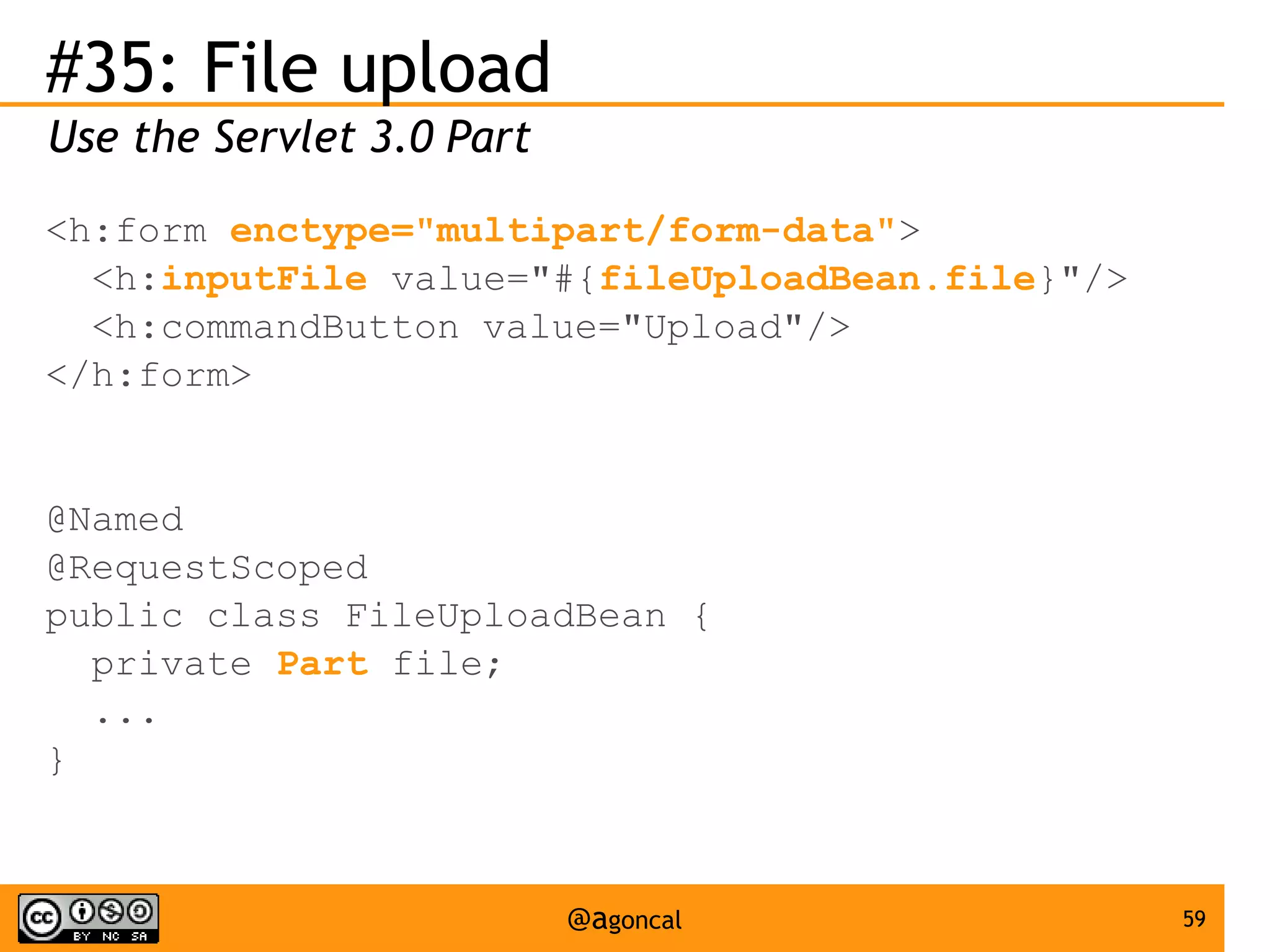
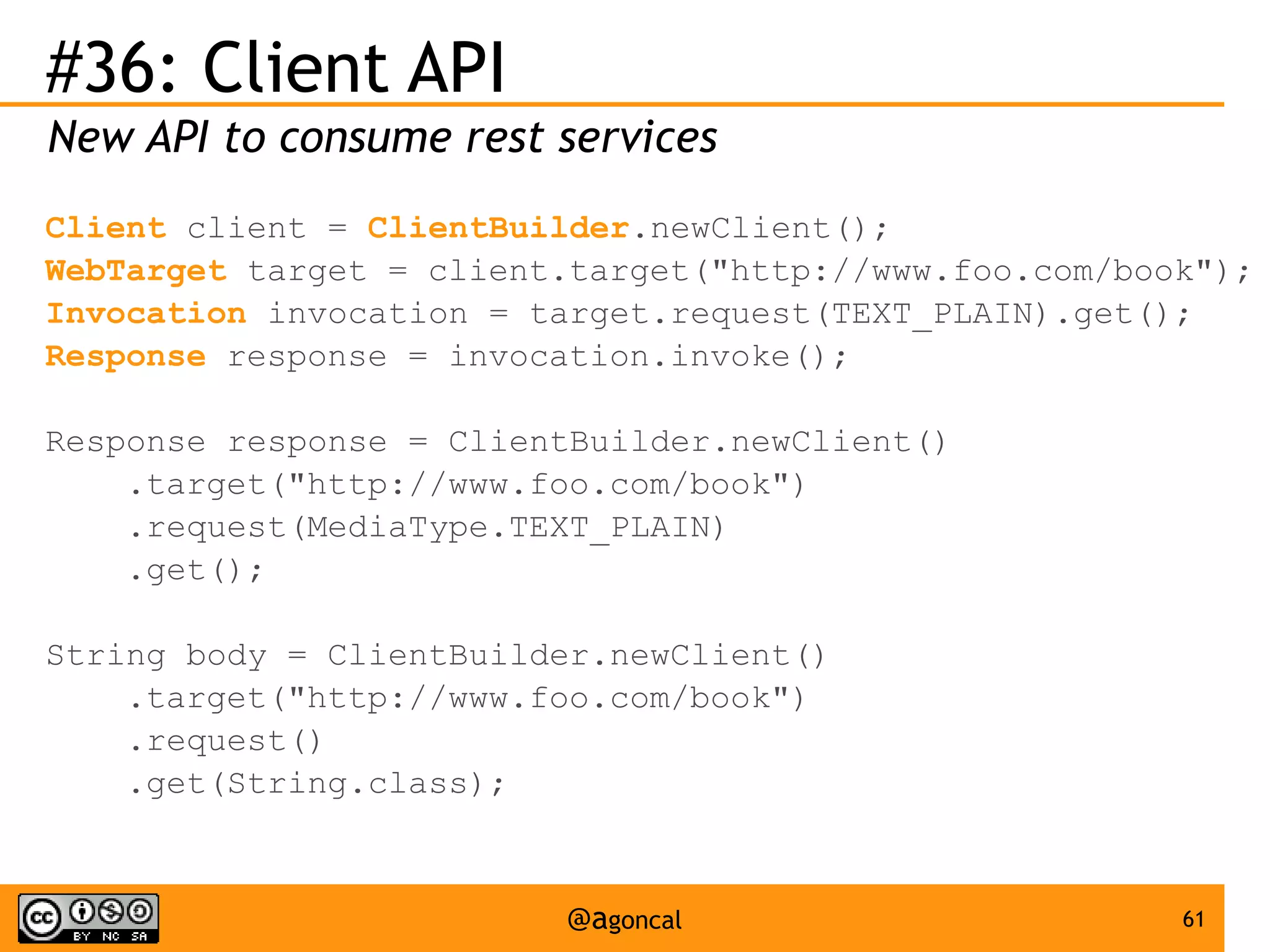
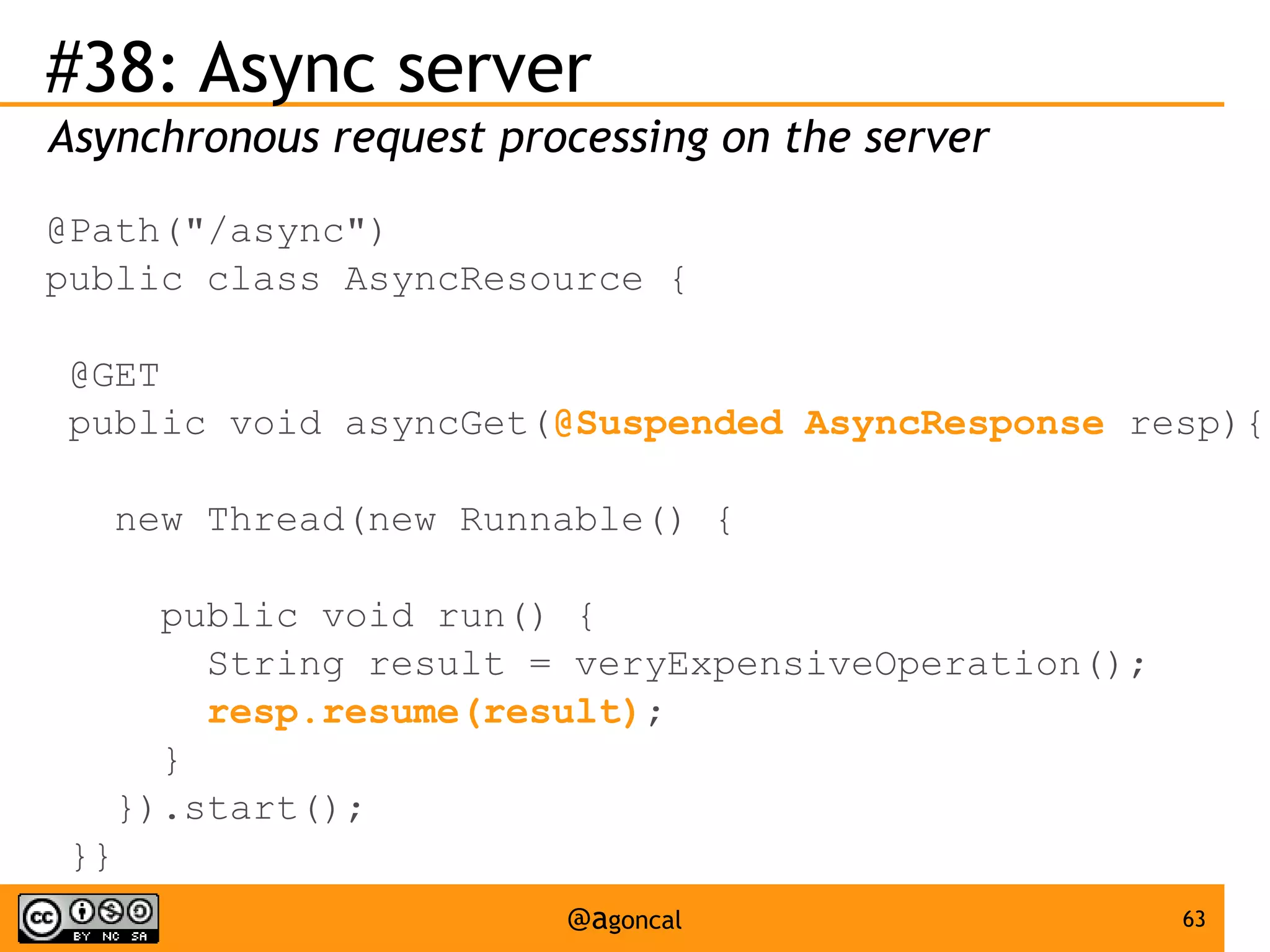
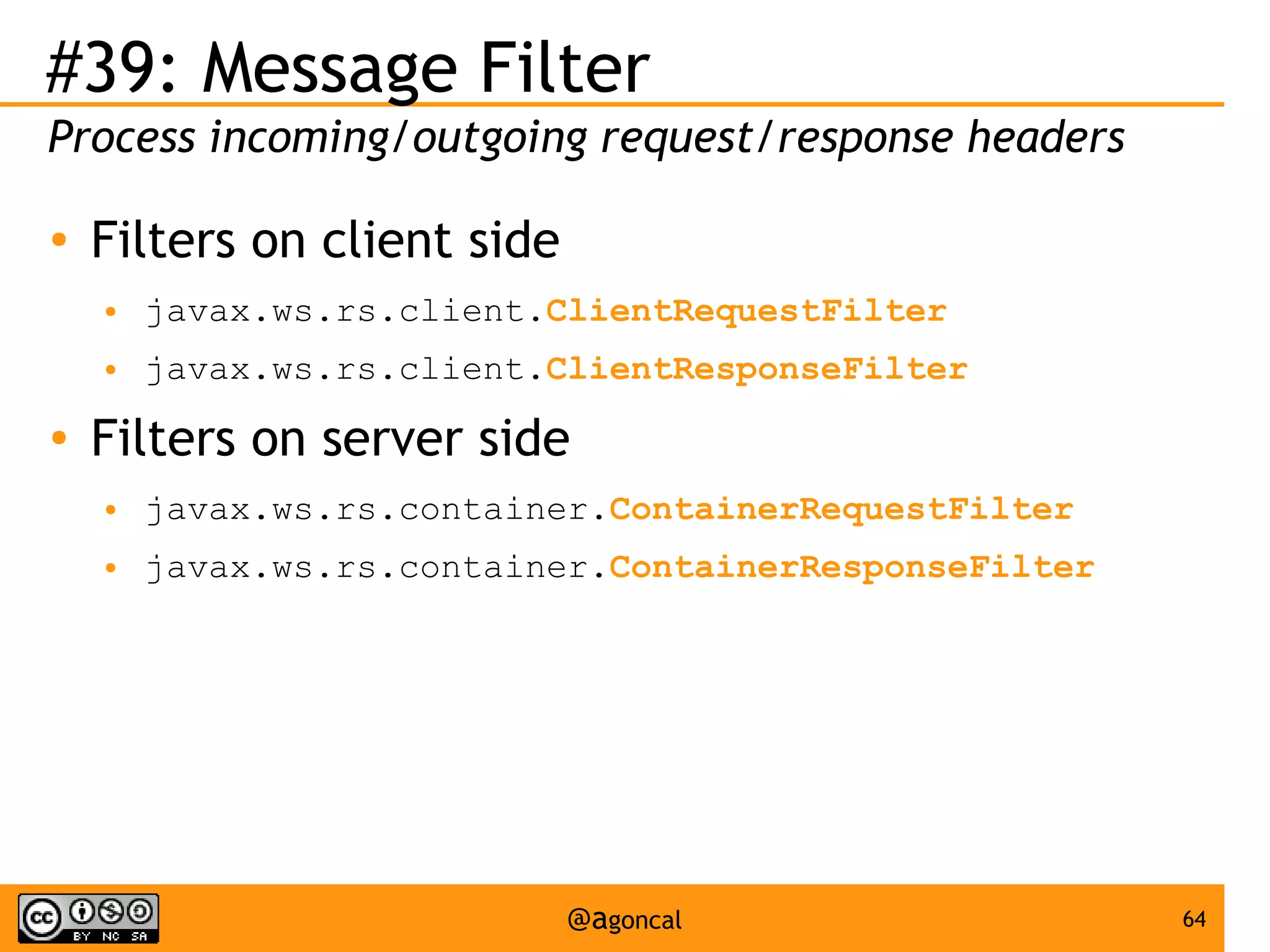
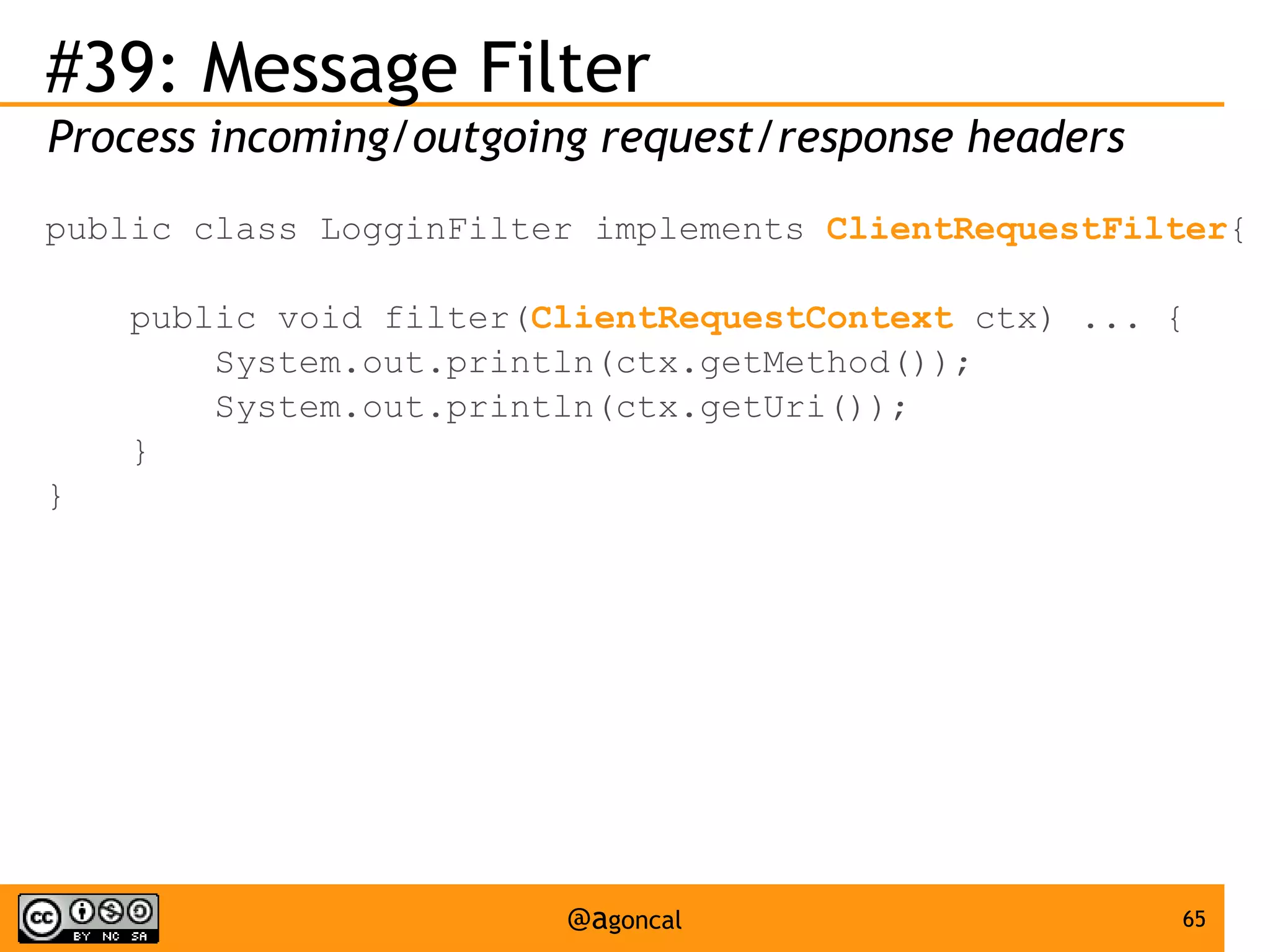
