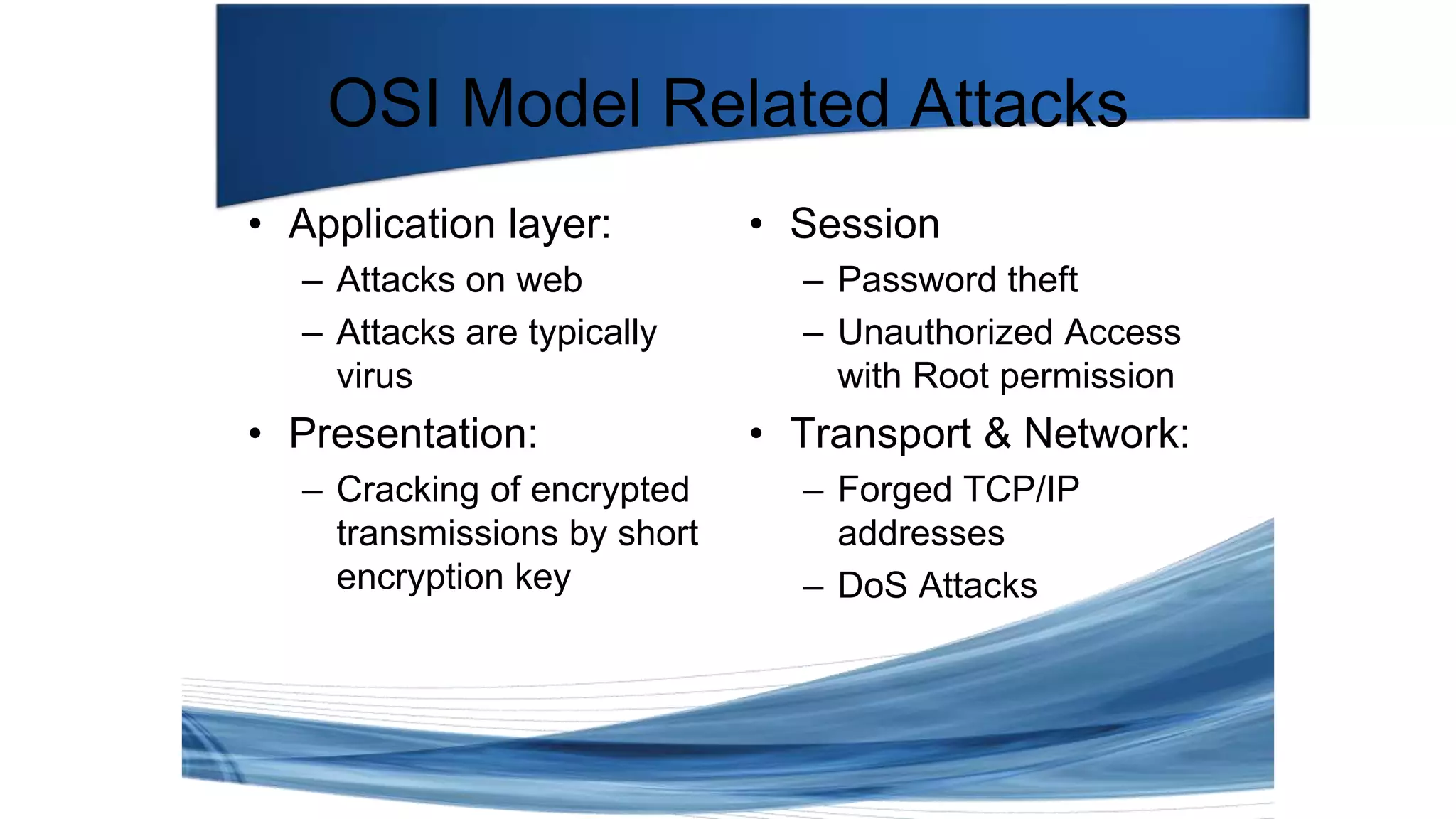
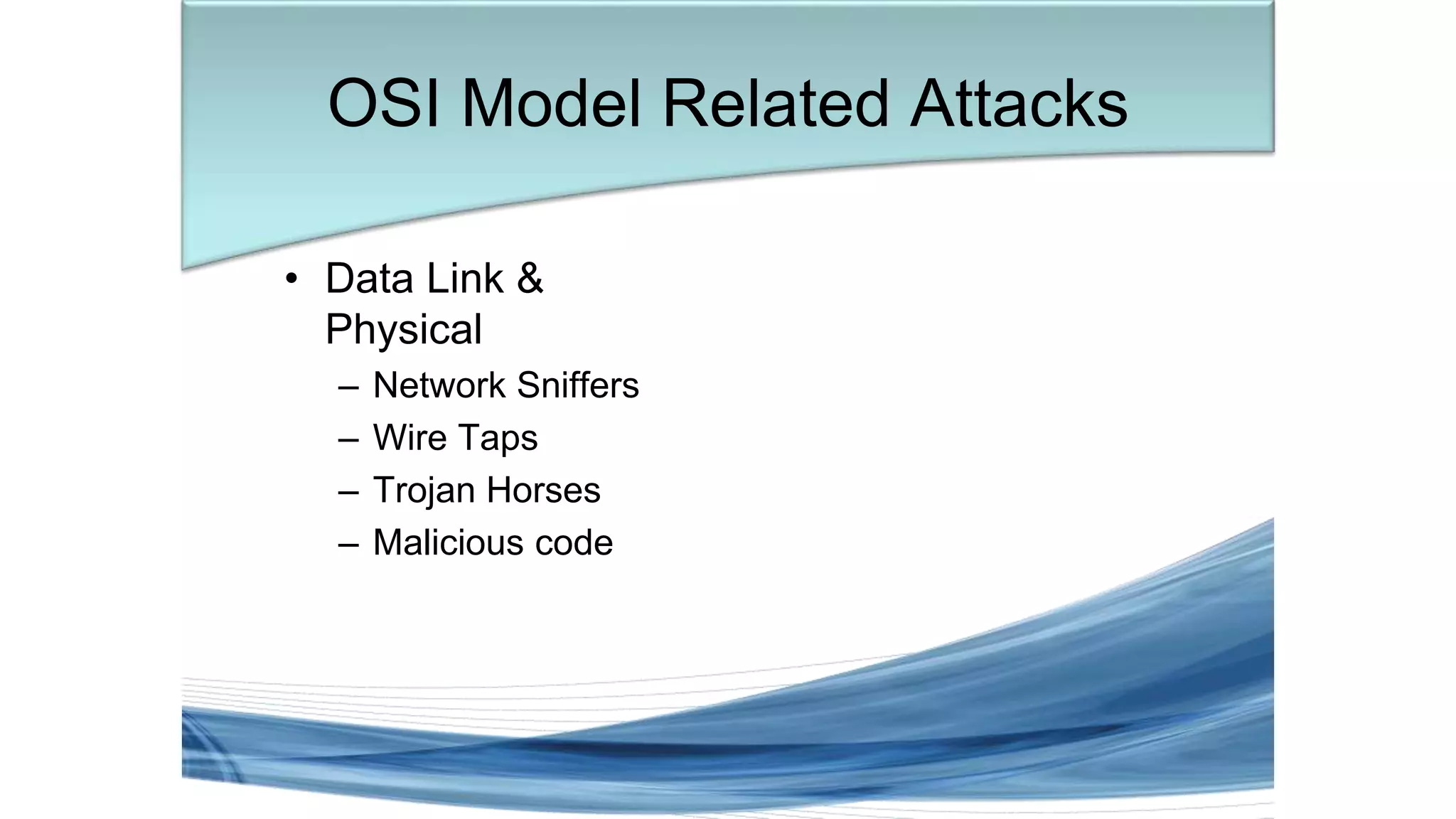
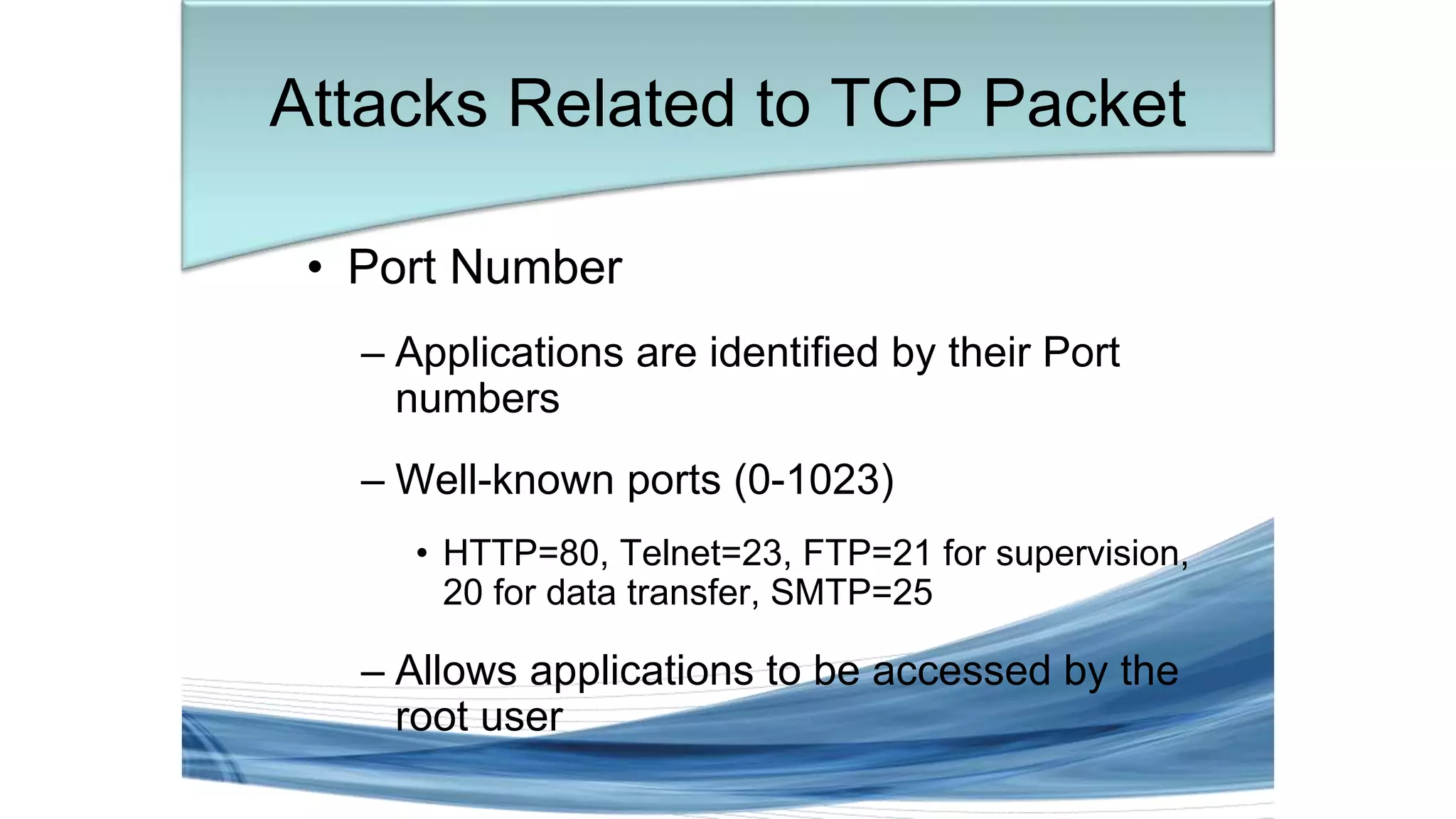
