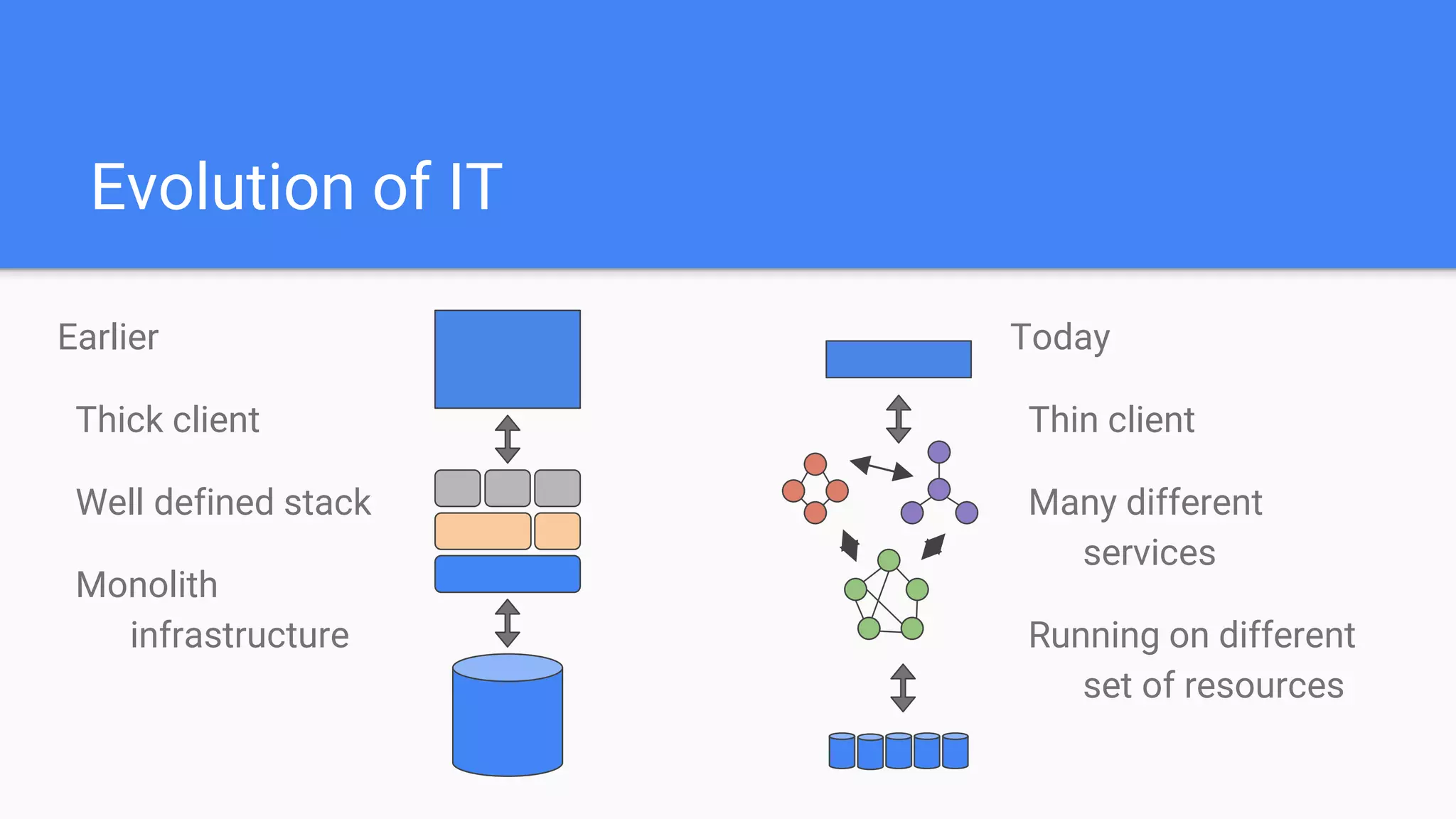
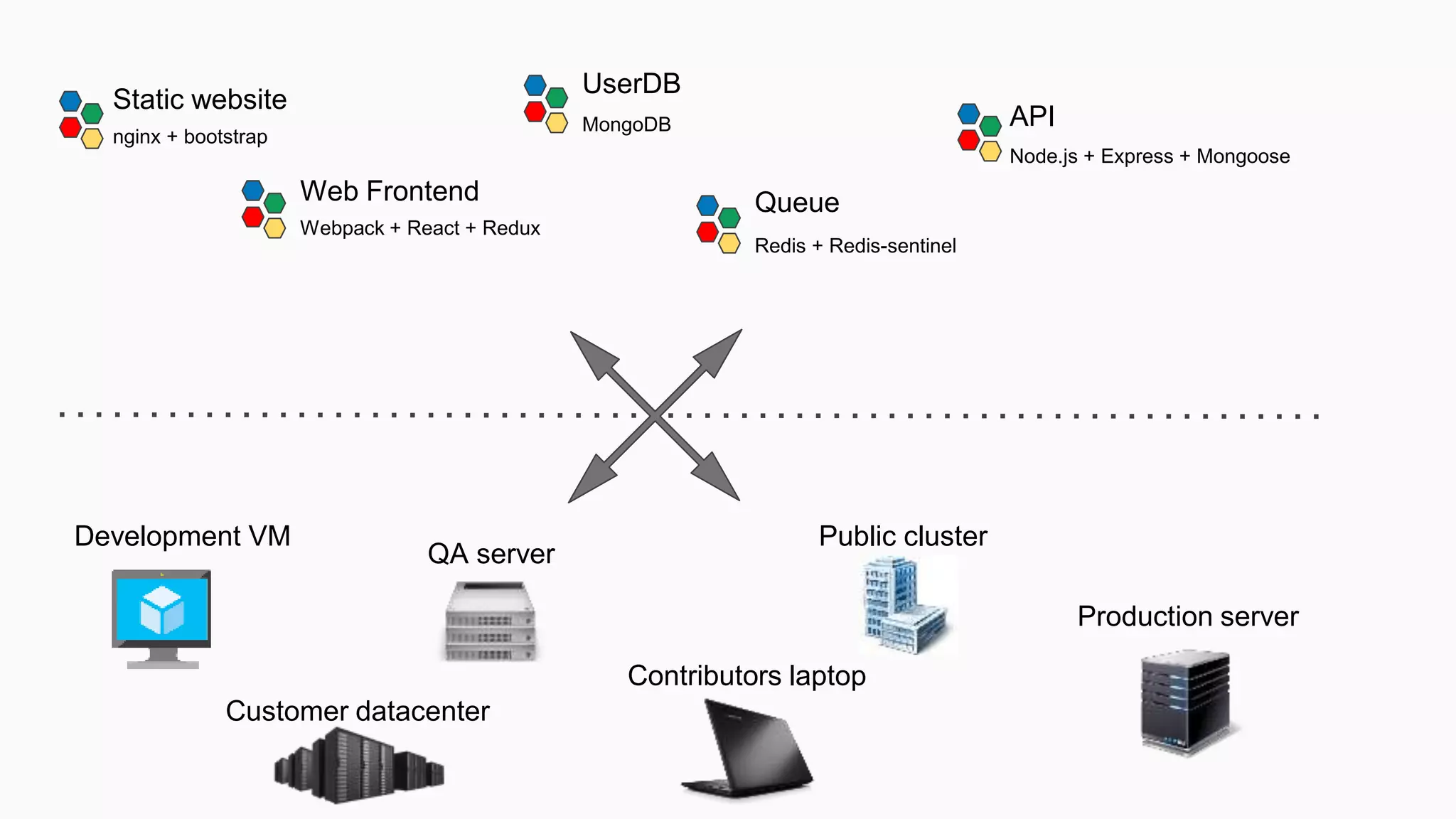
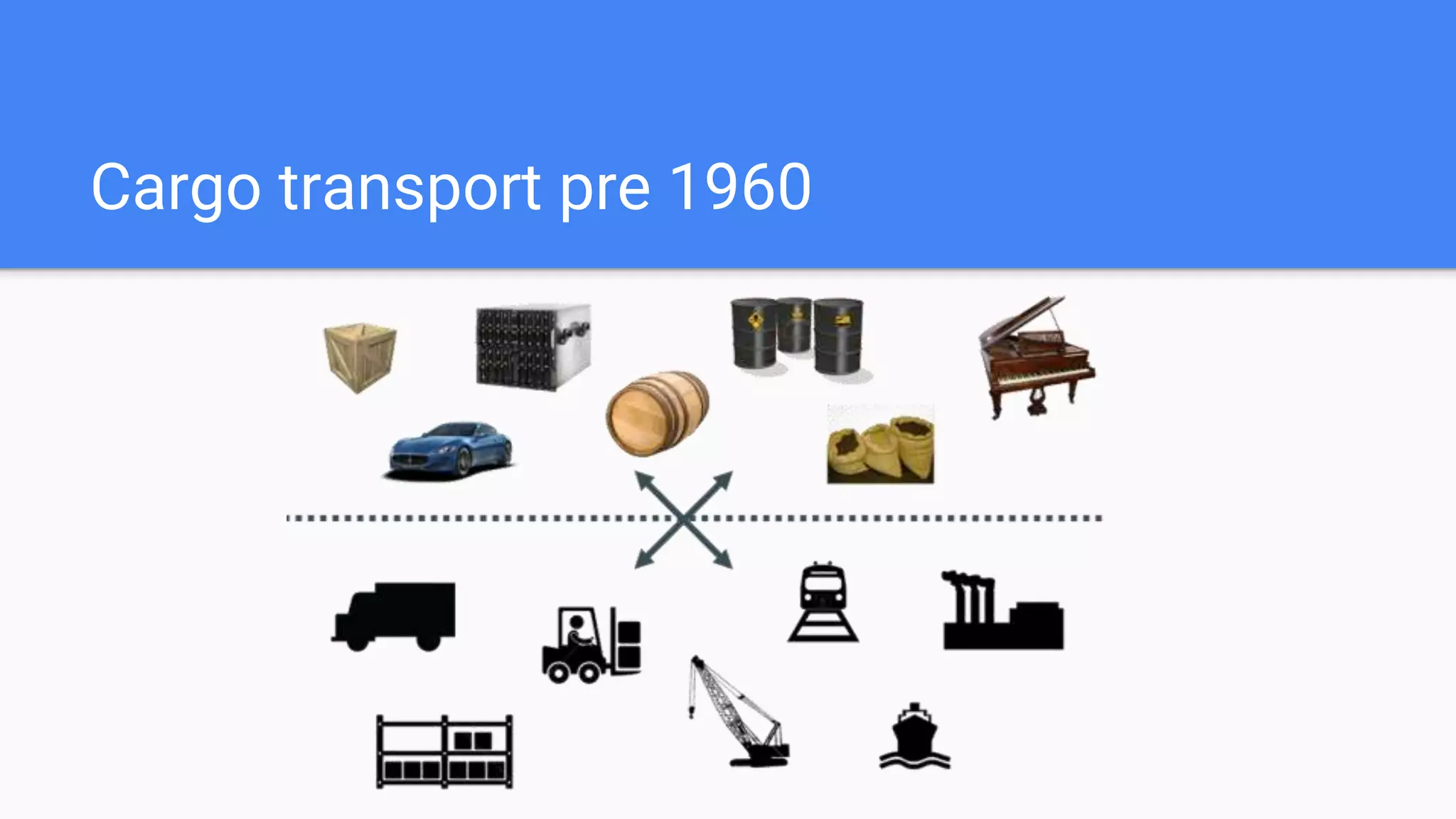