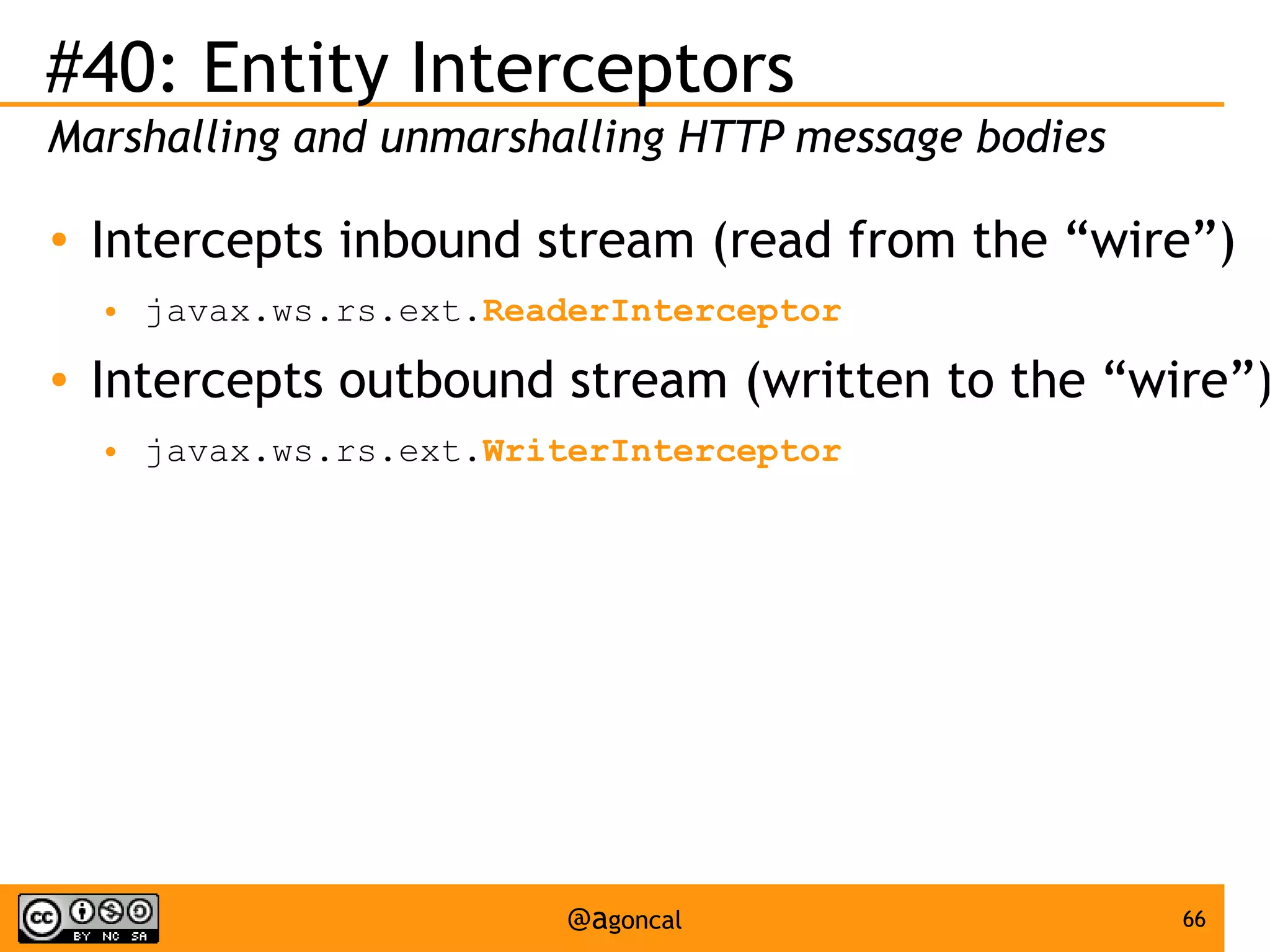
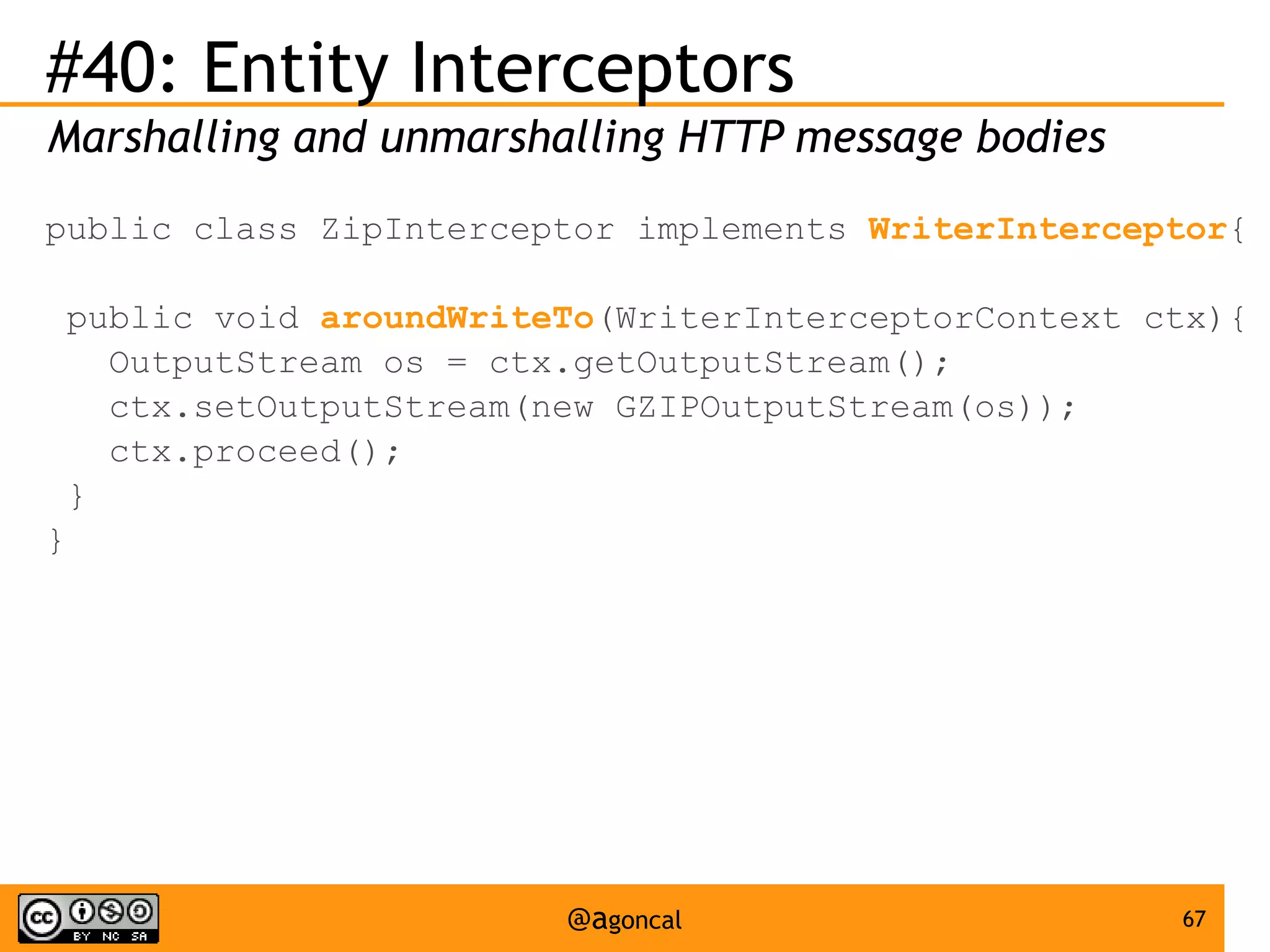
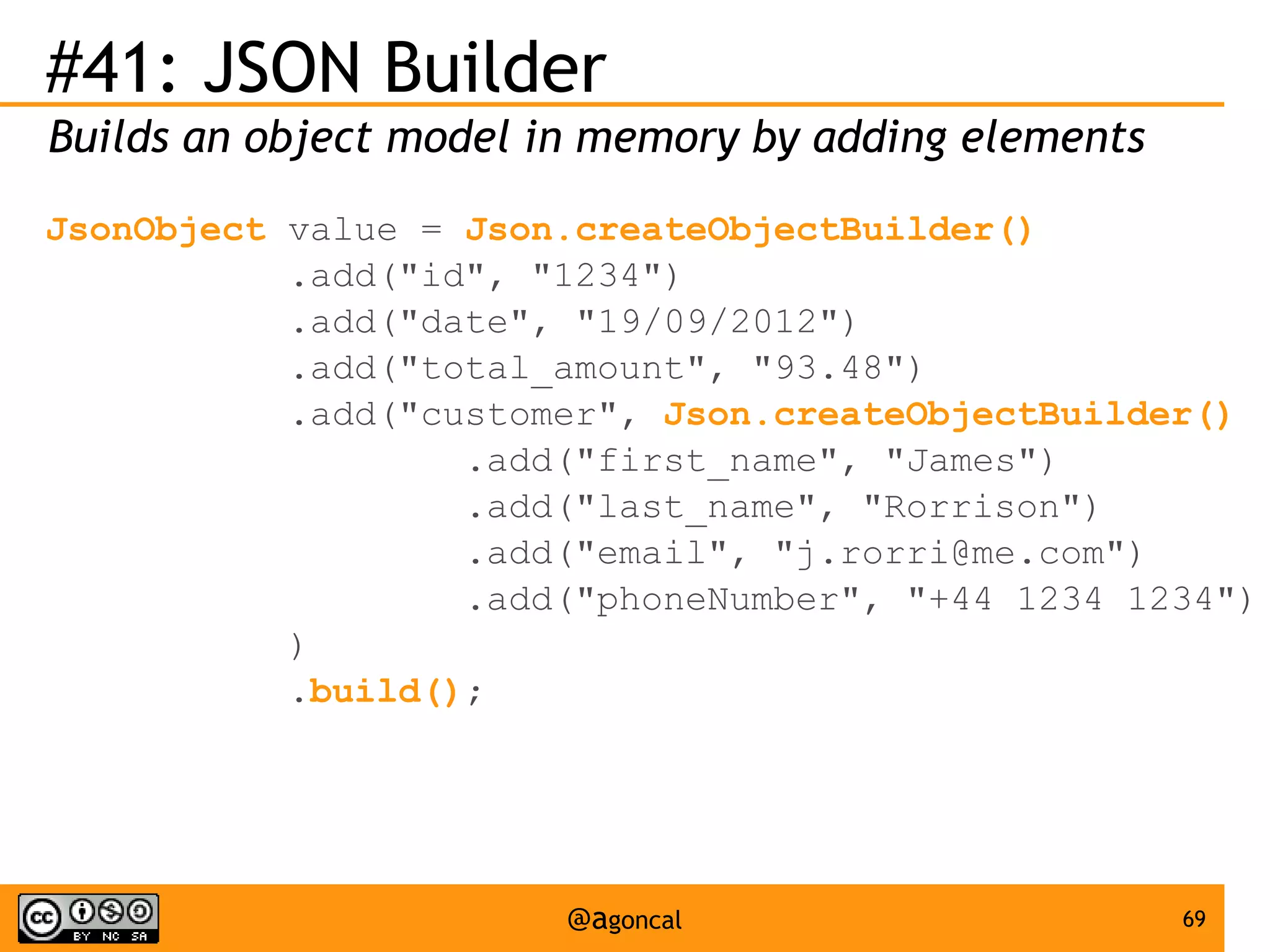
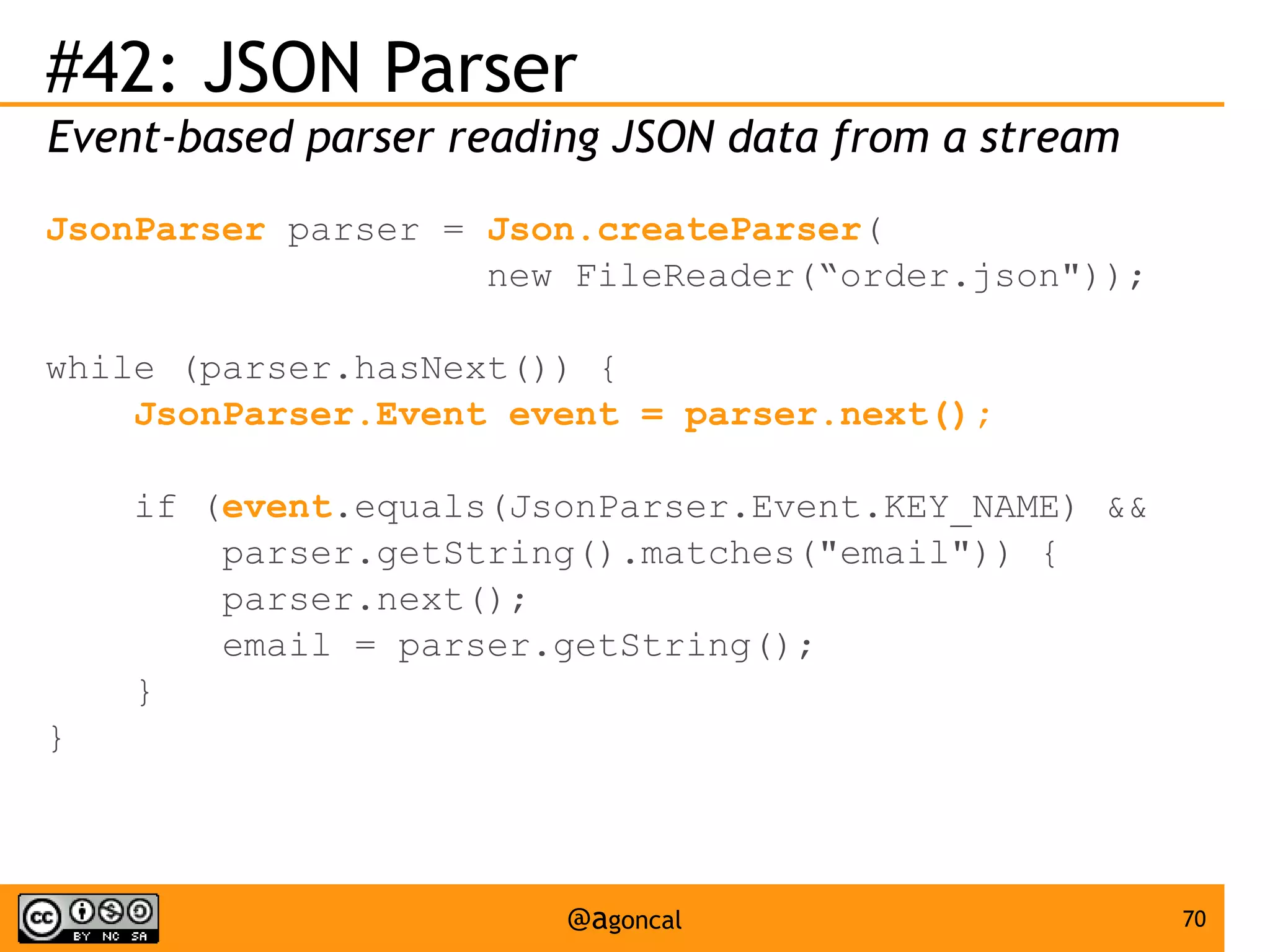
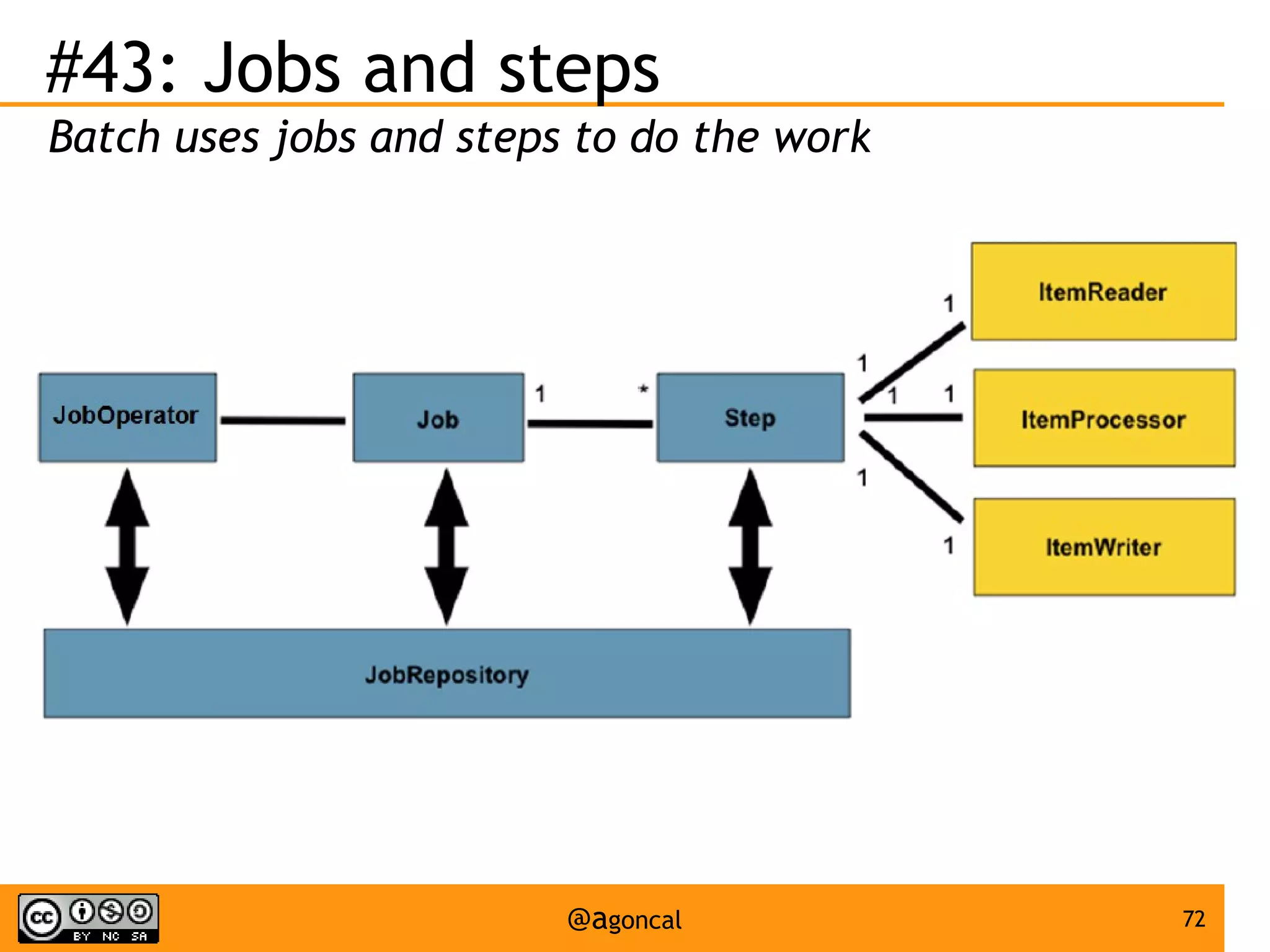
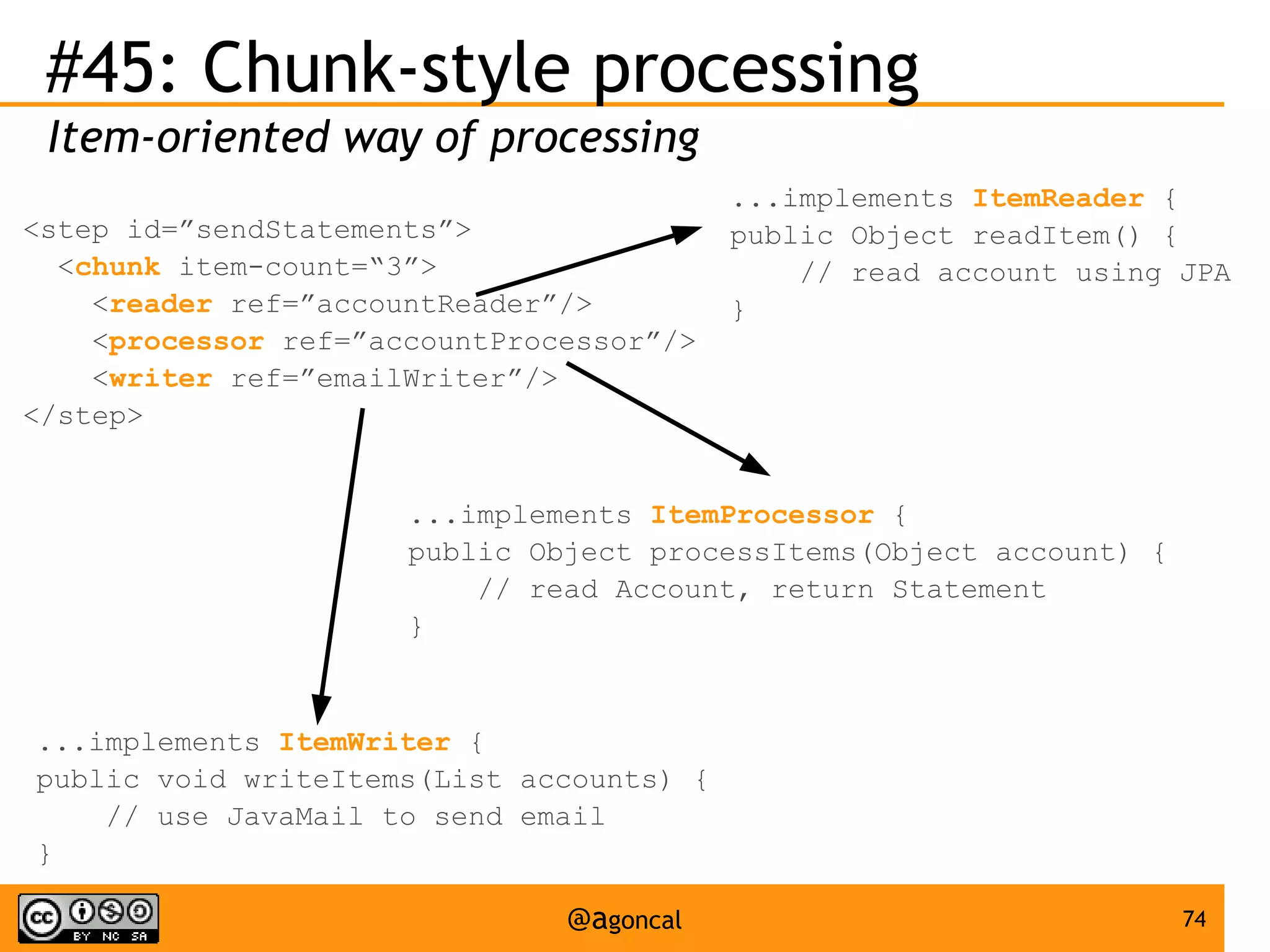