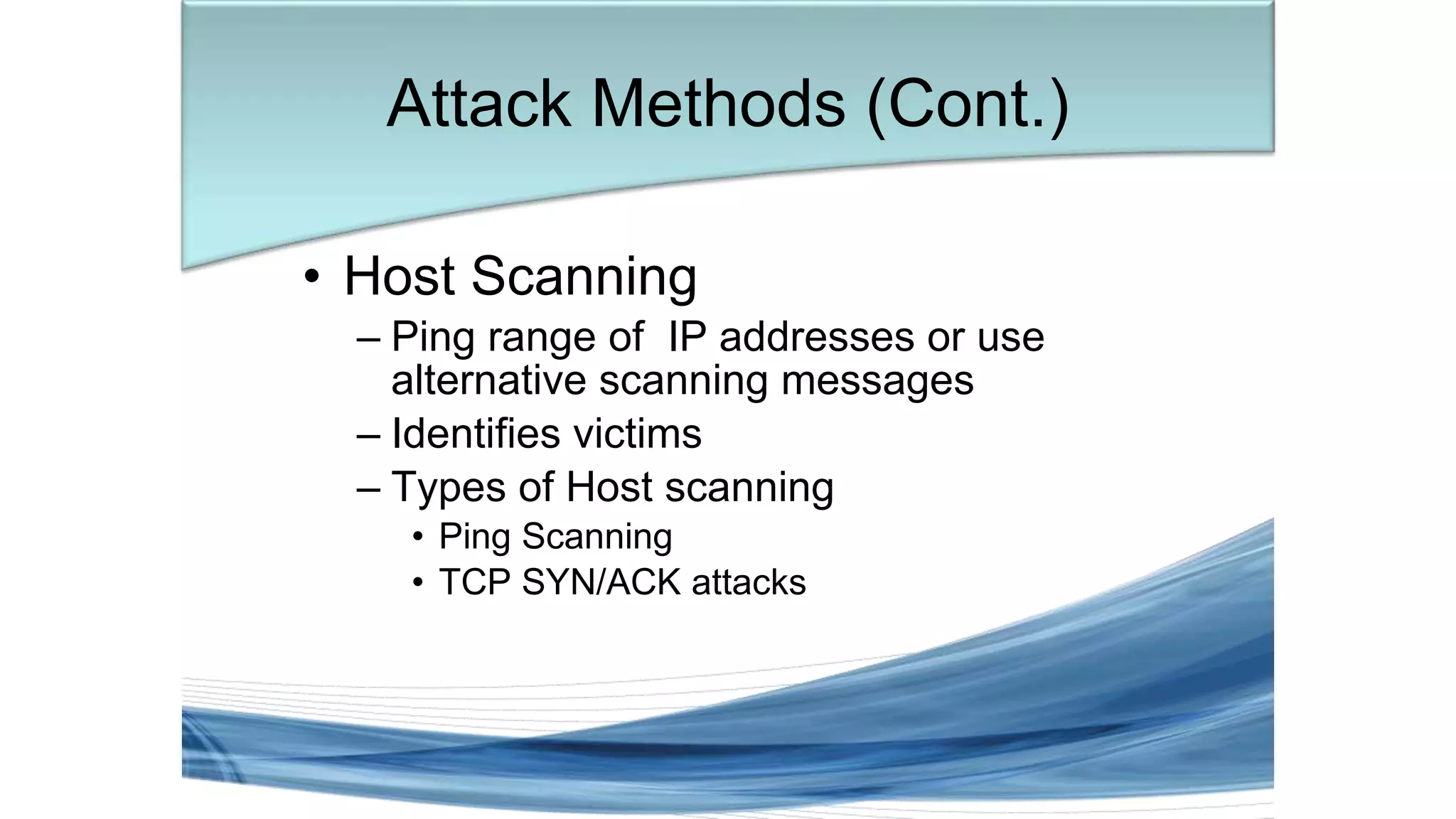
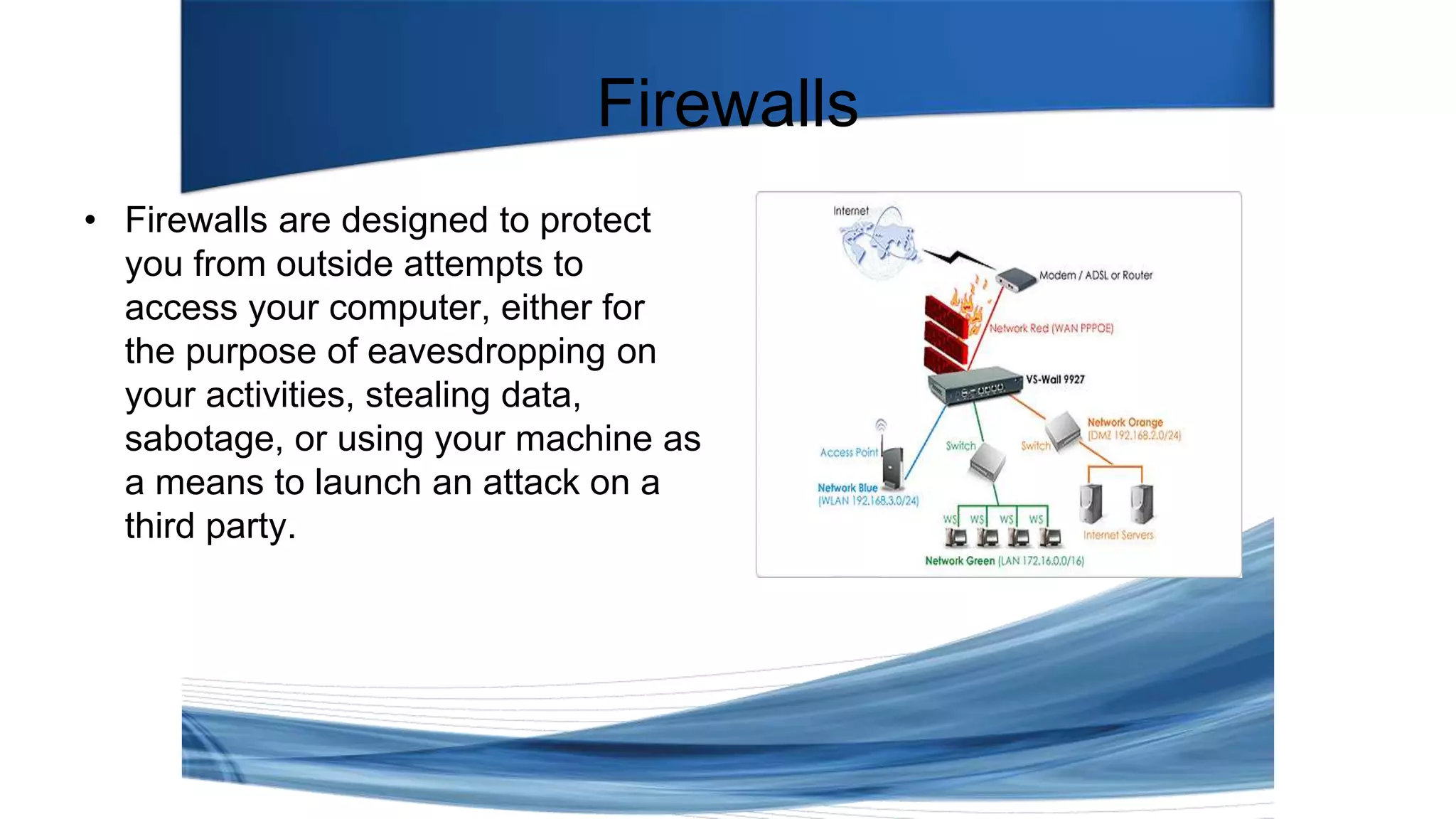
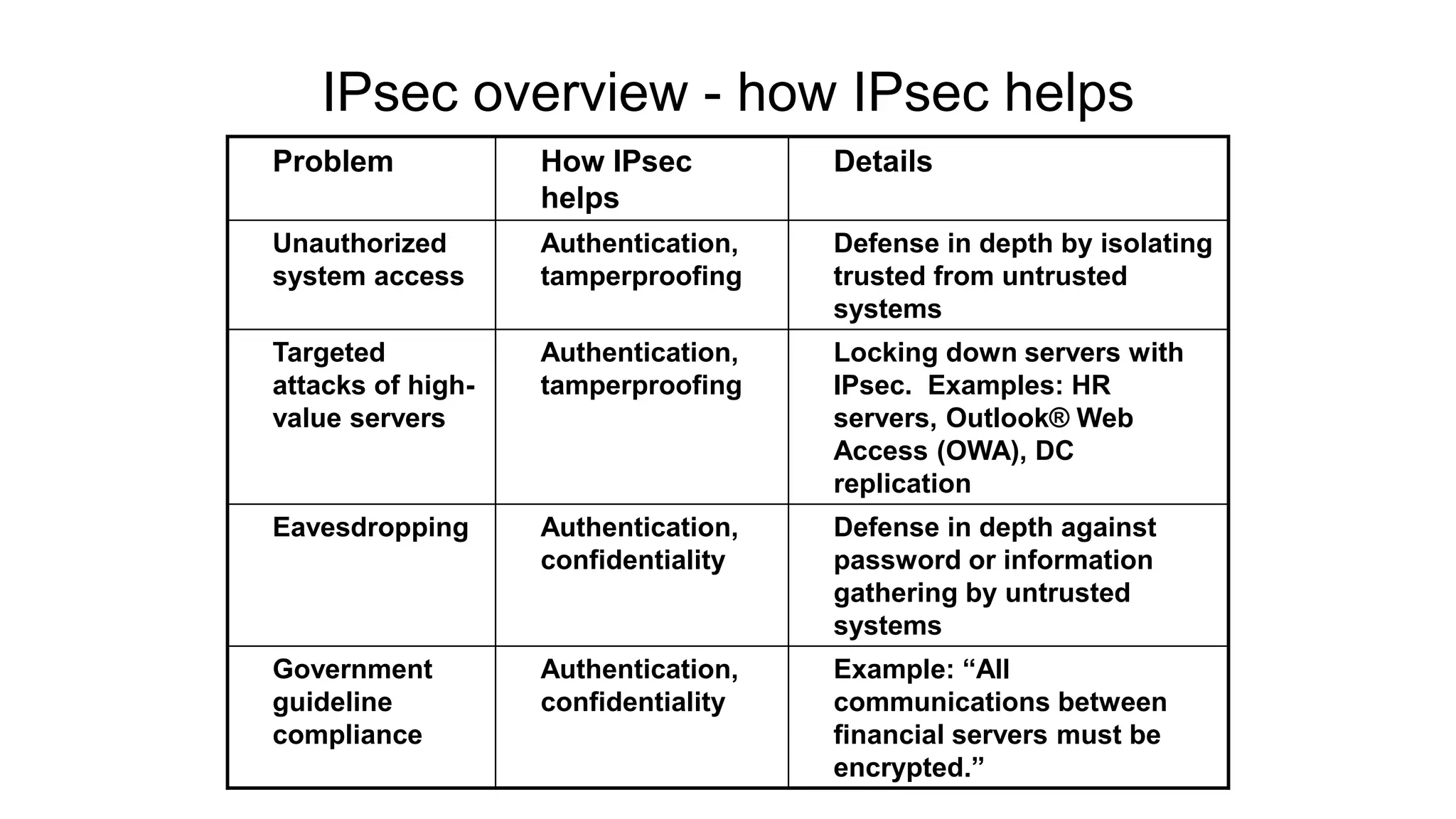
