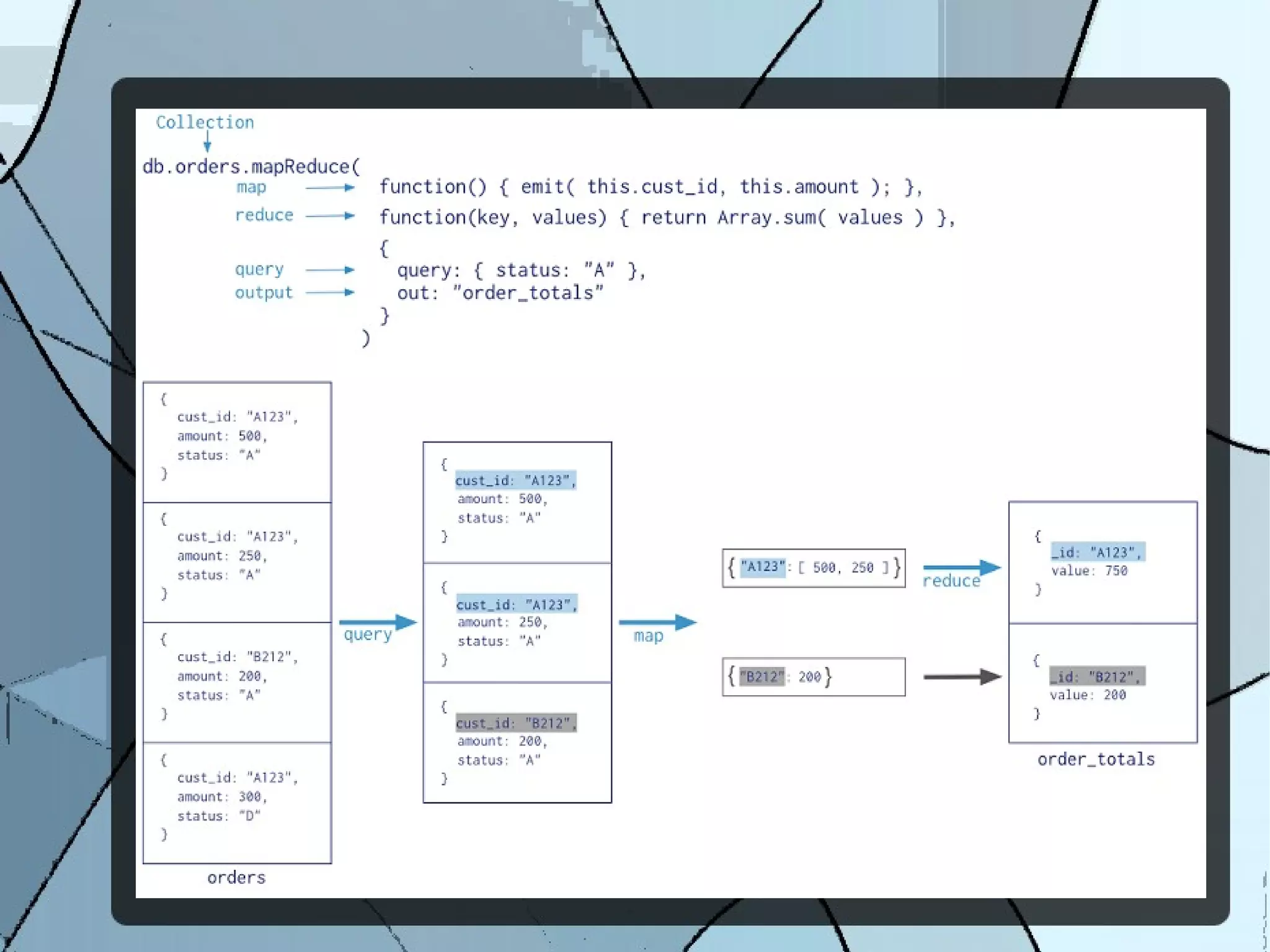
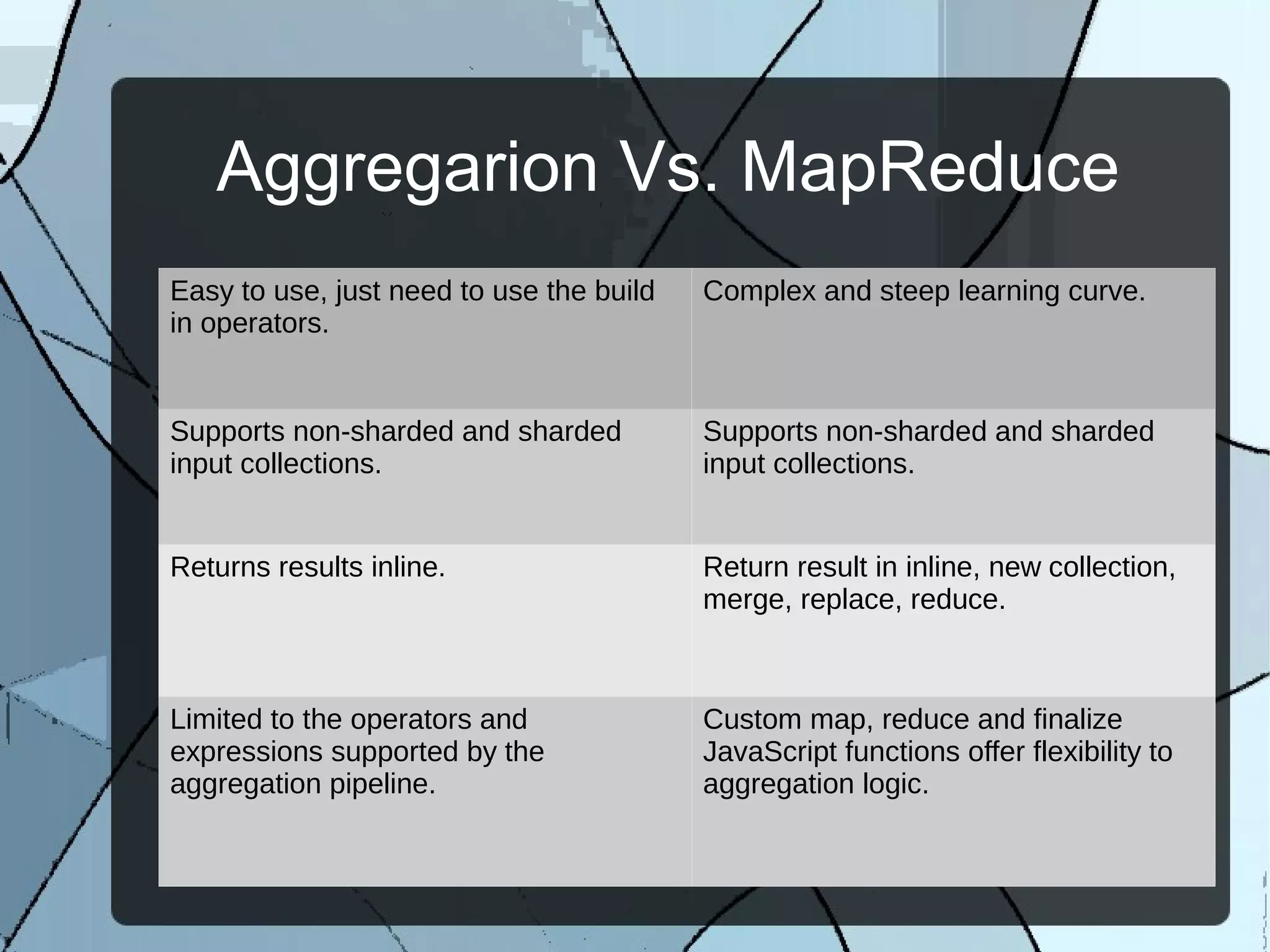
The document discusses MongoDB's aggregation framework. It defines aggregation as gathering data together to perform computations and return computed results. The aggregation framework in MongoDB uses pipelines similar to UNIX pipes to perform aggregation operations like $group, $match, $project, etc. on data. It also supports map-reduce operations and provides connectors to Hadoop. The document provides examples of translating common SQL queries to the aggregation framework and discusses concepts like optimization, restrictions and references for further reading.