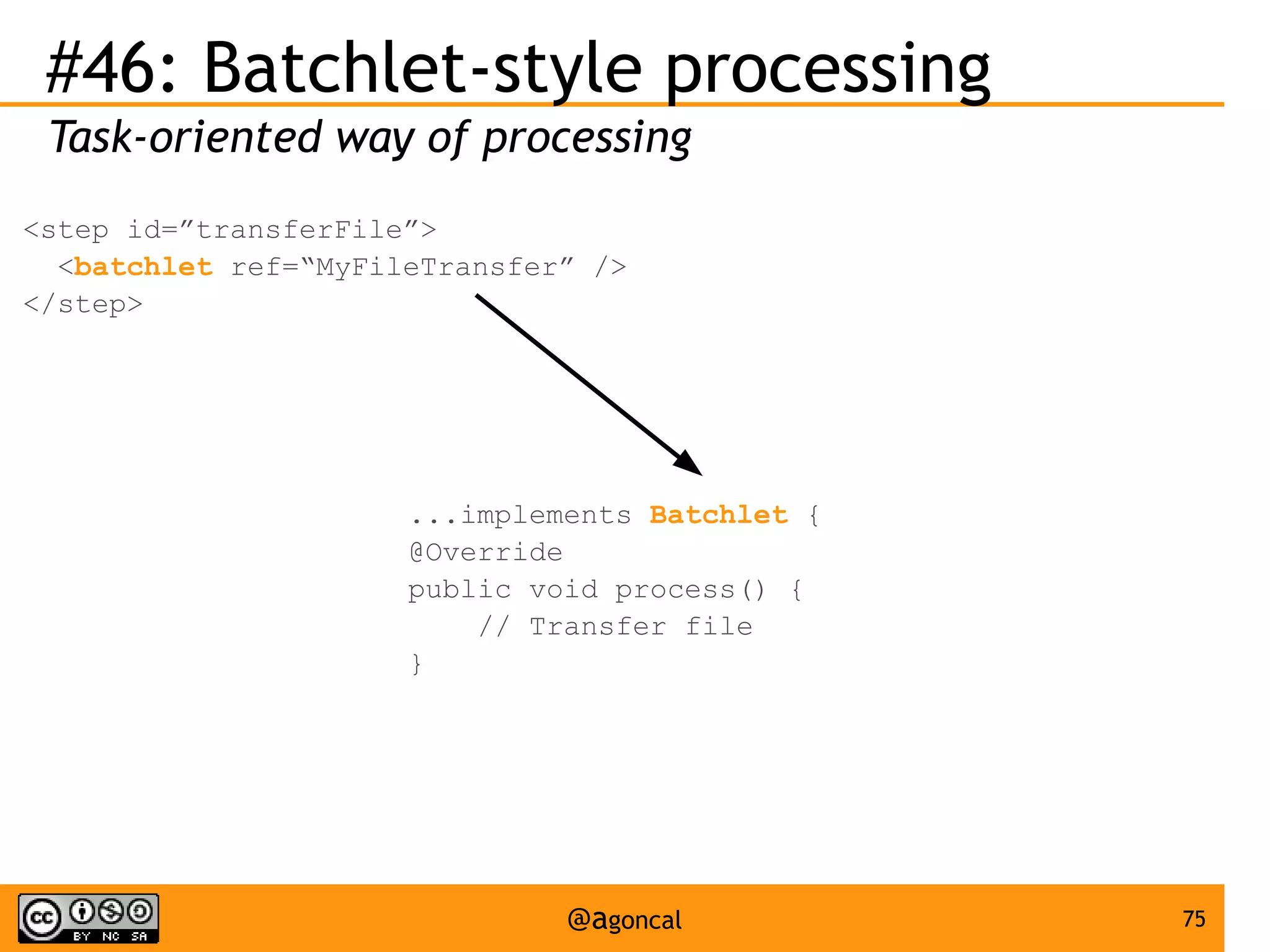
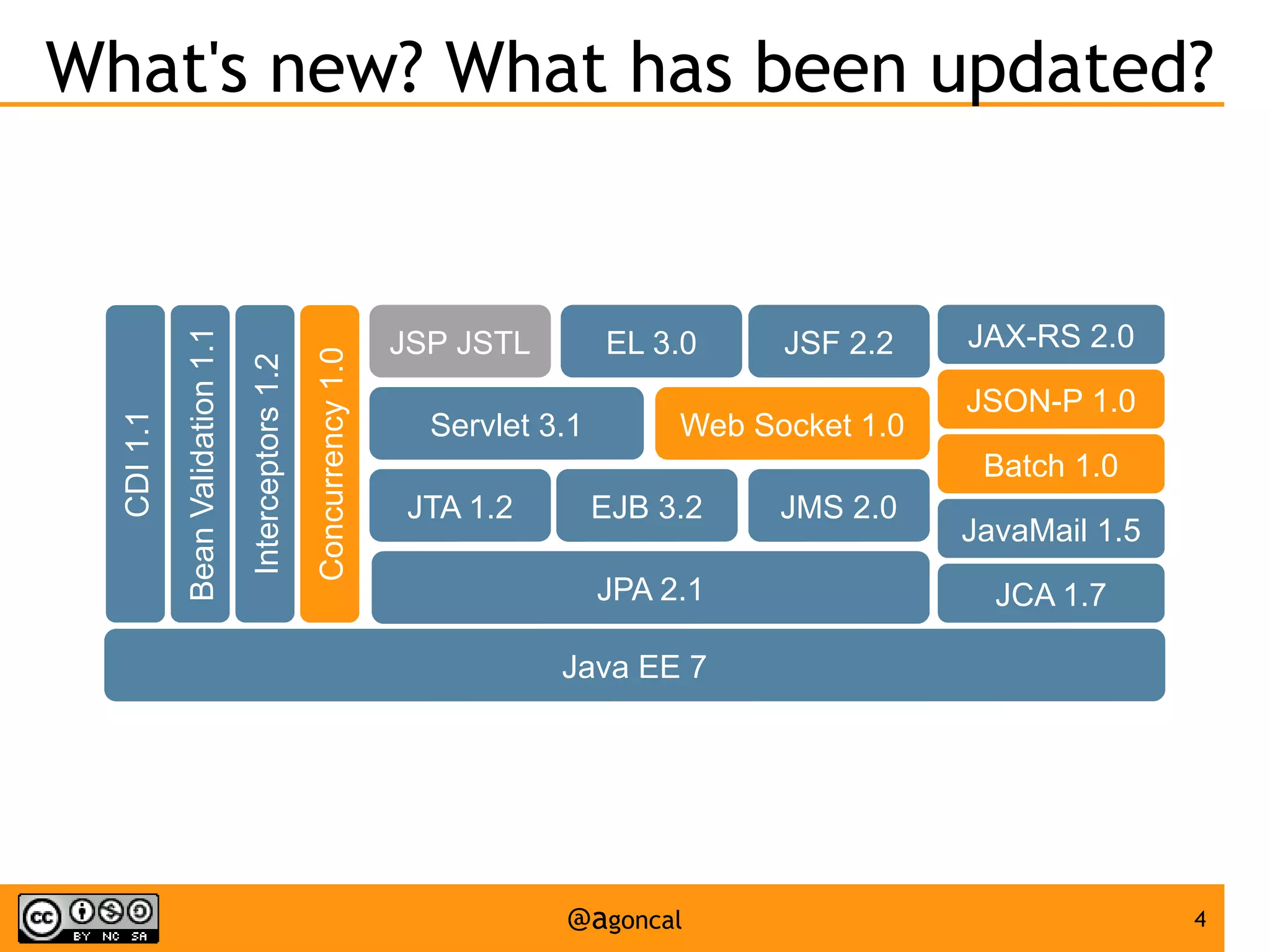
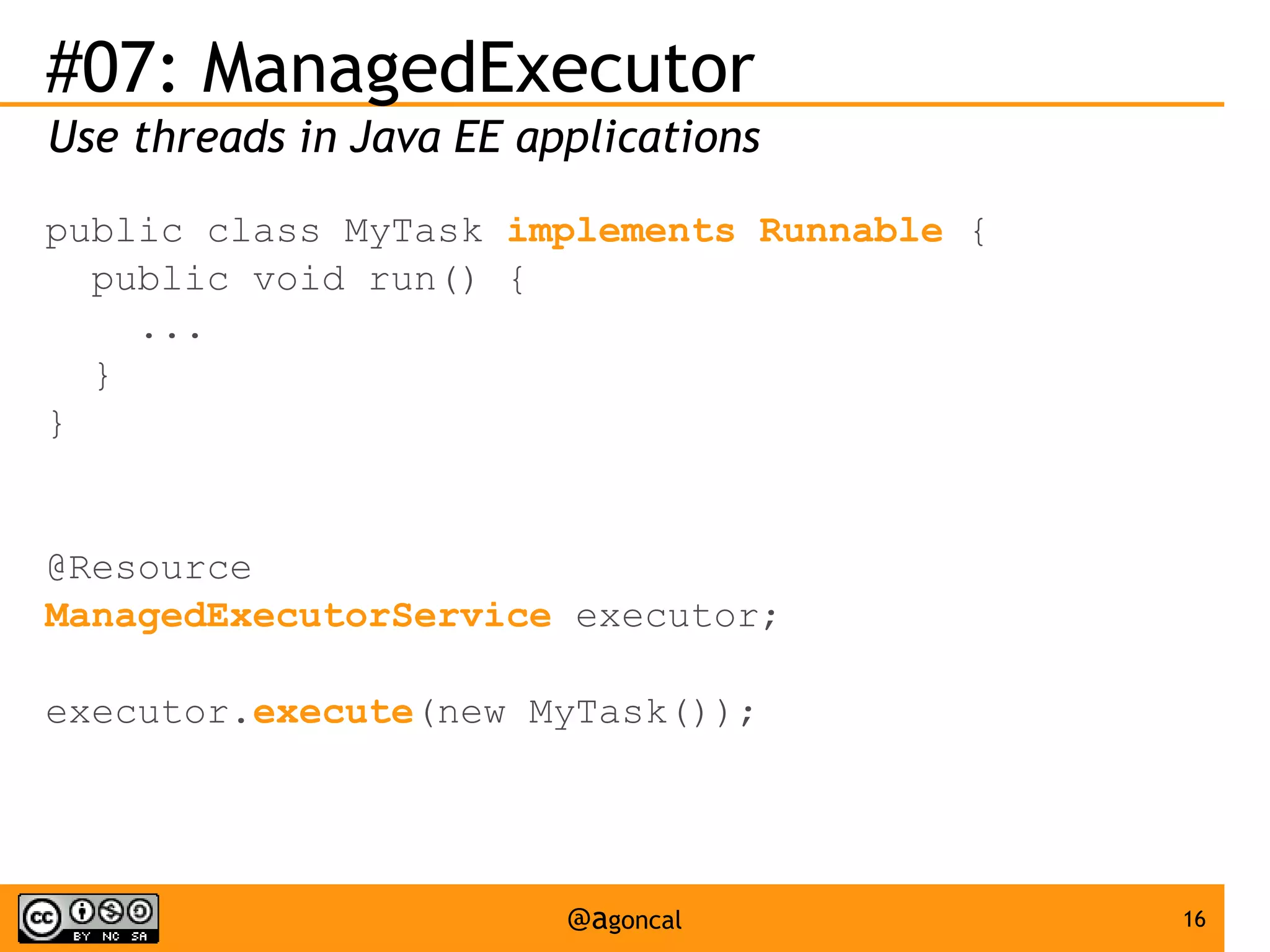
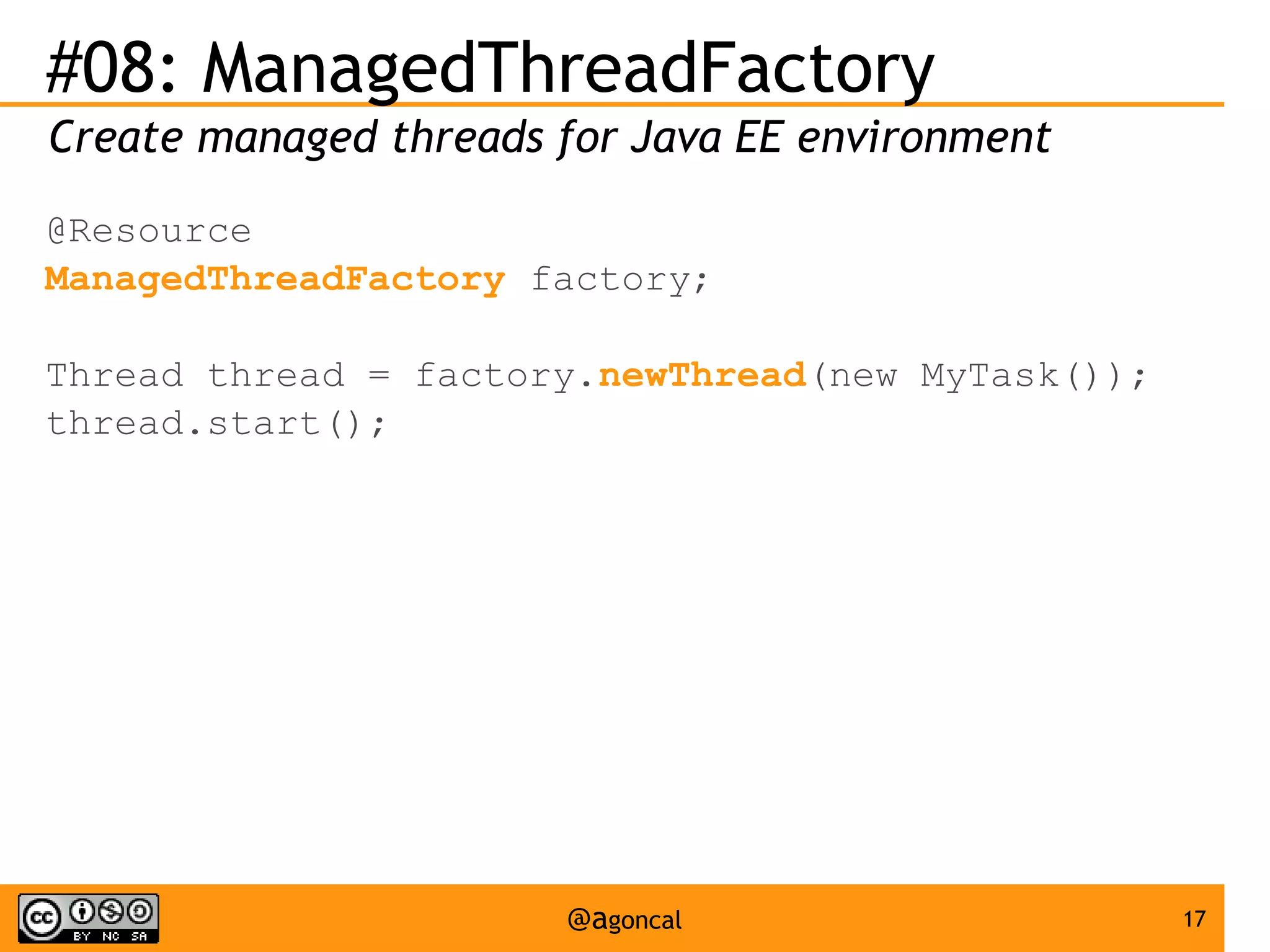
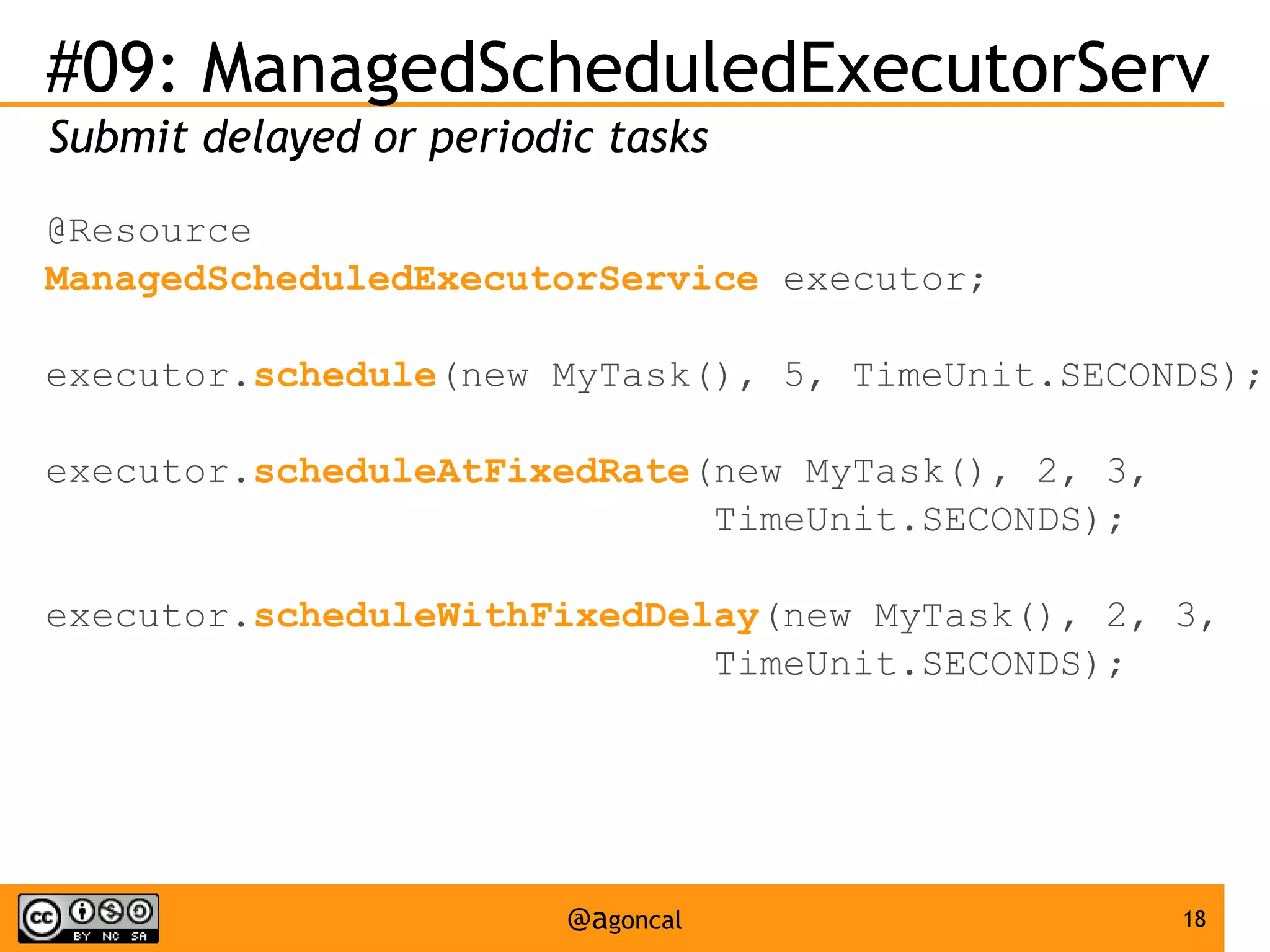