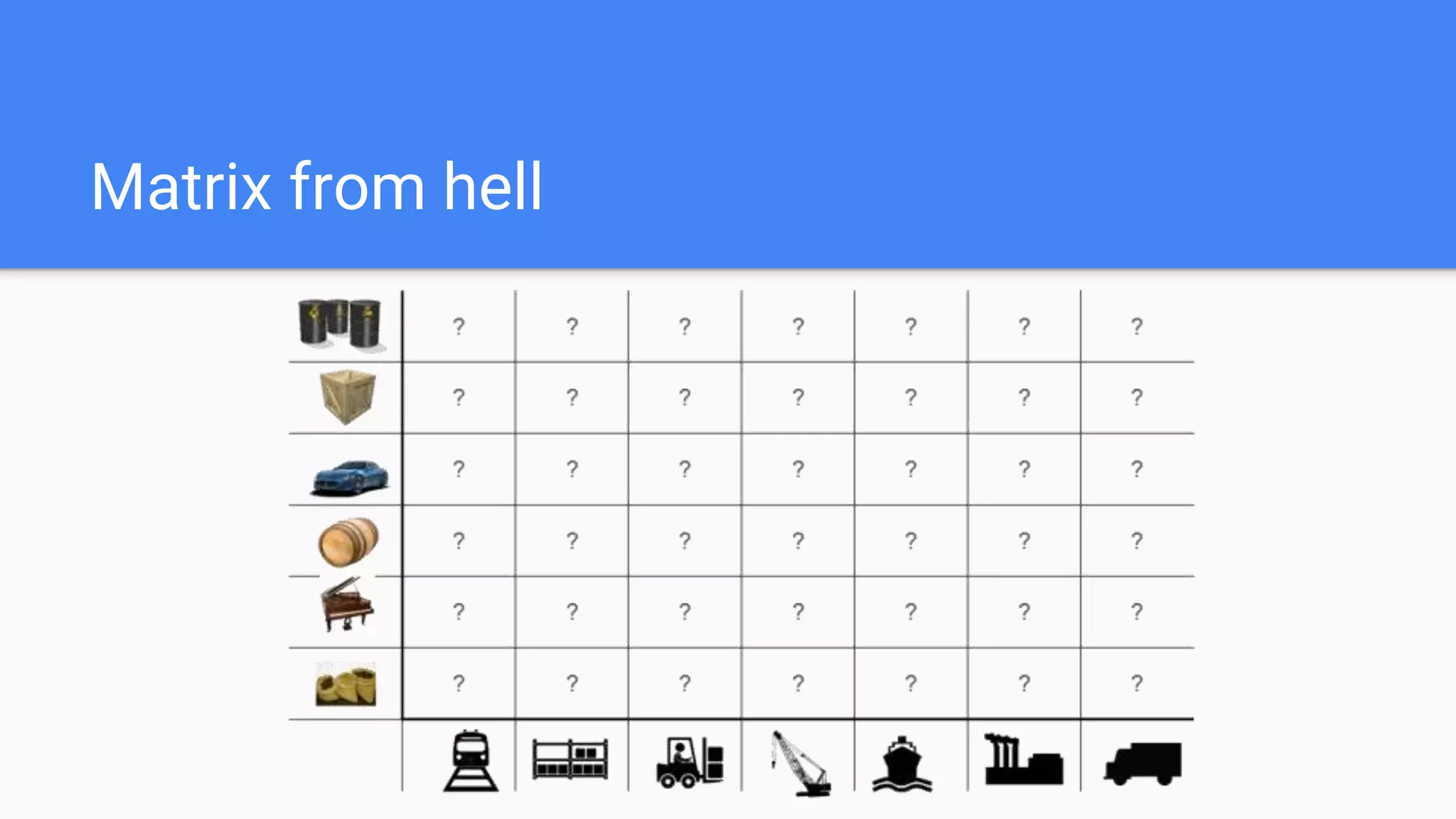
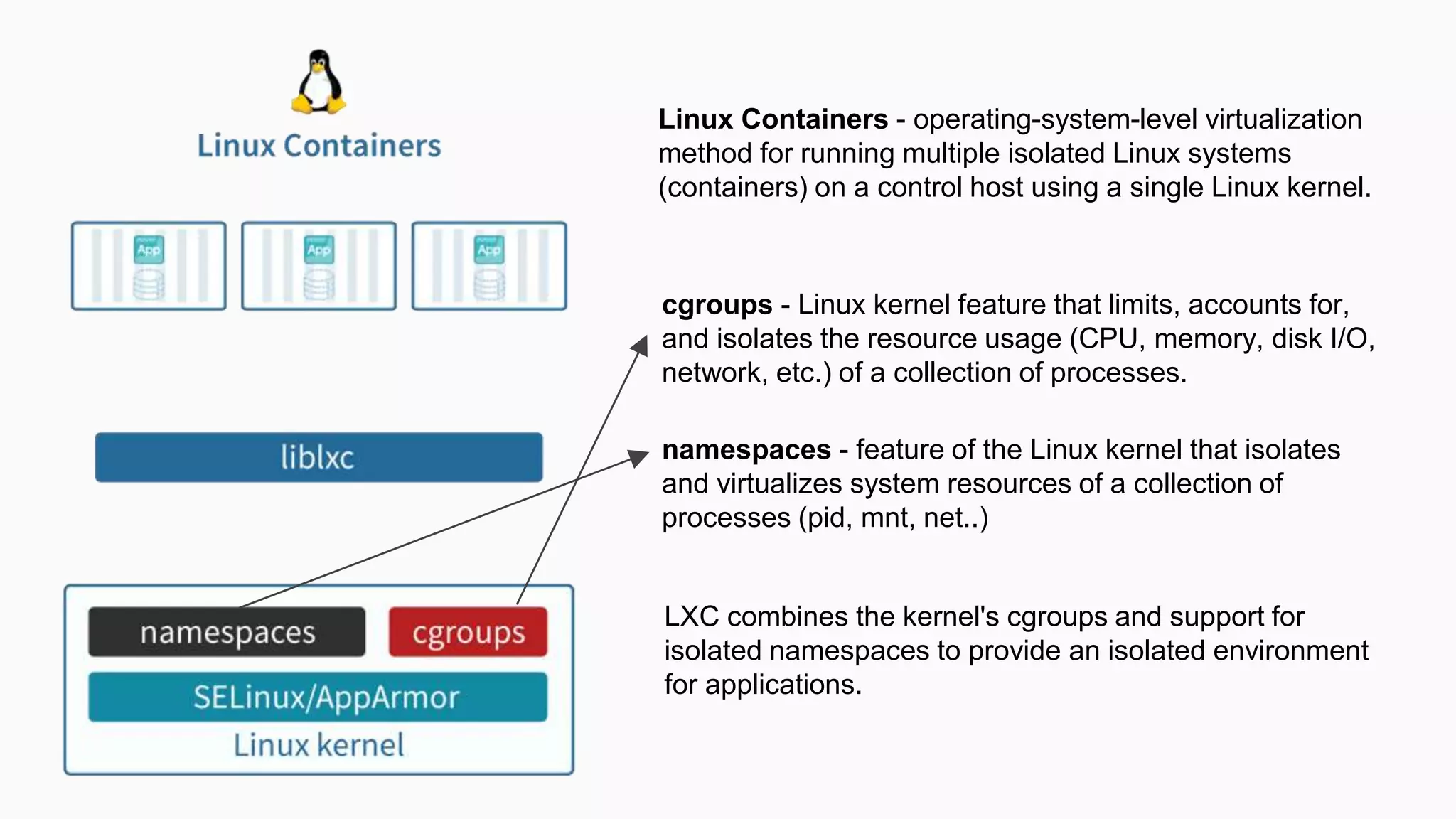
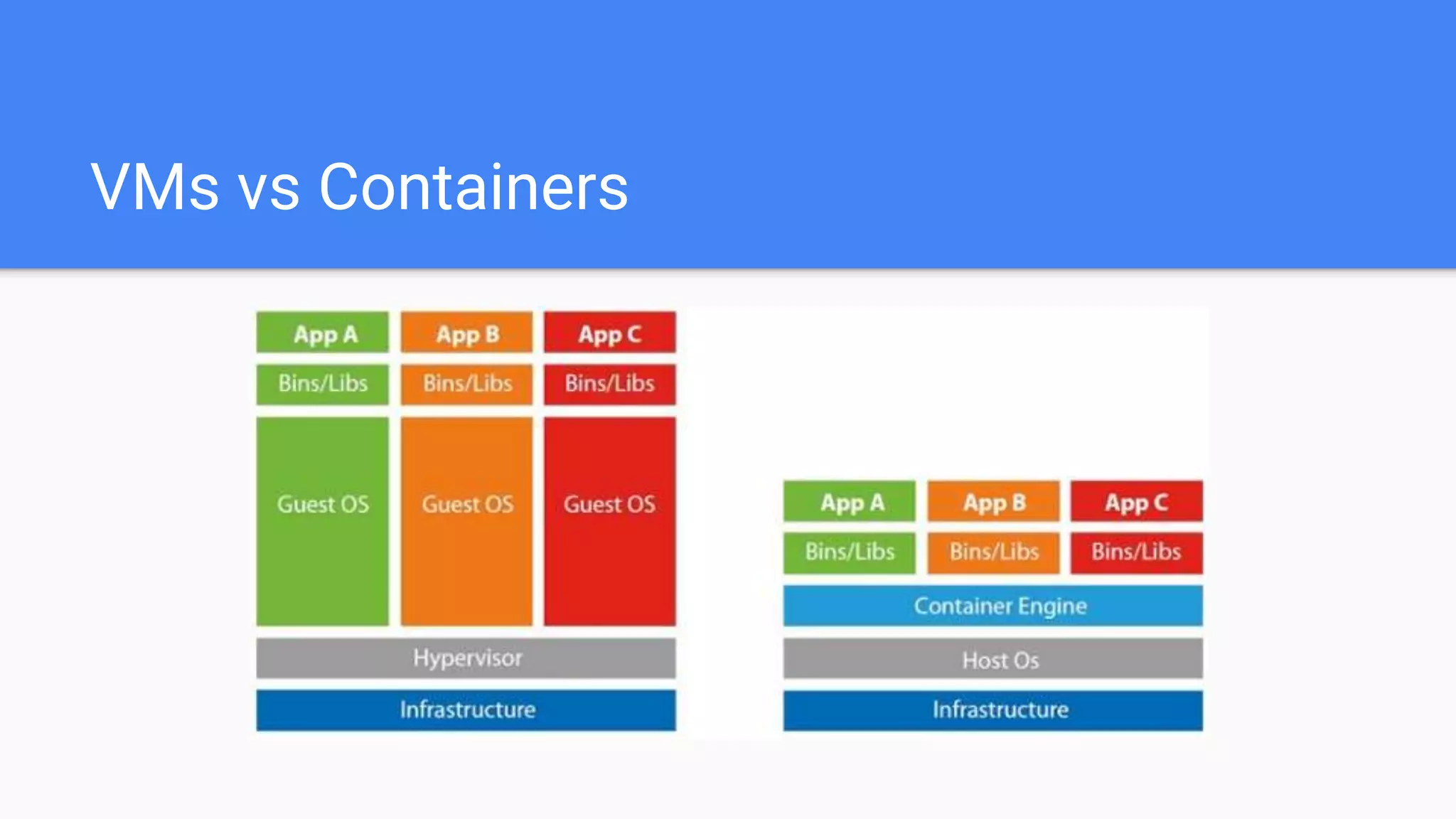
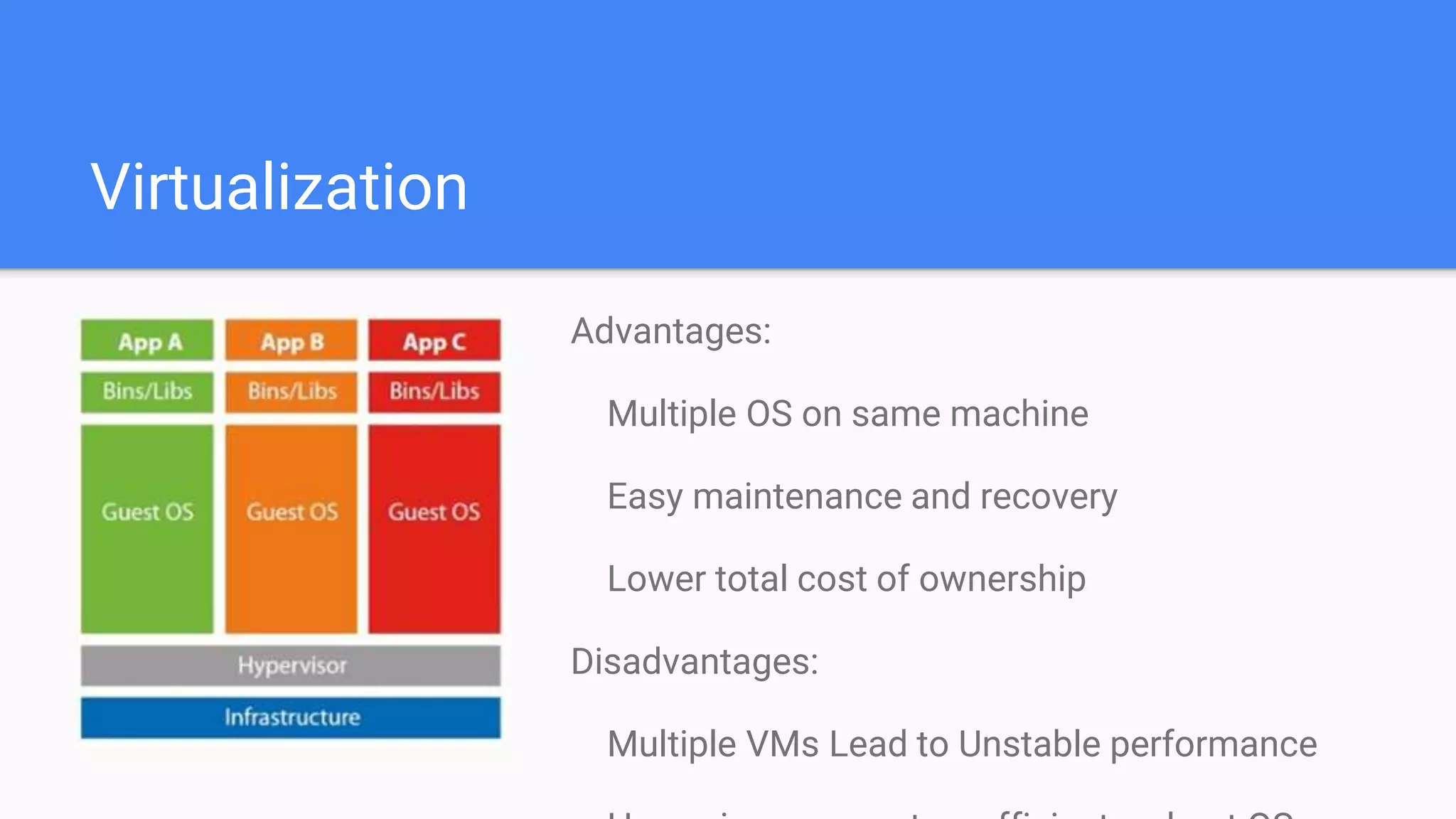