![Examples
SQL Query Aggregation Query
SELECT COUNT(*) AS COUNT
FROM EMPLOYEE
db.employee.aggregate([
{$group: {_id:null, count: { $sum:1} } }
])
Explaination :
Group by : on nothing
Sum : Just add 1 to count field for each
record
SELECT SUM(SALARY) AS TOTAL
FROM EMPLOYEE
db.employee.aggregate([
{$group: {_id:null, total:
{ $sum:”$salary”} } }
])
Explaination :
Group by : on nothing
Sum: do the sum of value of salary
field of each doc and put result in total.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aggregationinmongo-140327064744-phpapp02/75/Aggregation-Framework-in-MongoDB-Overview-Part-1-11-2048.jpg)
![Example Cont.
SELECT DEPARTMENT_ID,
SUM(SALARY) AS TOTAL FROM
EMPLOYEE GROUP BY
DEPARTMENT_ID ORDER BY
TOTAL
db.employee.aggregate( [
{ $group: { _id: “$department_id”, total:
{ $sum:”$salary” } },
{ $sort: { total : 1 } } }
] )
Explanation:
Group by : department,
Sum : salary,
Order by : total of salary for each
department](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aggregationinmongo-140327064744-phpapp02/75/Aggregation-Framework-in-MongoDB-Overview-Part-1-12-2048.jpg)
![Example Cont.
SELECT DEPT_ID, SUM(SALARY)
AS TOTAL FROM EMPLOYEE
WHERE AGE>25 GROUB BY
DEPT_ID, HAVING TOTAL > 5000
db.employee.aggregate( [
{ $match : { age : {$gt: 25 } } }
{ $group: { _id: “$dept_id”, total:
{ $sum: ”$salary” } } },
{ $match: { total: {$gt:5000 } } }
] )
Explanation:
Group by : department id,
Sum : salary,
Having: on total of each department
salary](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aggregationinmongo-140327064744-phpapp02/75/Aggregation-Framework-in-MongoDB-Overview-Part-1-13-2048.jpg)
![Example Cont.
SELECT DEPT_ID, SUM(SALARY) AS
TOTAL FROM EMPLOYEE WHERE
AGE>25 GROUB BY DEPT_ID,
HAVING TOTAL > 5000
db.employee.aggregate( [
{ $match : { age : {$gt: 25 } } }
{ $group: { _id: “$dept_id”, total:
{ $sum: ”$salary” } } },
{ $match: { total: {$gt:5000 } } }
] )
Explanation:
Group by : department id,
Sum : salary,
Having: on total of each department
salary](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aggregationinmongo-140327064744-phpapp02/75/Aggregation-Framework-in-MongoDB-Overview-Part-1-14-2048.jpg)
![$unwind Operator
Decompose the embedded array into flat
document and relate each entry in the
array with outer fields.
Example :-
{ _id: “blog”, tags: [ “social”, “economic” ] }
{ _id: “blog”, { _id: “blog”
tags: “social” } tags: “economic” }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aggregationinmongo-140327064744-phpapp02/75/Aggregation-Framework-in-MongoDB-Overview-Part-1-15-2048.jpg)


![Projection Optimization
● $project
● Reduce the amount of data passing
through channels of operation and will help
in performace improvement.
● Below example will only emit salary.
db.employee.aggregate(
[ {$match: {“name”: “xyz” } }
{ $project: { salary:1, _id:0} } ]
)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aggregationinmongo-140327064744-phpapp02/75/Aggregation-Framework-in-MongoDB-Overview-Part-1-19-2048.jpg)