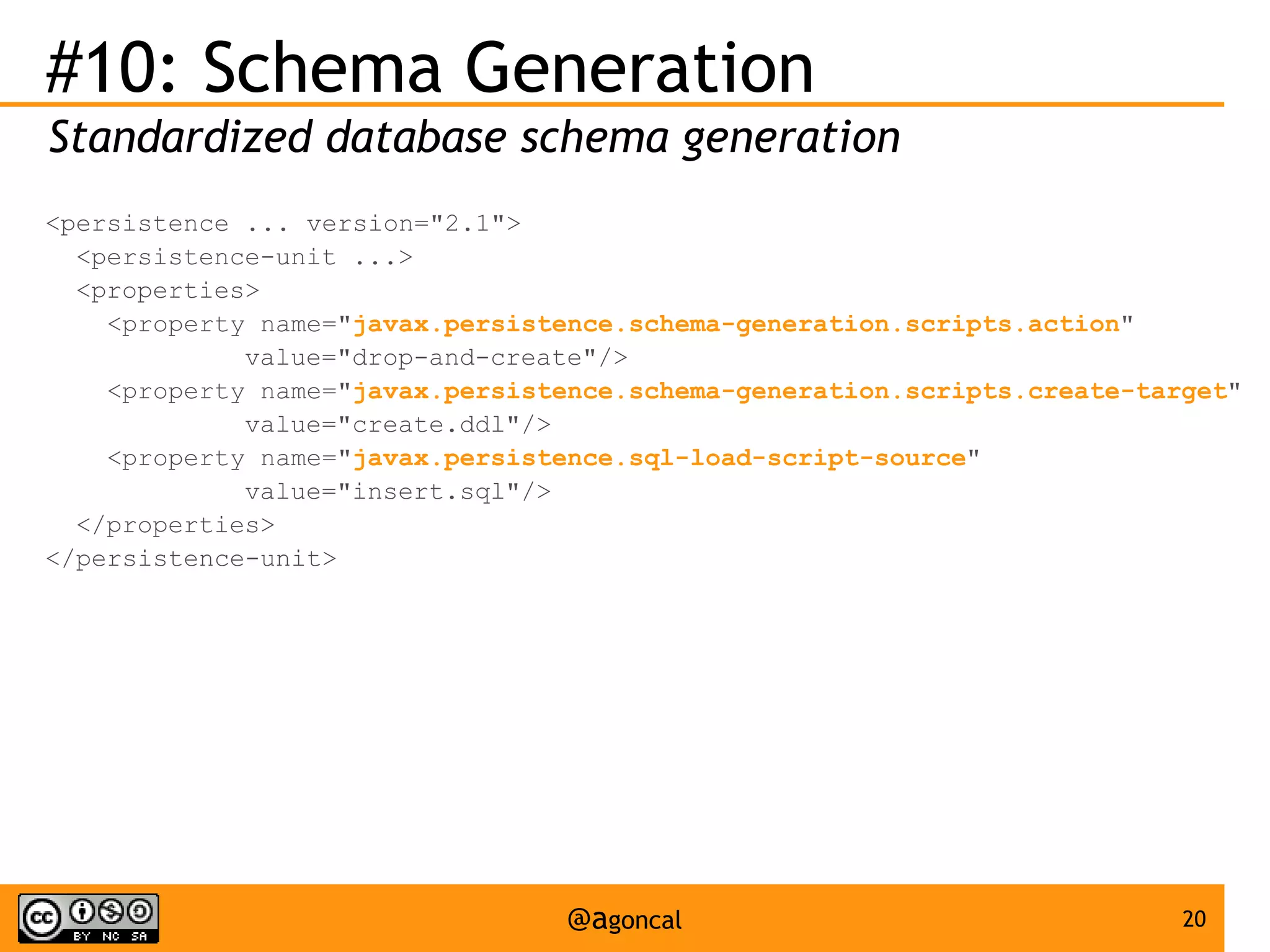
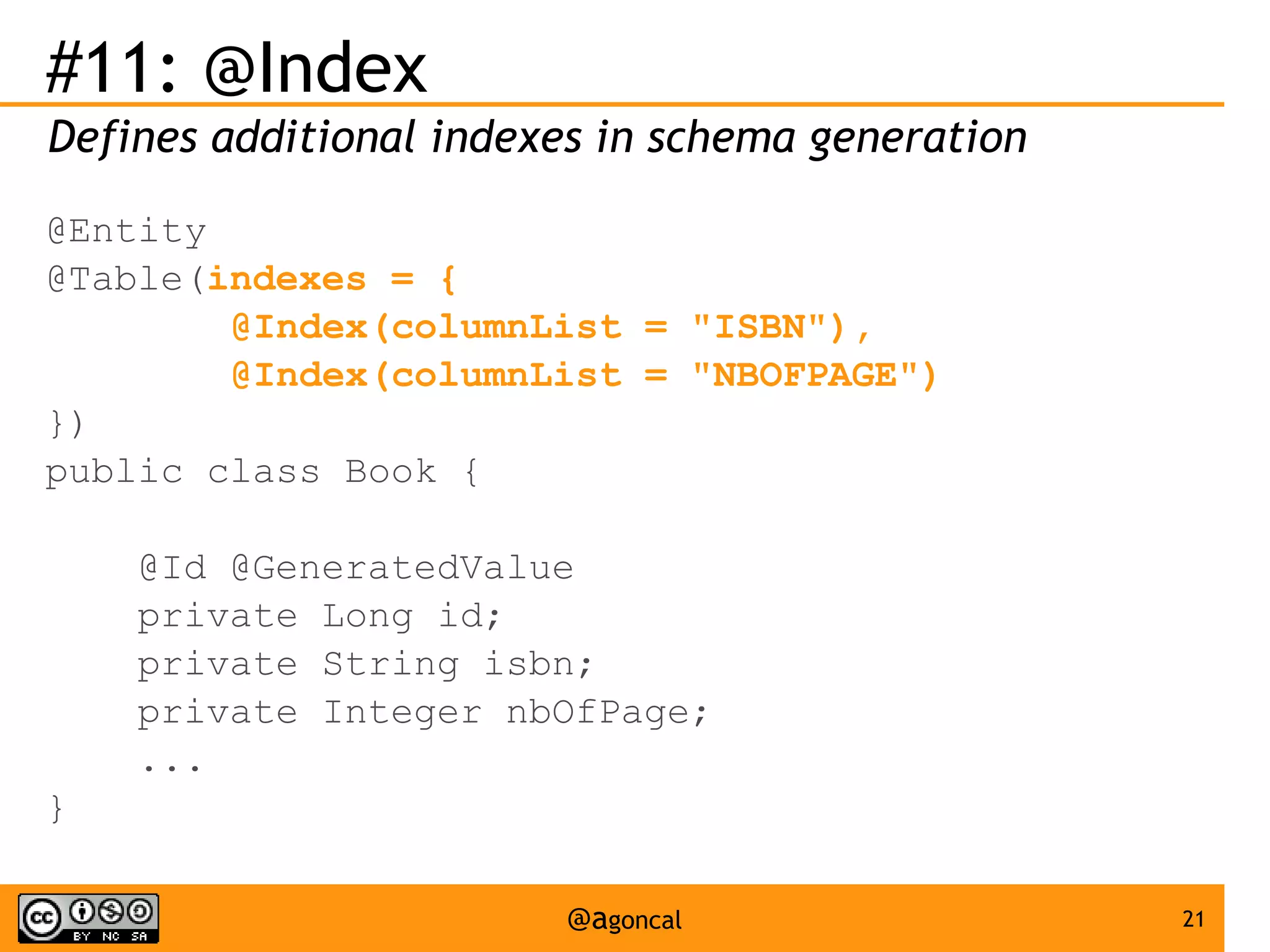
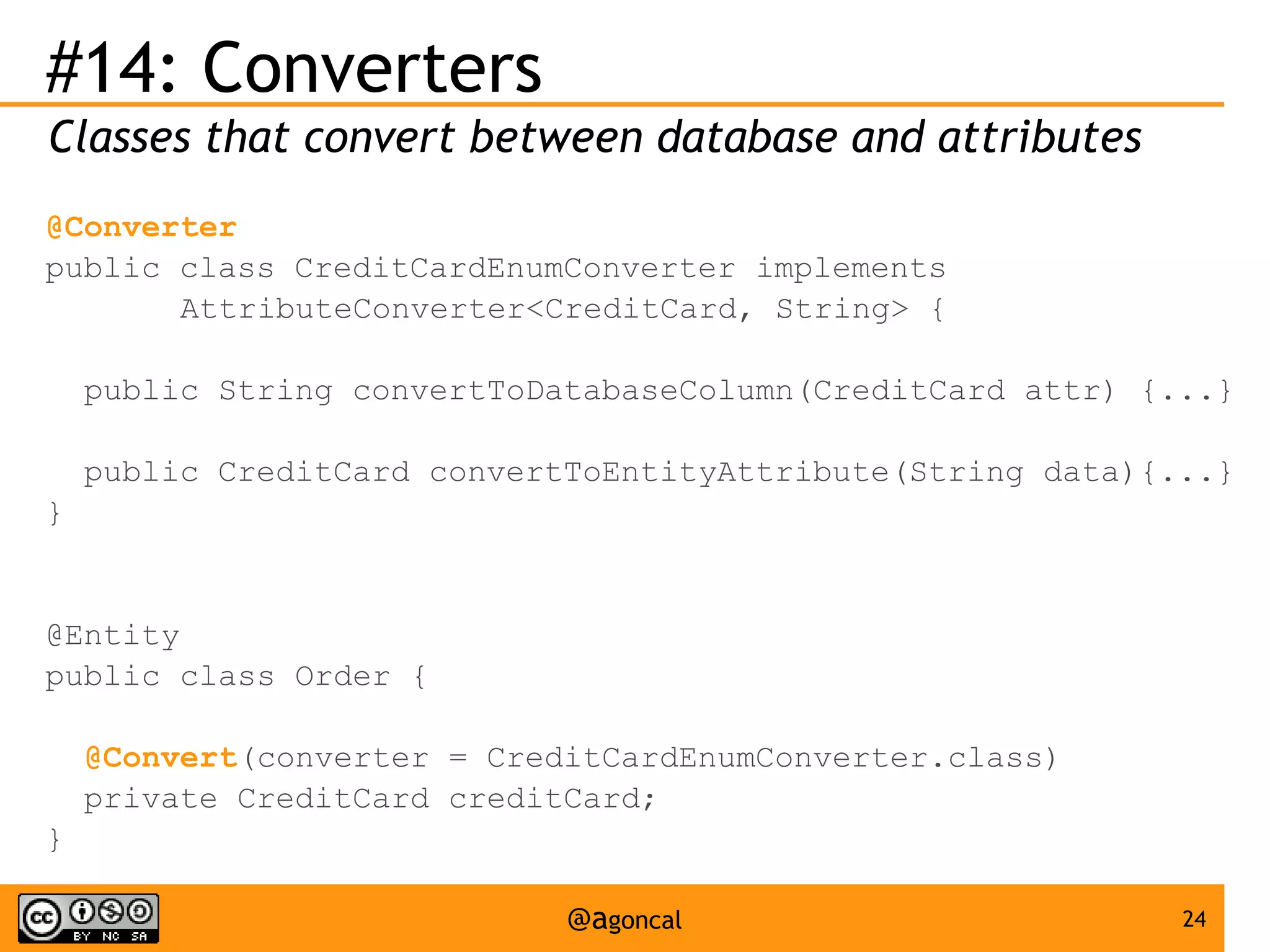
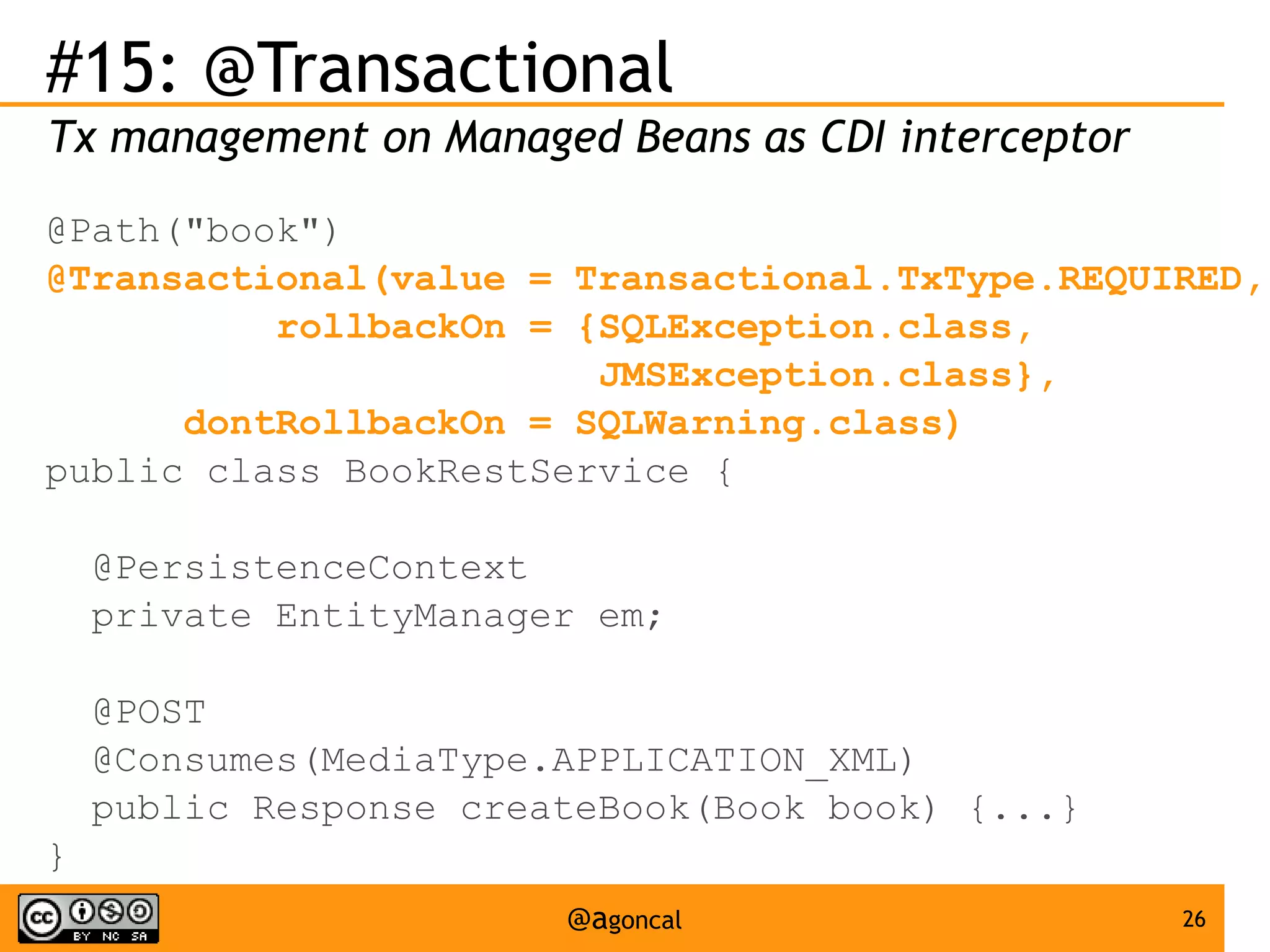
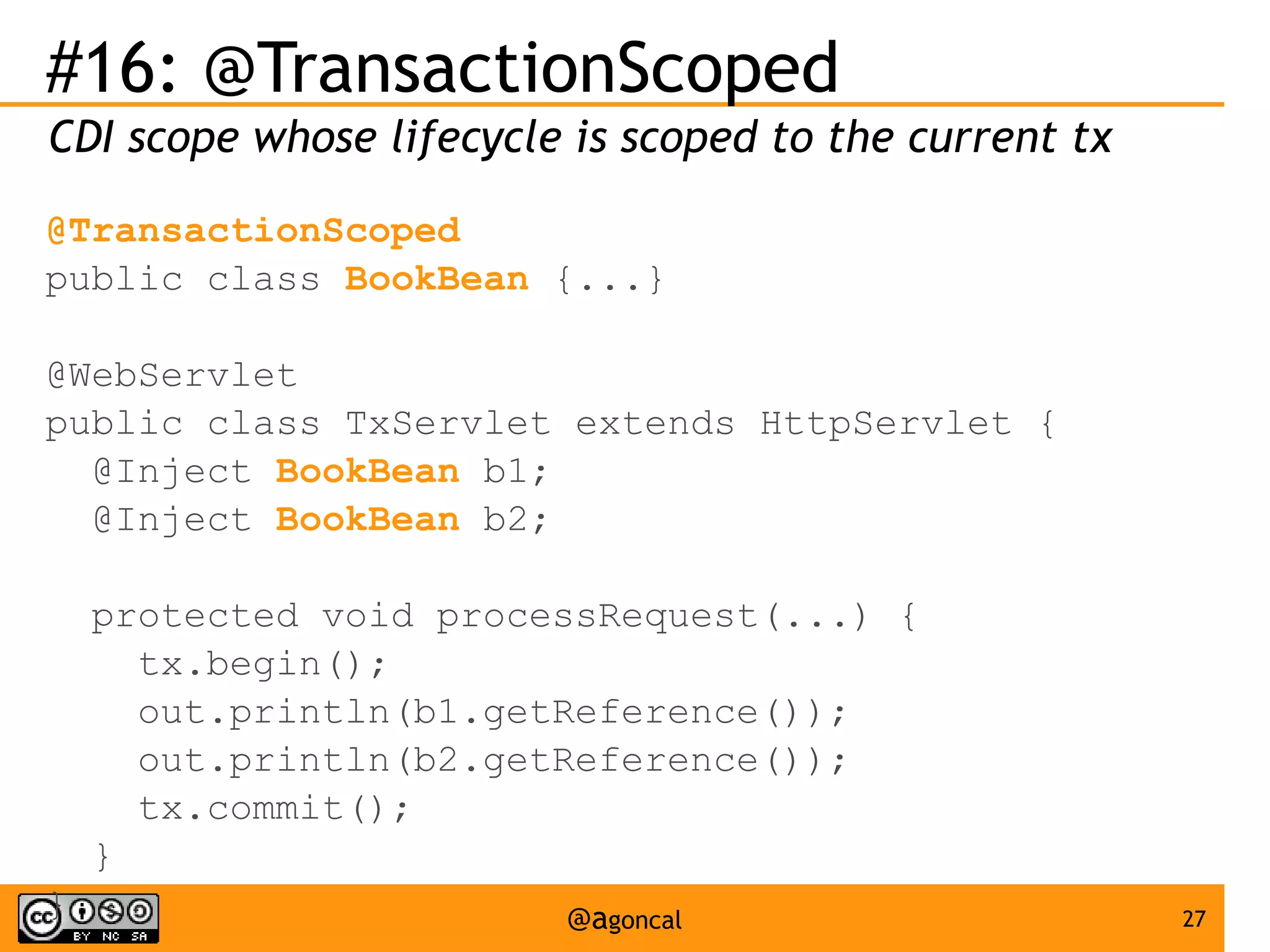
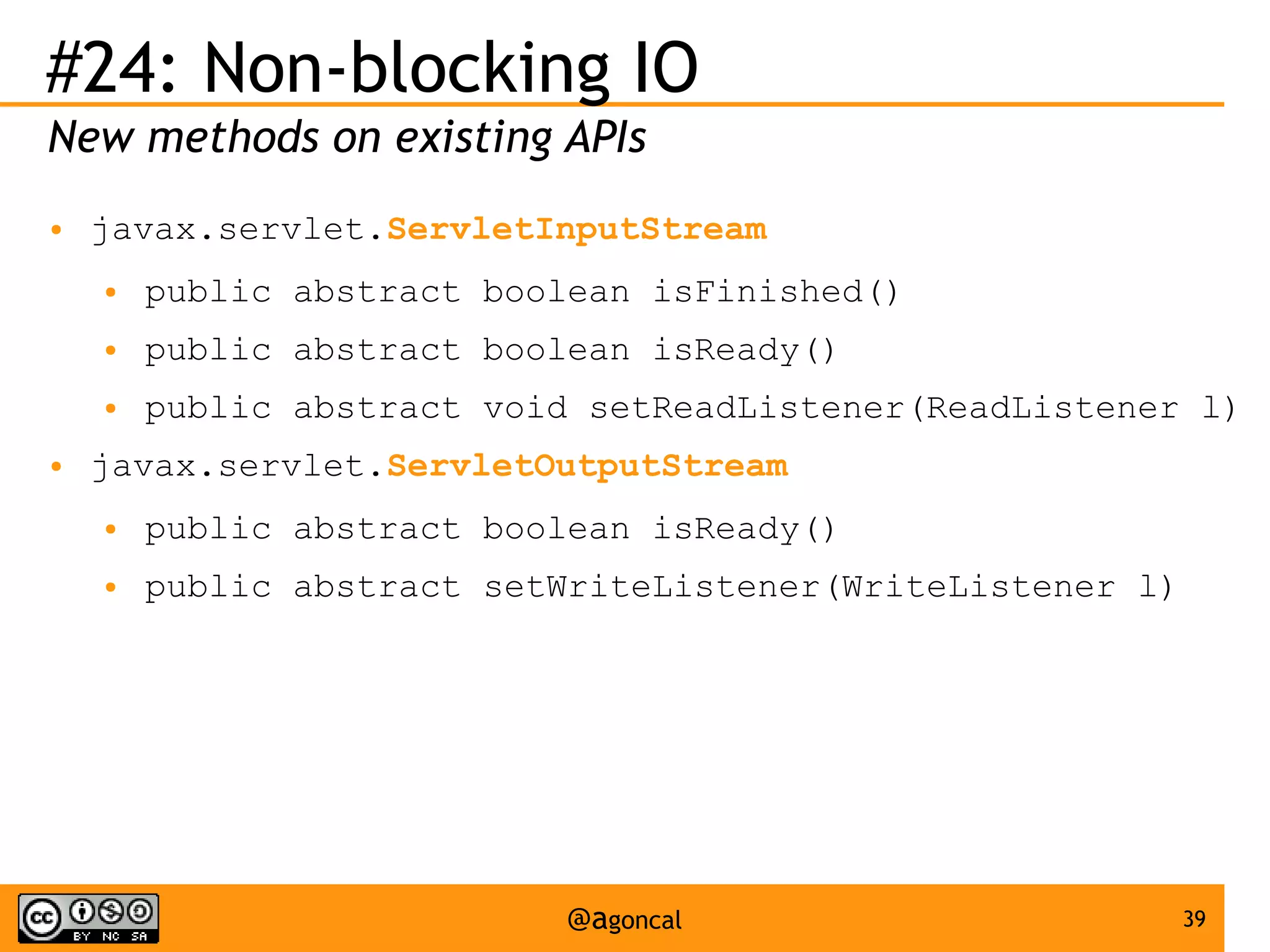