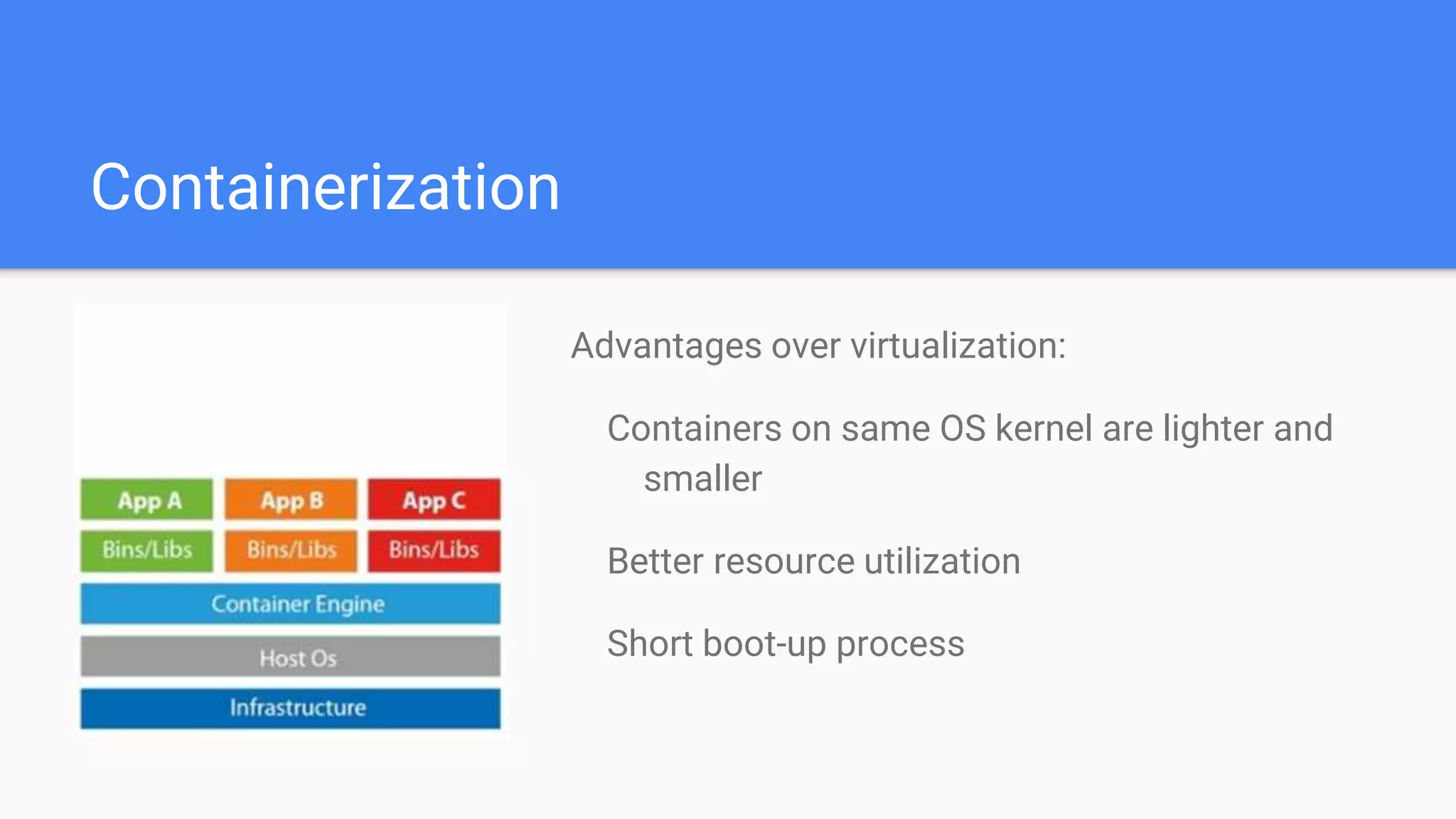
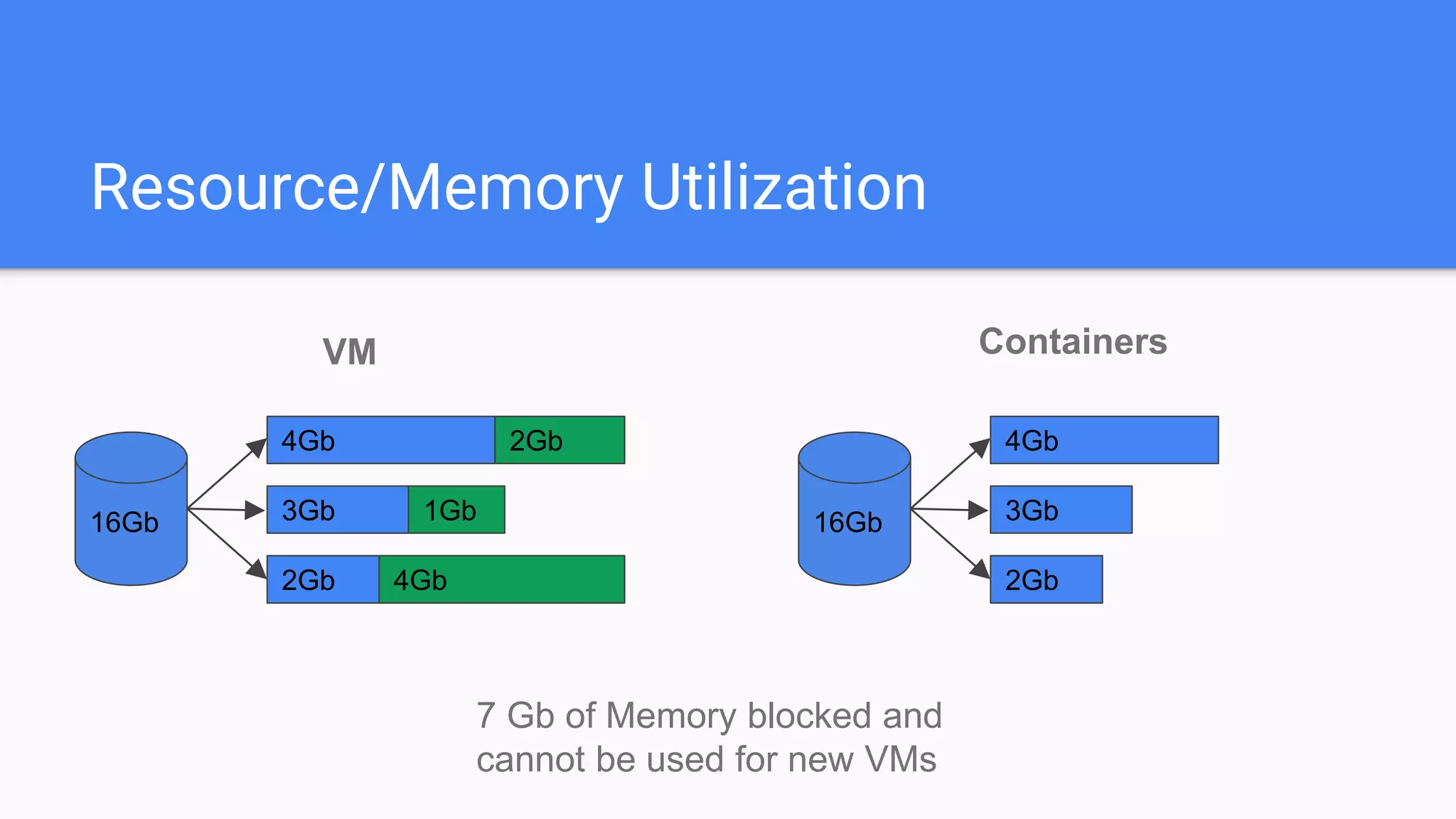
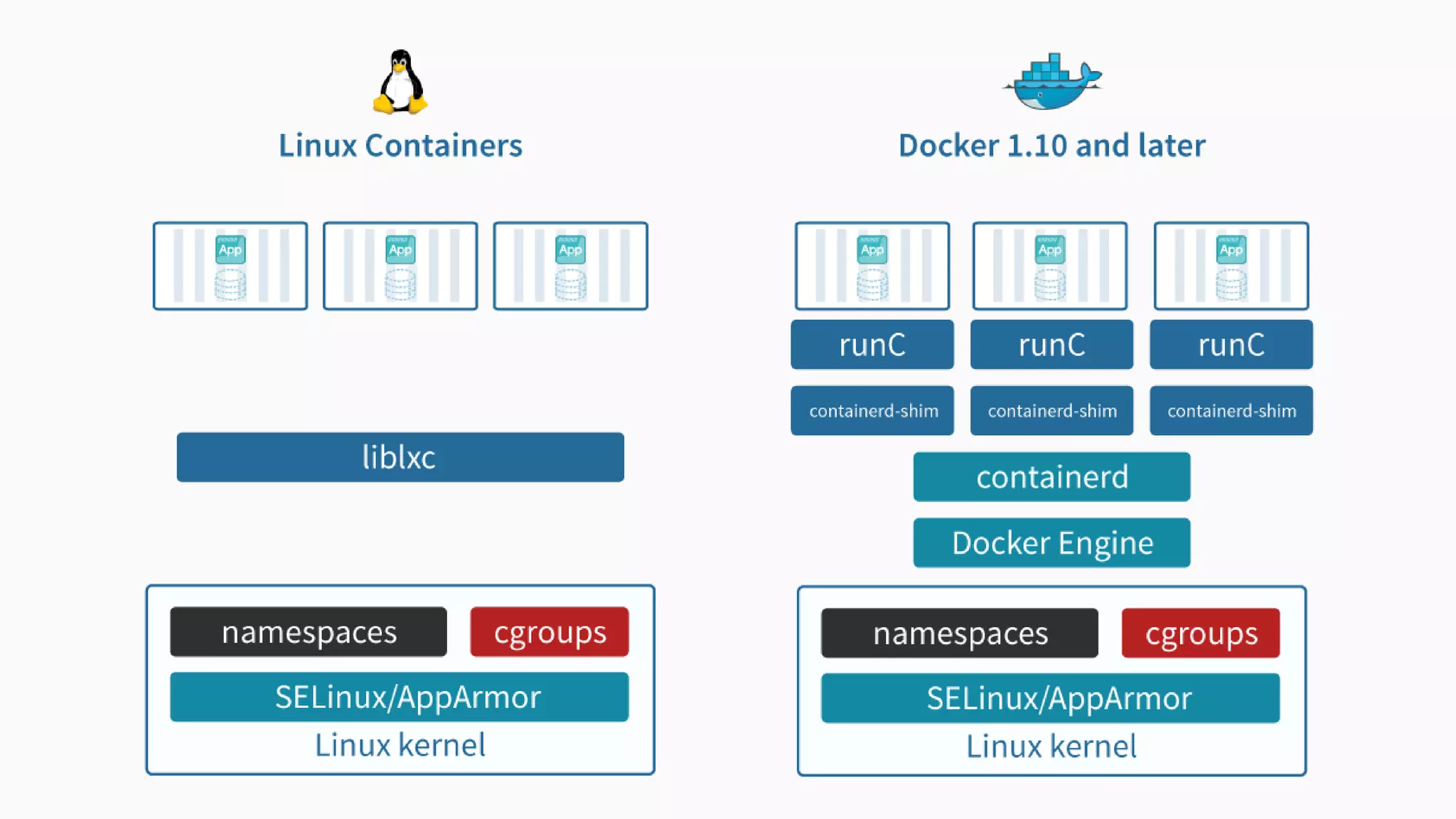