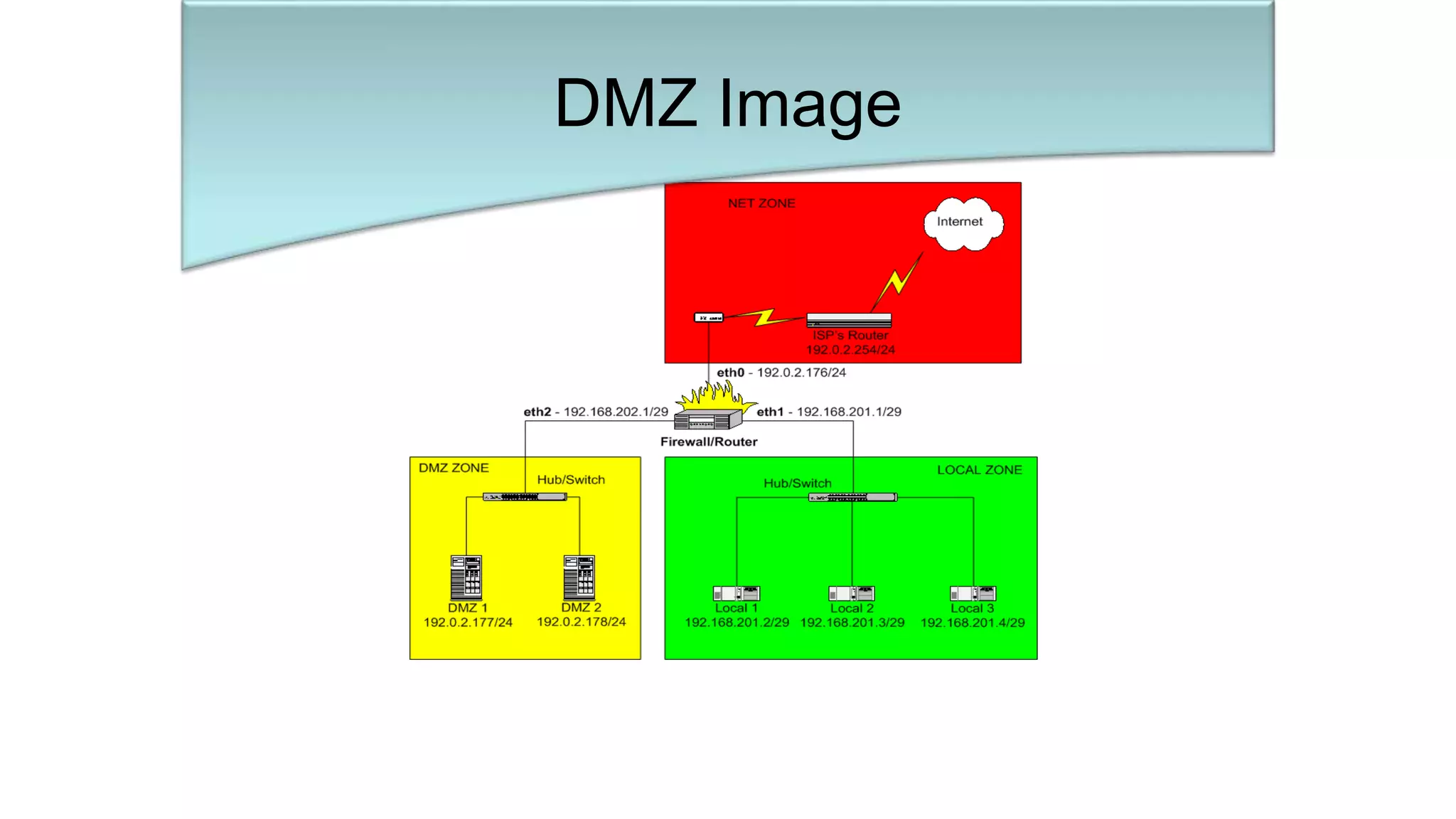
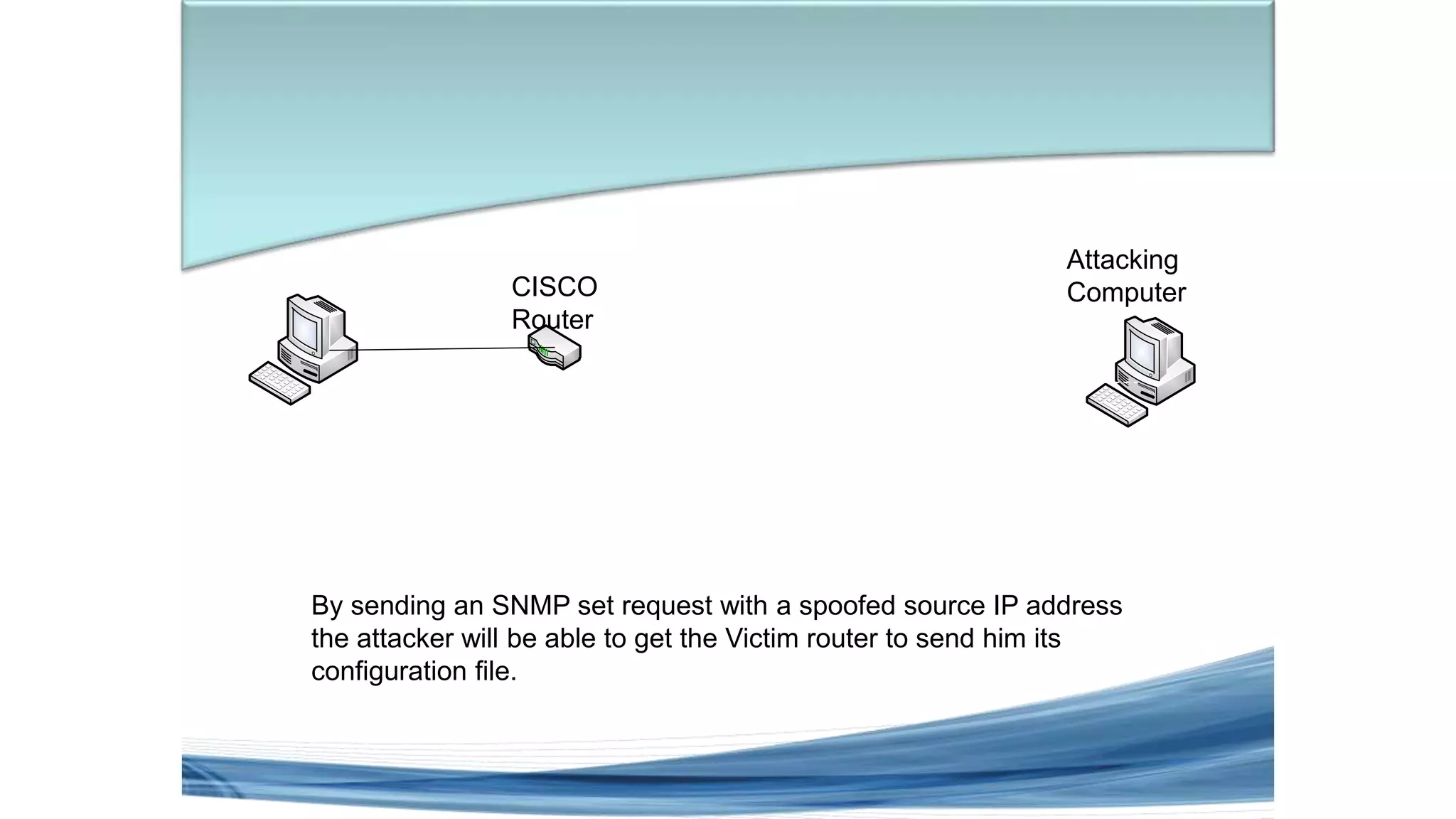
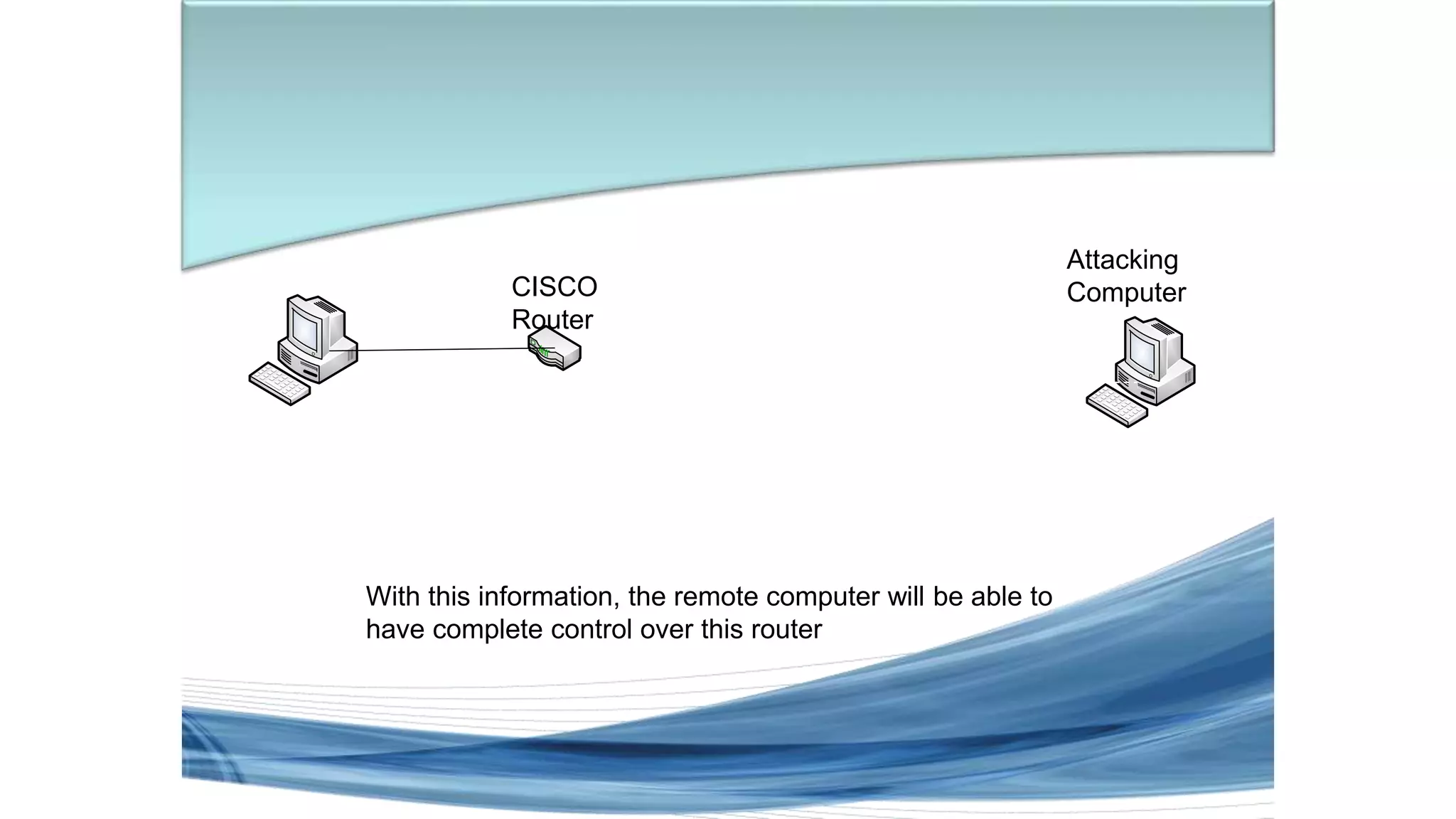
This document discusses various types of network security attacks and methods to prevent them. It covers physical access attacks, social engineering attacks, penetration attacks like scanning and malware. It also discusses attacks on the OSI and TCP/IP models like at the session, transport and network layers. Prevention methods covered include firewalls, proxies, IPSec, security policies and hardening hosts. Specific switch and router vulnerabilities are examined like ARP poisoning, SNMP, spanning tree attacks. Countermeasures for switches include BPDU guard, root guard.