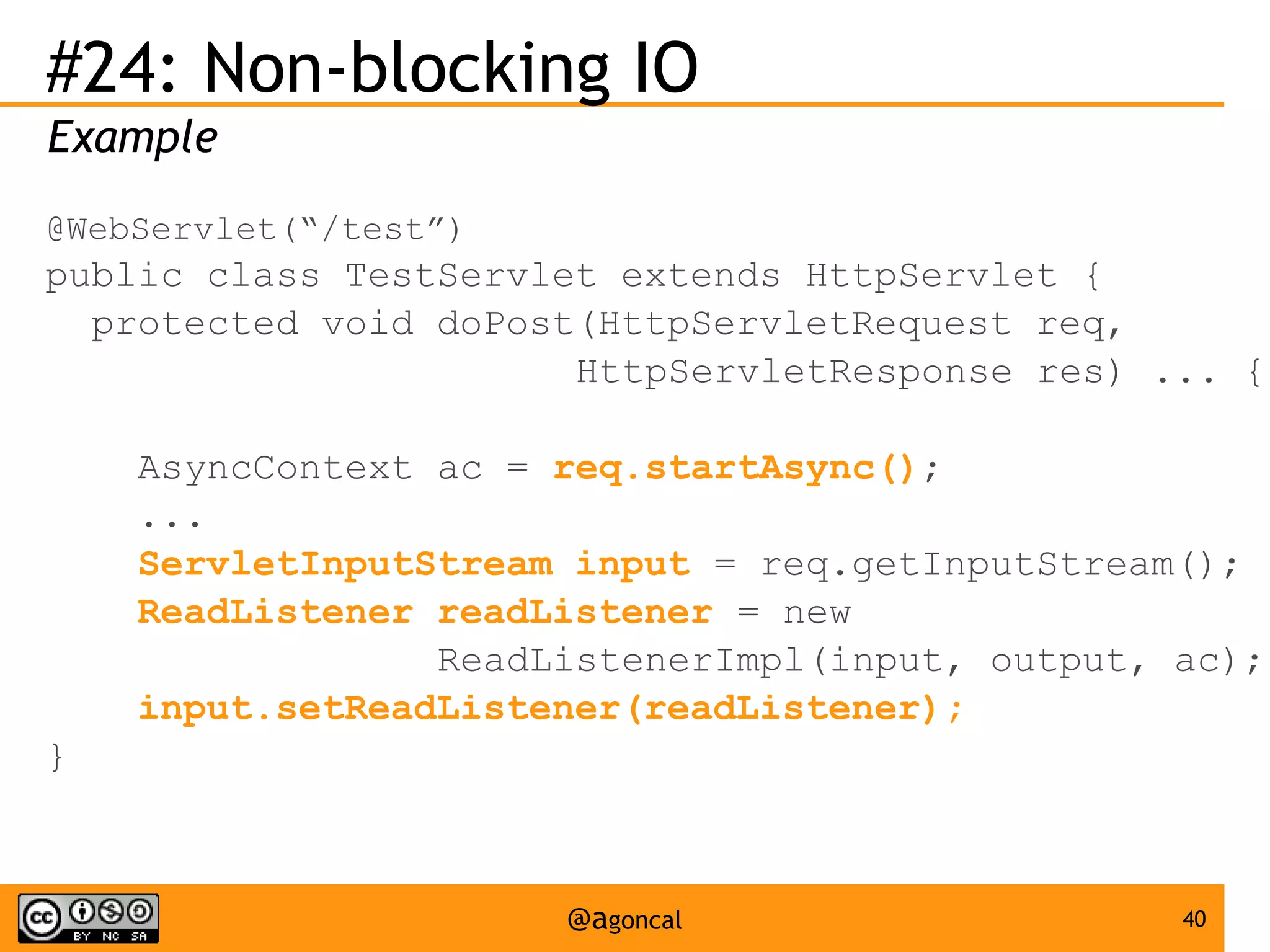
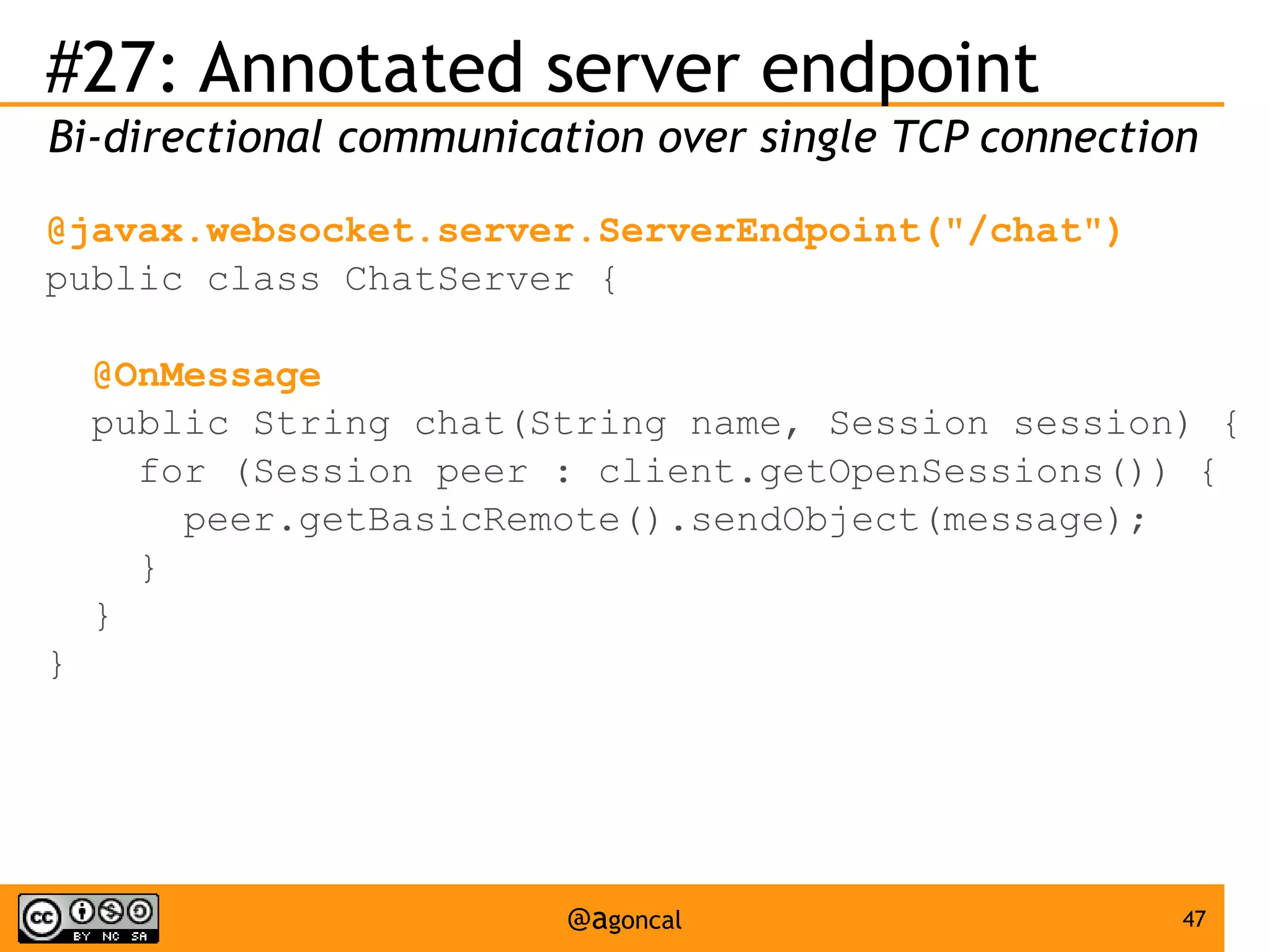
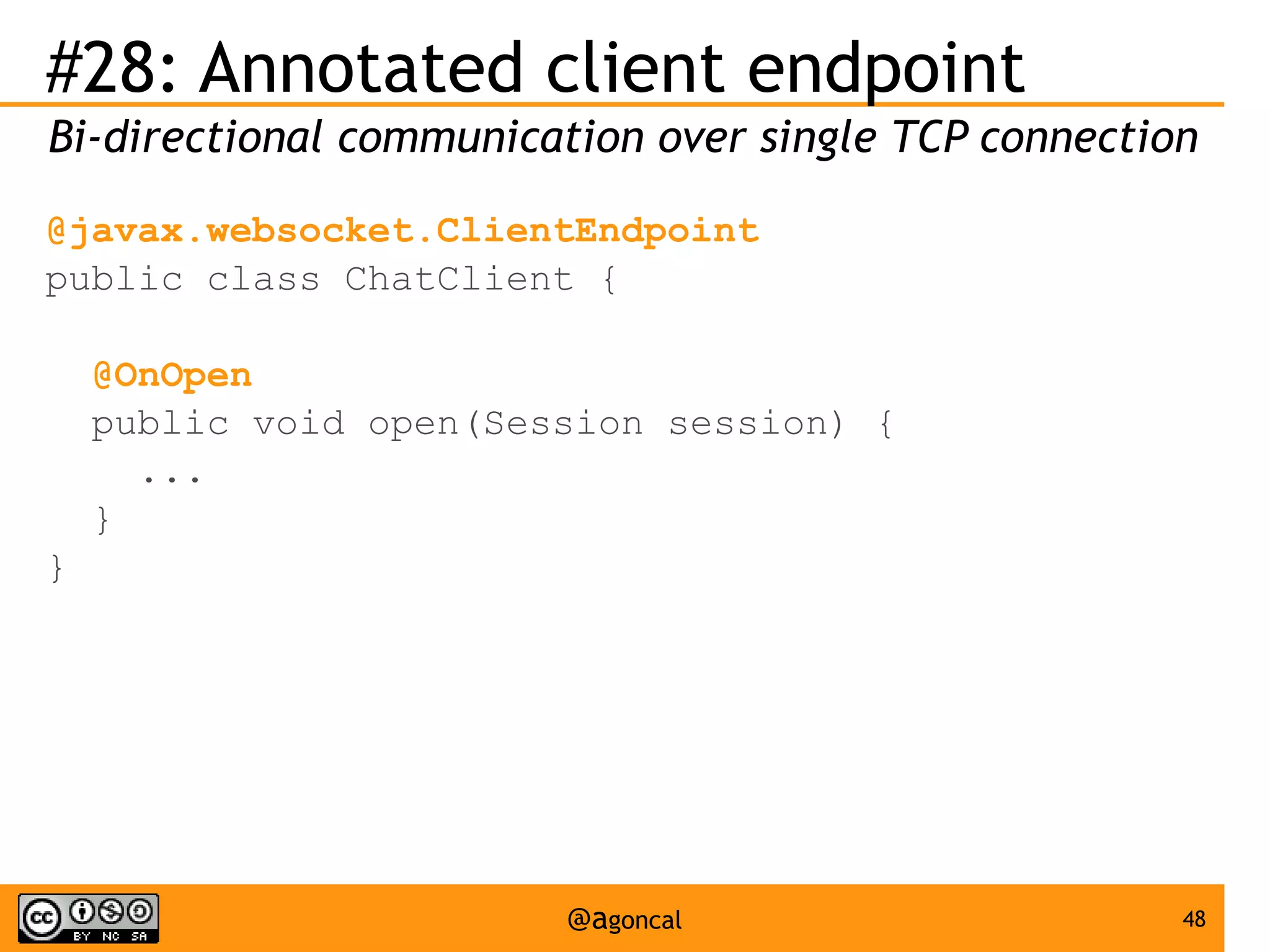
The document outlines the new features introduced in Java EE 7, specifically for Java EE 6 developers, detailing updates across various specifications including Concurrency, CDI, Bean Validation, and more. Key enhancements include support for non-blocking I/O in Servlets, improved API for WebSocket communication, and new features in JPA and JAX-RS for better performance and usability. The document serves as a comprehensive guide to understanding these innovations and their practical applications in Java EE 7 development.






