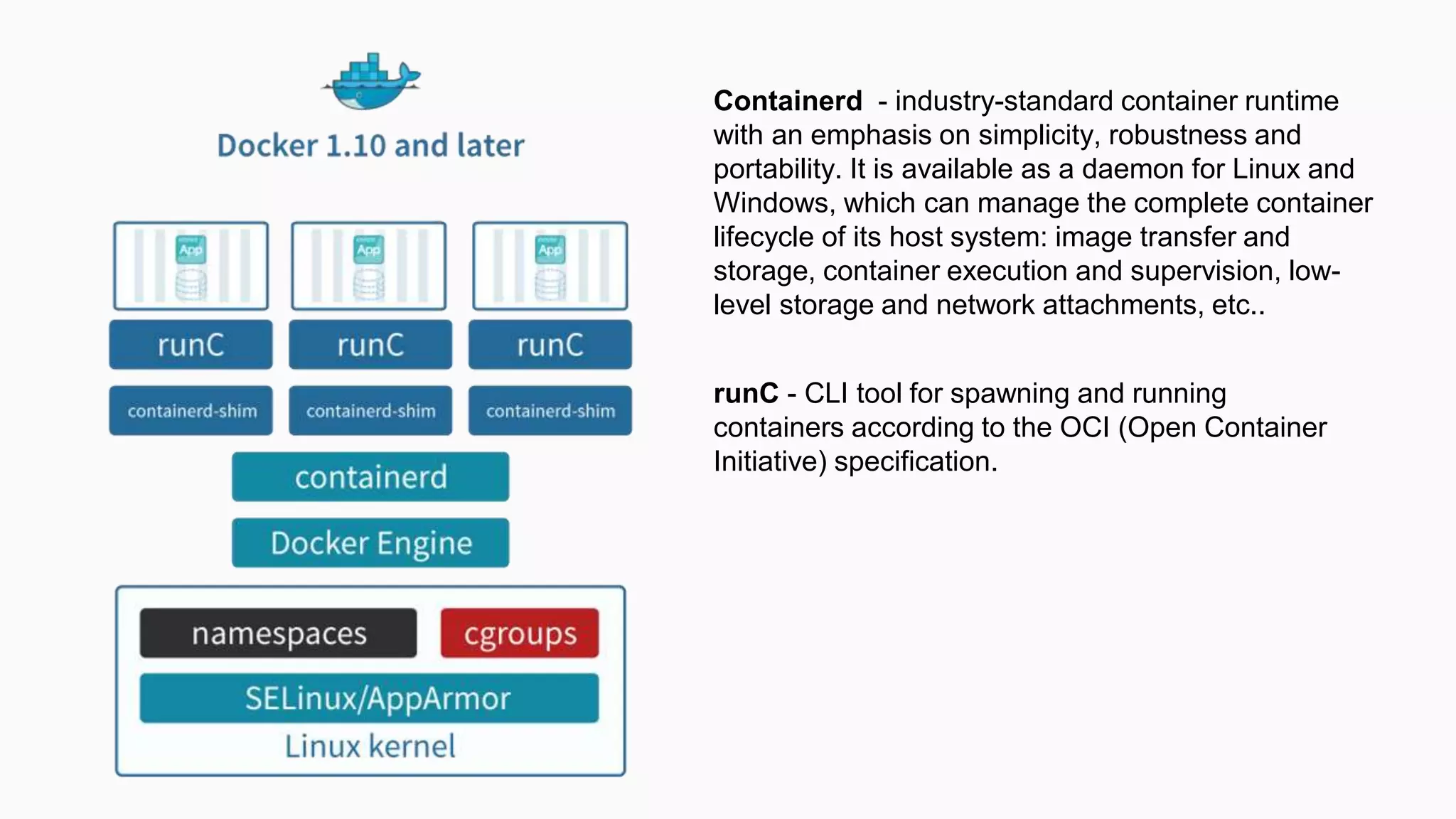
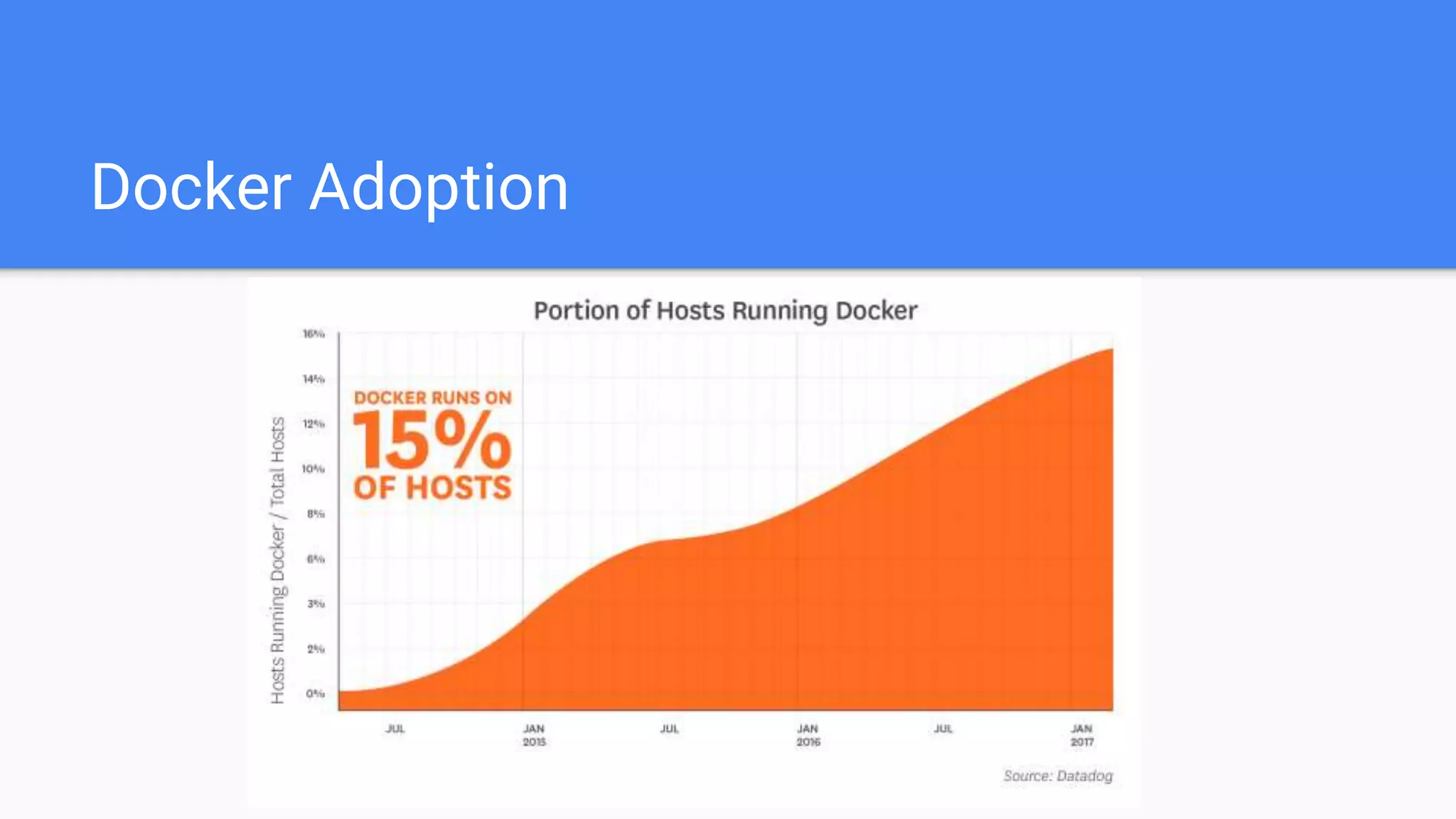
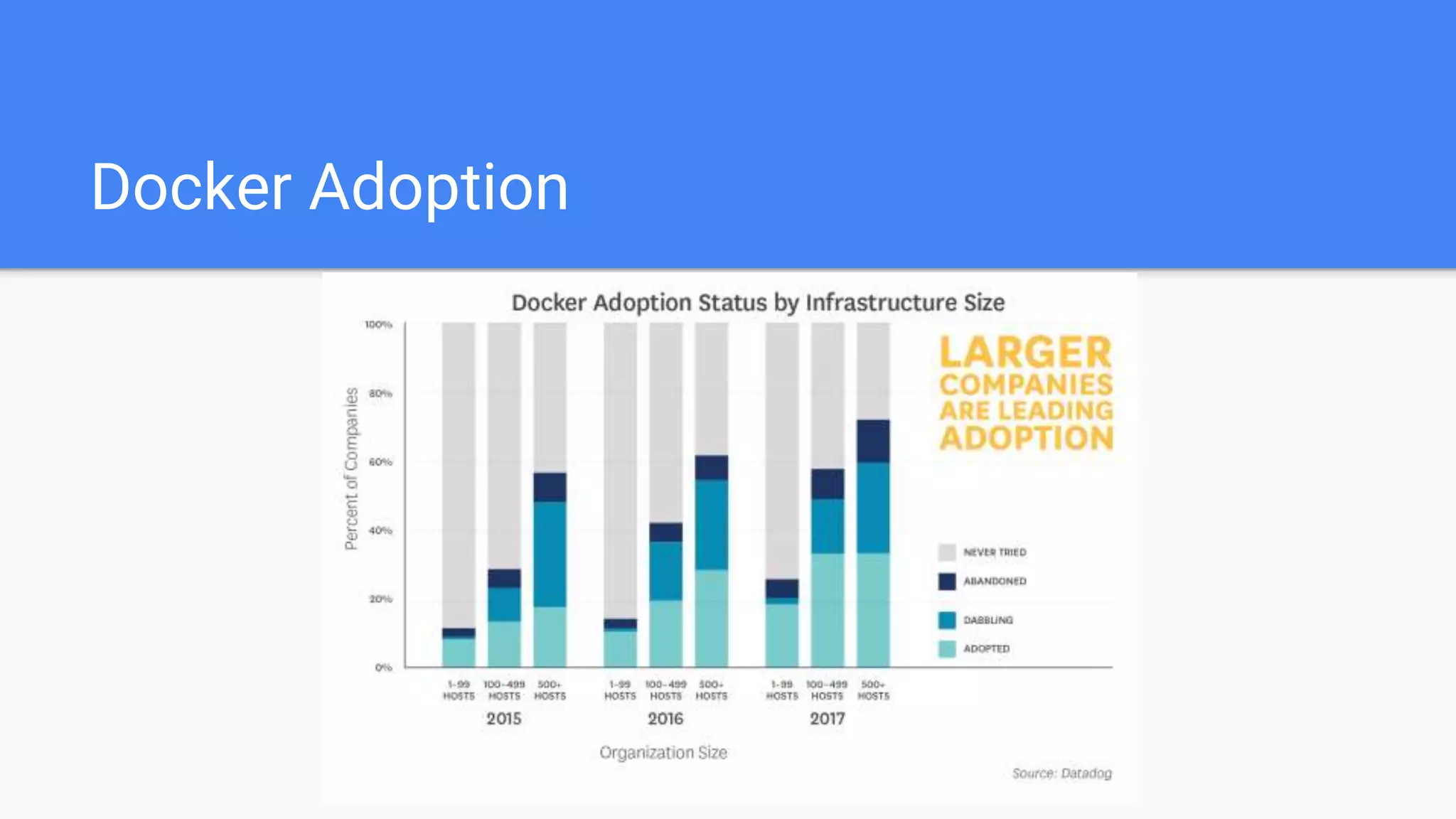
