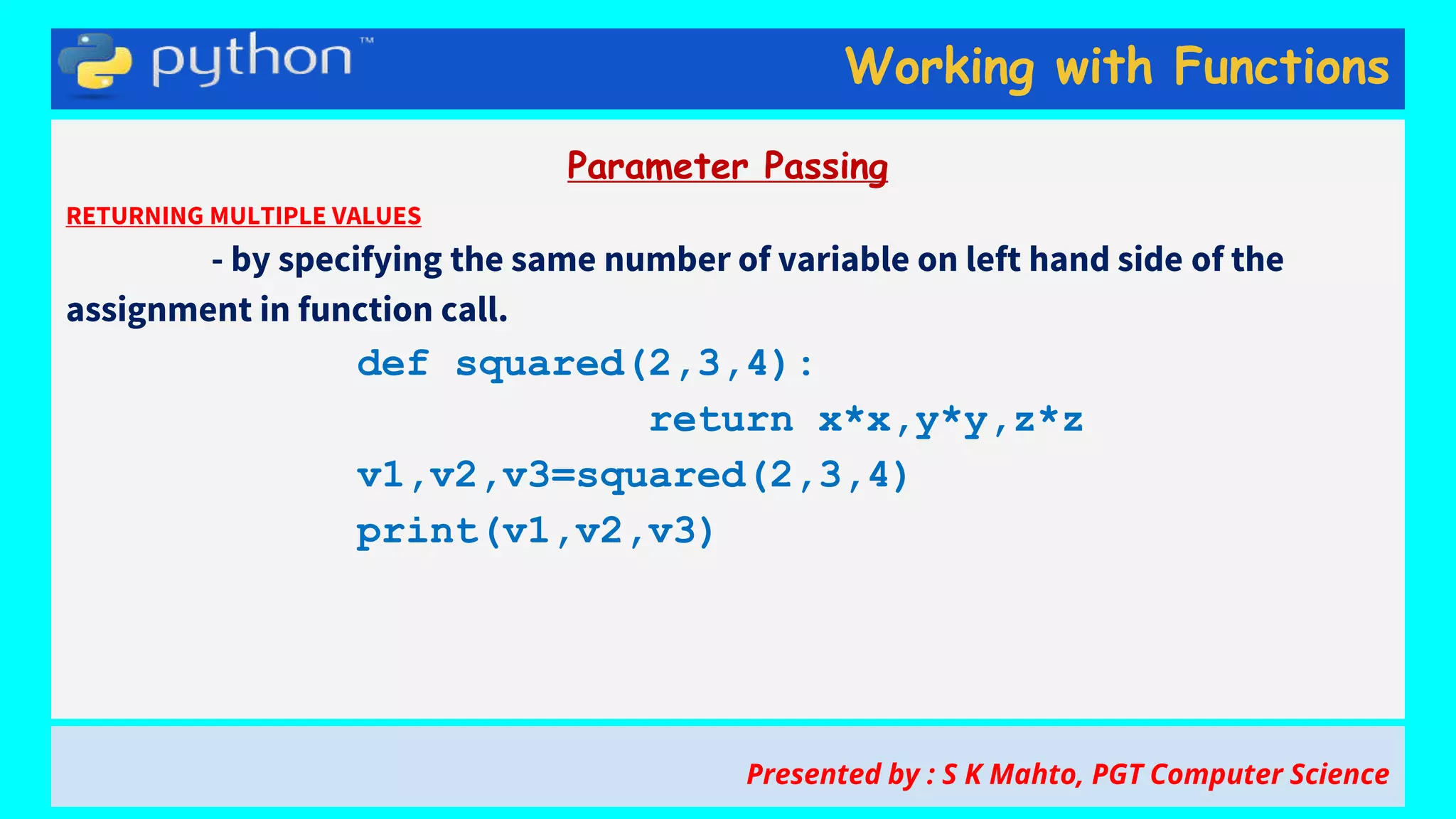
This document contains slides from a presentation on working with functions and parameter passing in Python. It discusses different types of parameters like positional/required arguments, default arguments, keyword arguments, and variable length arguments. It also covers returning values from functions, including returning multiple values using a tuple. Examples are provided to illustrate passing arguments by reference vs. value, combining argument types, and returning values. The presentation was given by S K Mahto, PGT Computer Science.