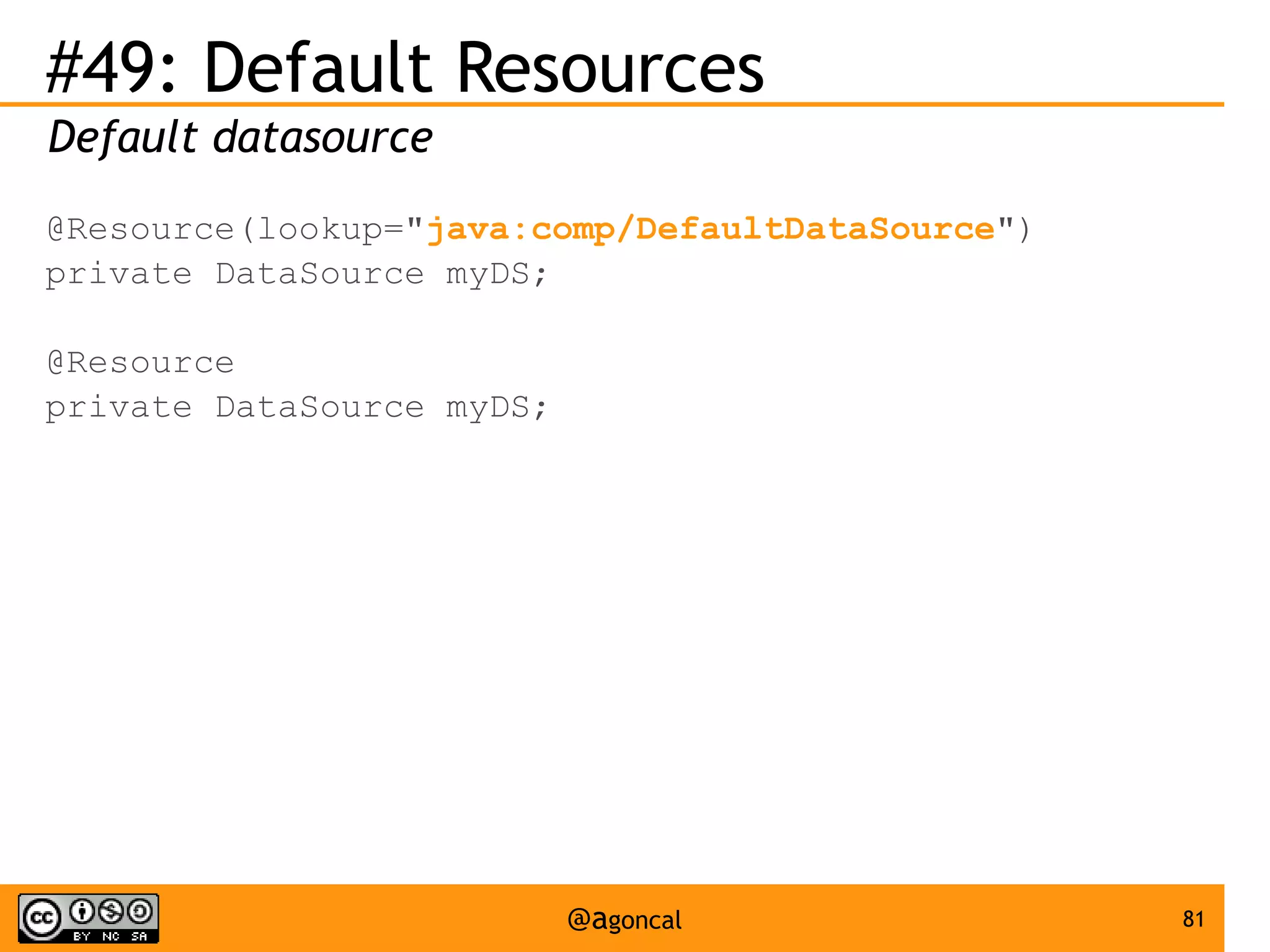
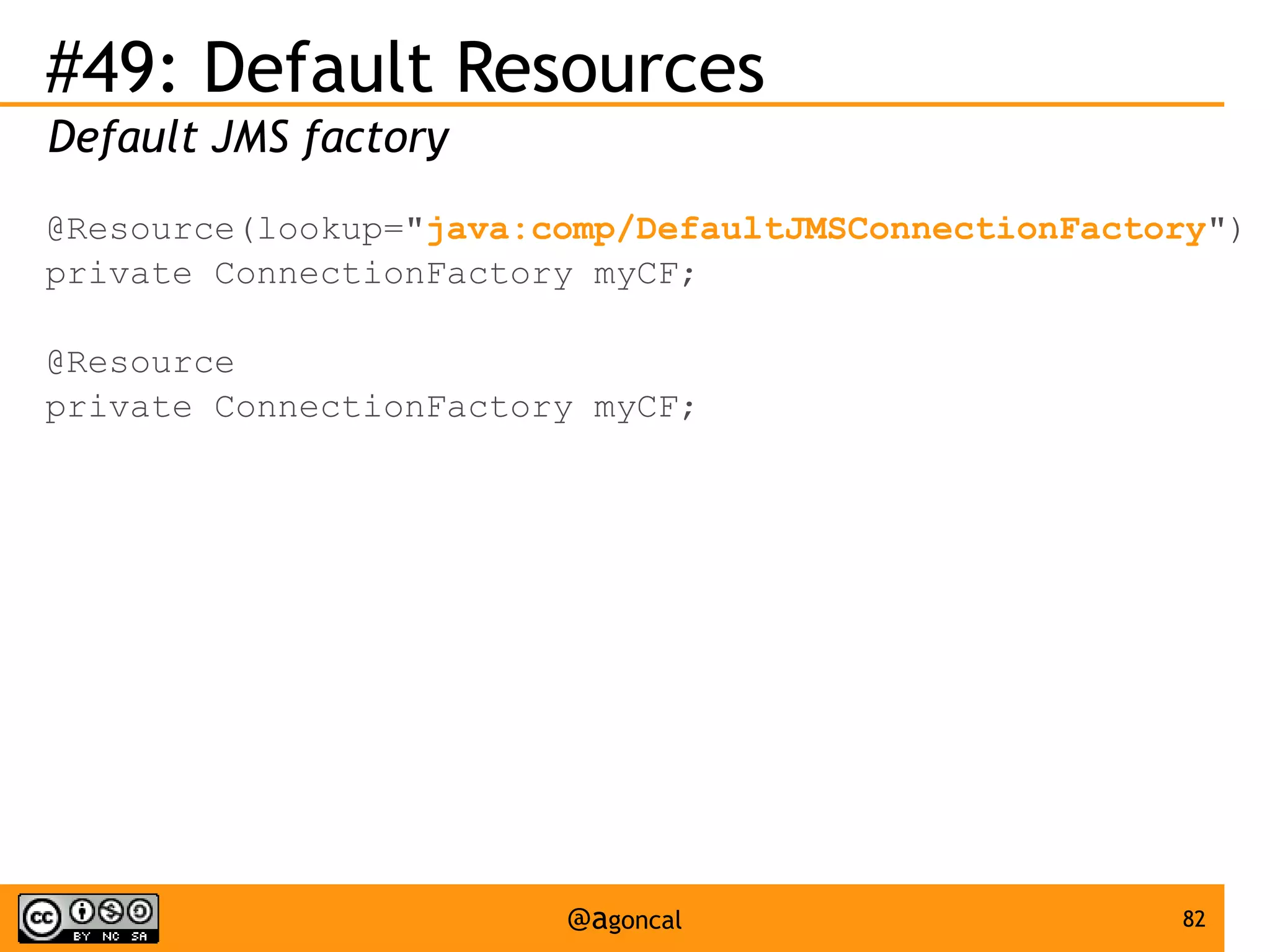
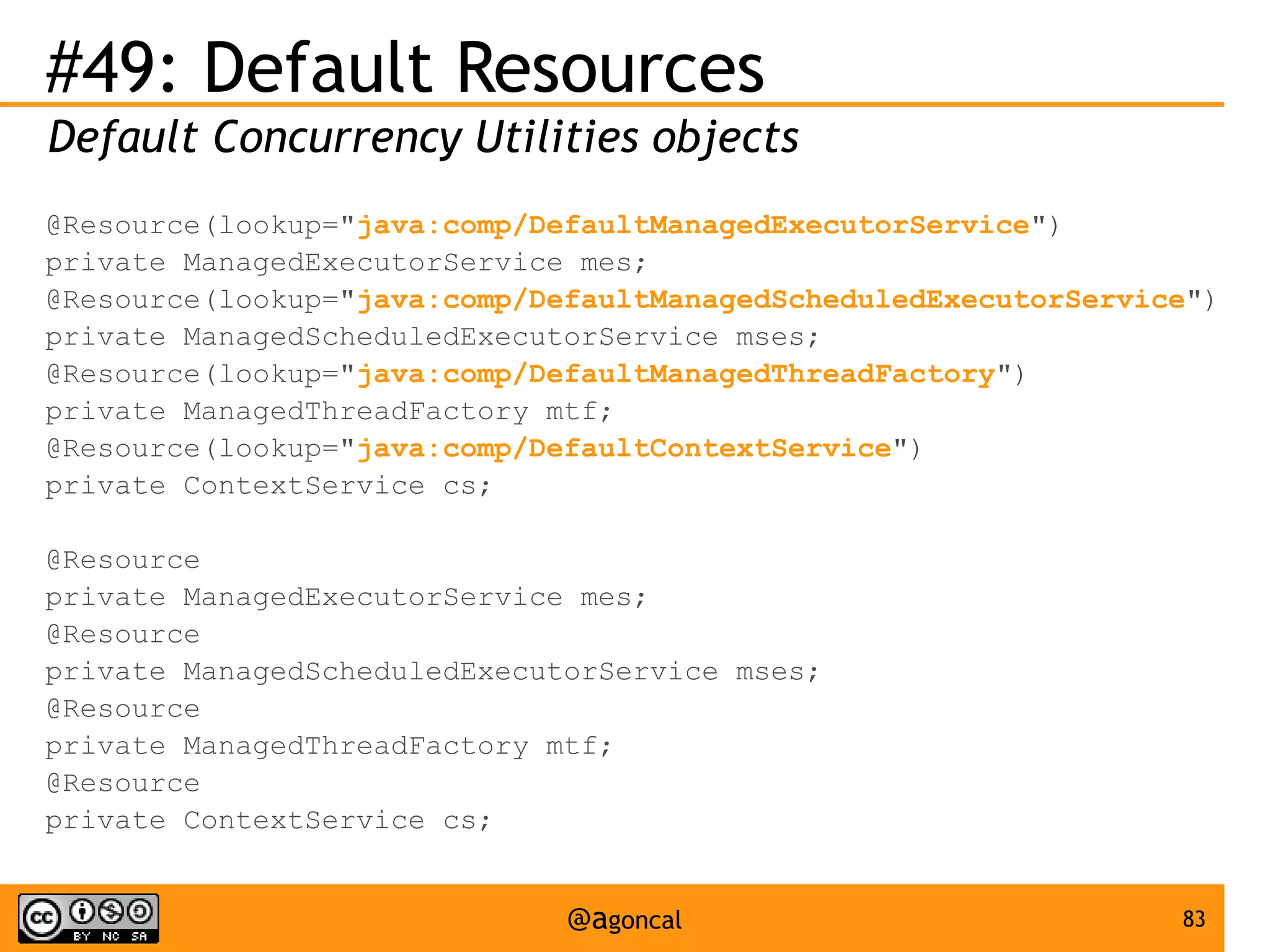
![#30: ELProcessor
Use EL in a stand-alone environment
ELProcessor el = new ELProcessor();
assert ((Integer)el.eval("a = [1, 2]; a[1]")) == 2;
el.defineBean("employee", new Employee("John"));
assert (el.eval("employee.name")).equals("John");
@agoncal
51](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2014-01-50newfeaturesofjavaee7in50minutes-140114040743-phpapp02/75/50-new-features-of-Java-EE-7-in-50-minutes-51-2048.jpg)