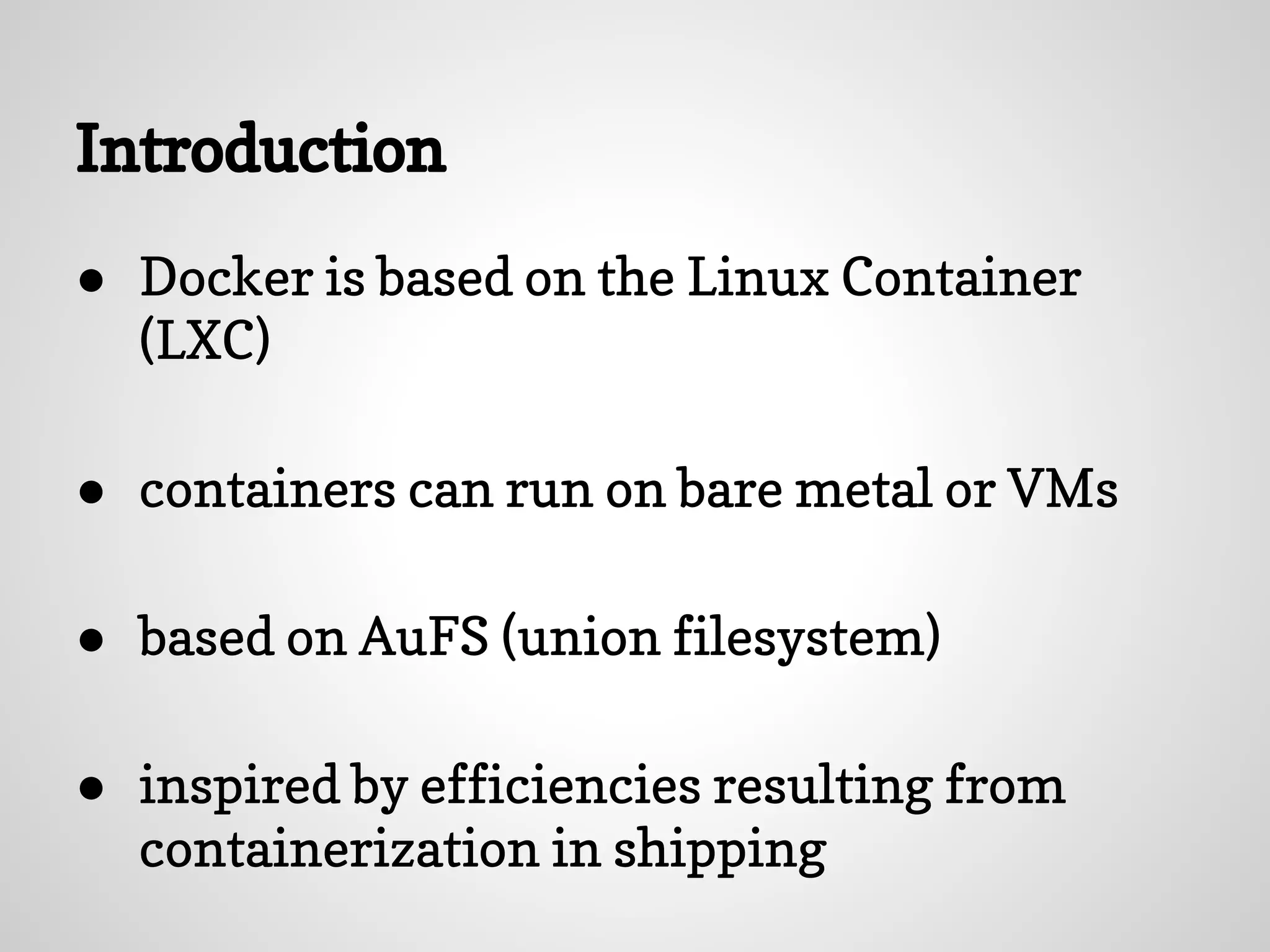
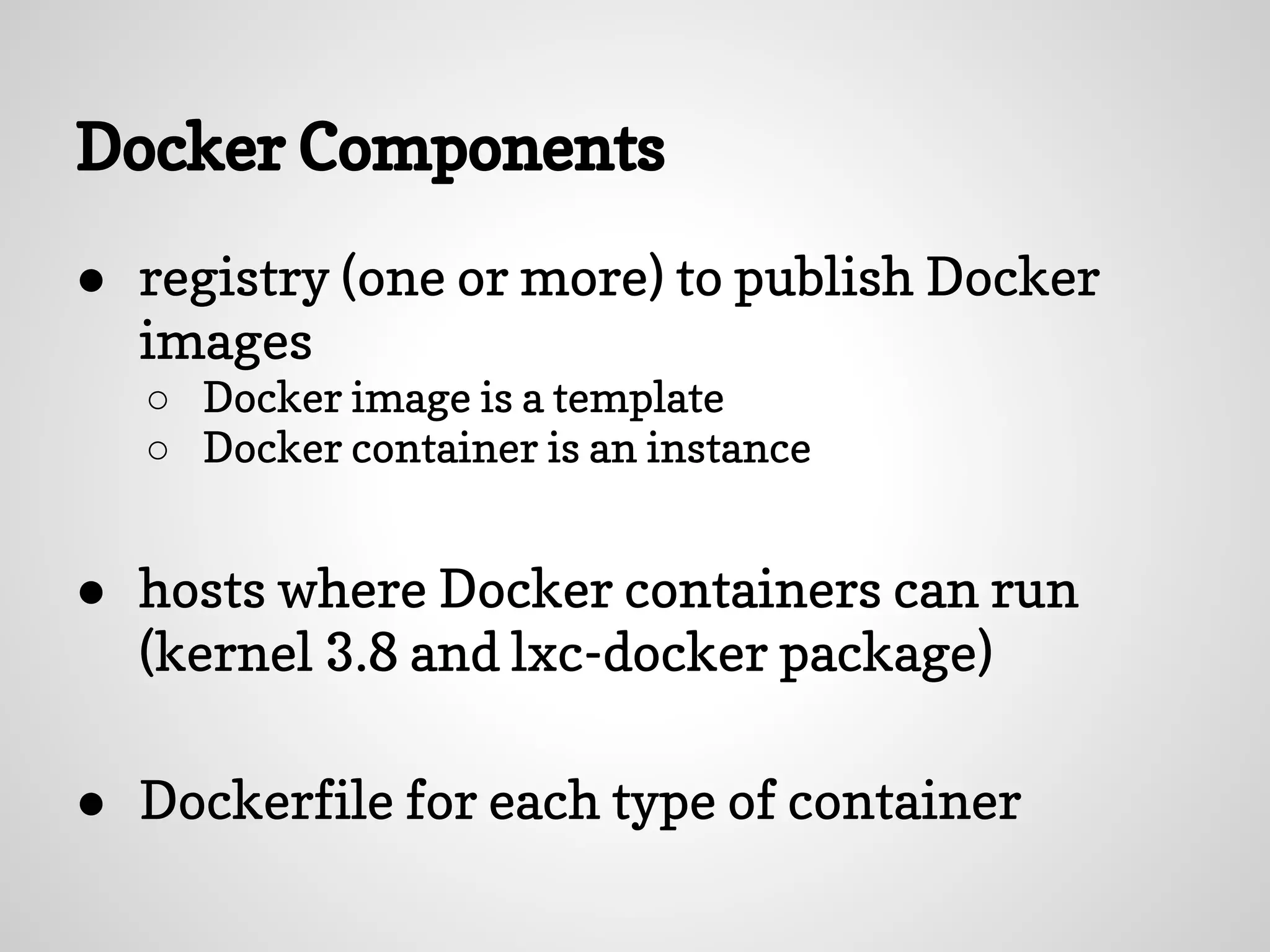
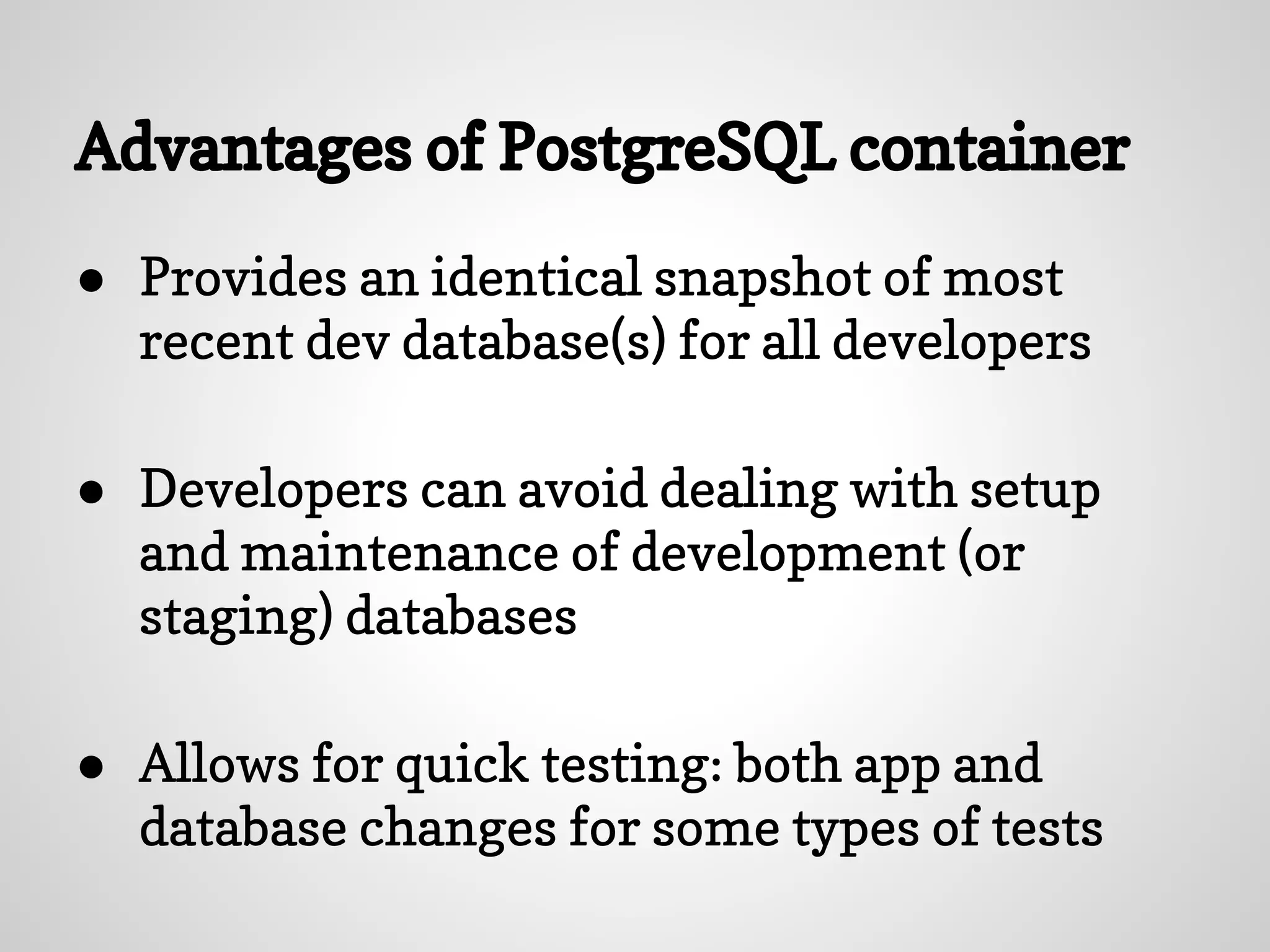
The document discusses setting up PostgreSQL using Docker, highlighting Docker's advantages such as lightweight containers, quick deployments, and a strong community. It outlines the Docker workflow involving creating a Dockerfile, building images, and running containers, along with the benefits of using a PostgreSQL container for development. The introduction of Docker at Gilt is also mentioned, emphasizing its role in improving development processes and testing capabilities.







![References
● Docker wiki [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Docker_
(software)]
● Docker getting started
[https://www.docker.io/gettingstarted/]
● Dockerfile tutorial
[http://www.docker.io/learn/dockerfile/]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/postgresqlsetupusingdocker-131212165829-phpapp02/75/PostgreSQL-Setup-Using-Docker-11-2048.jpg)