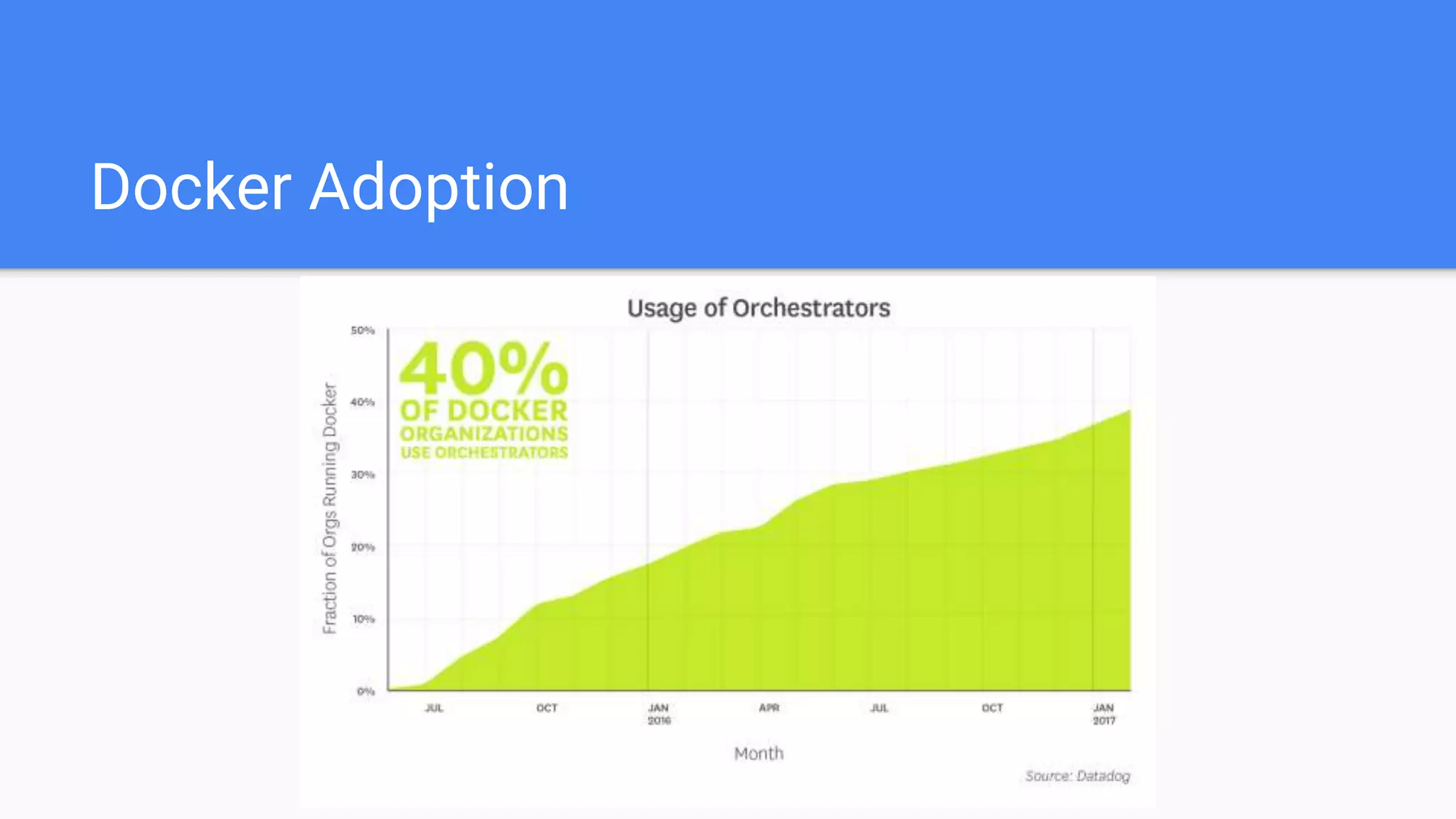
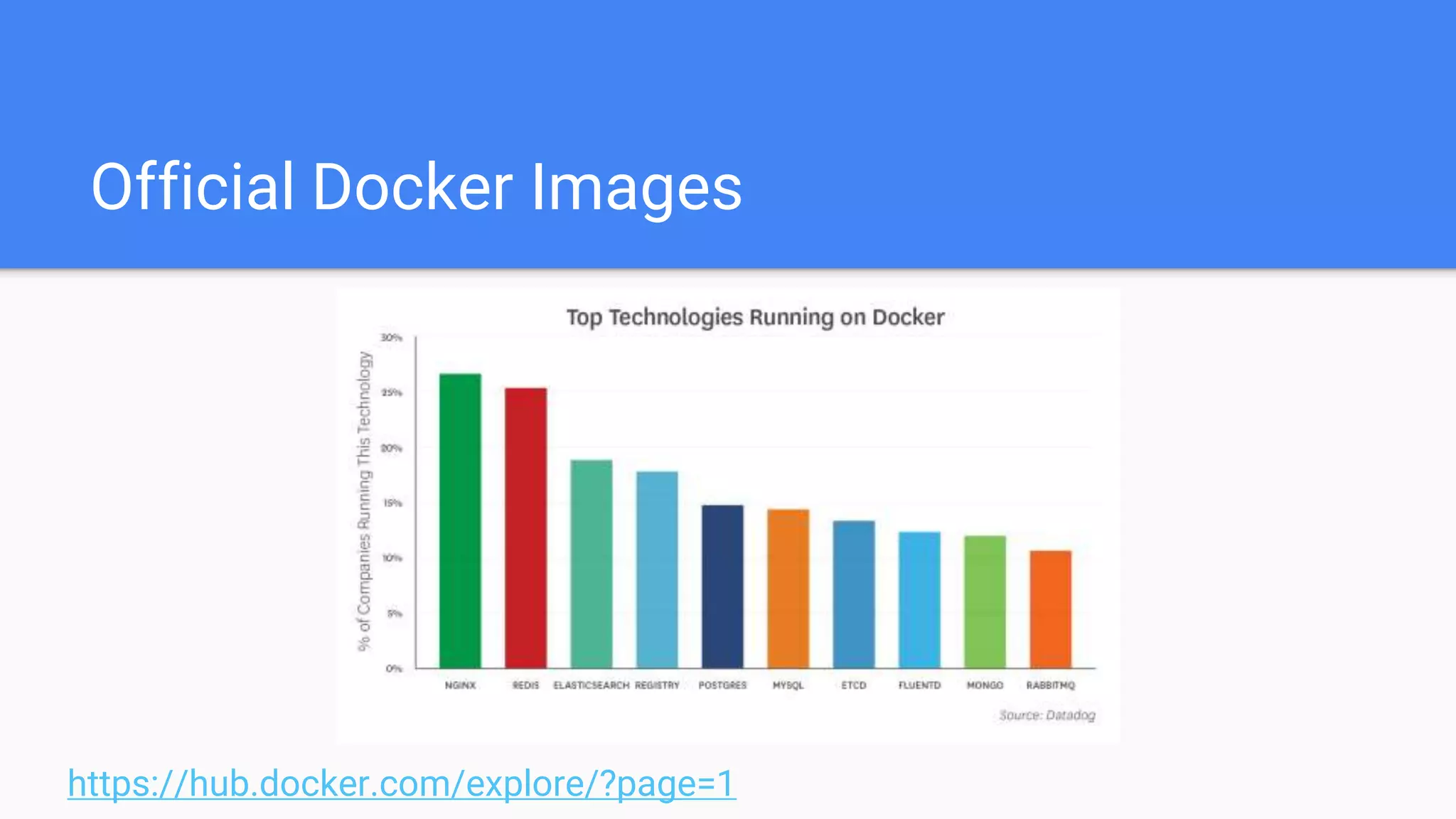
This document provides an agenda for a Docker Academy PRO course. It introduces Docker and containerization basics, including what containers are, how they work, and the challenges they solve compared to traditional virtual machines. It discusses Docker specifically, how it helps build and deploy applications, and how the Docker ecosystem works with components like Containerd and runC. Overall it serves as an introduction and overview to Docker and containerization concepts.