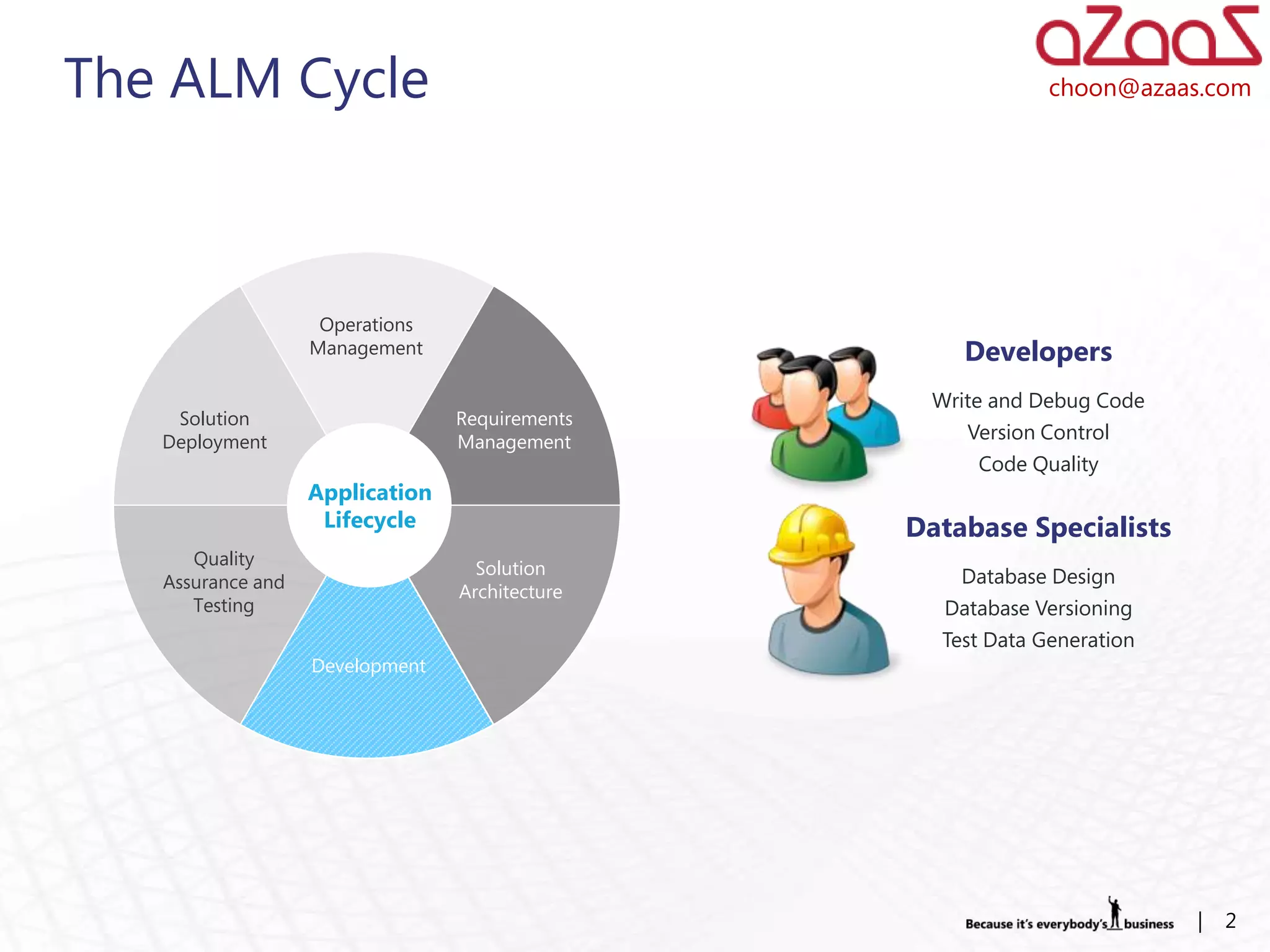
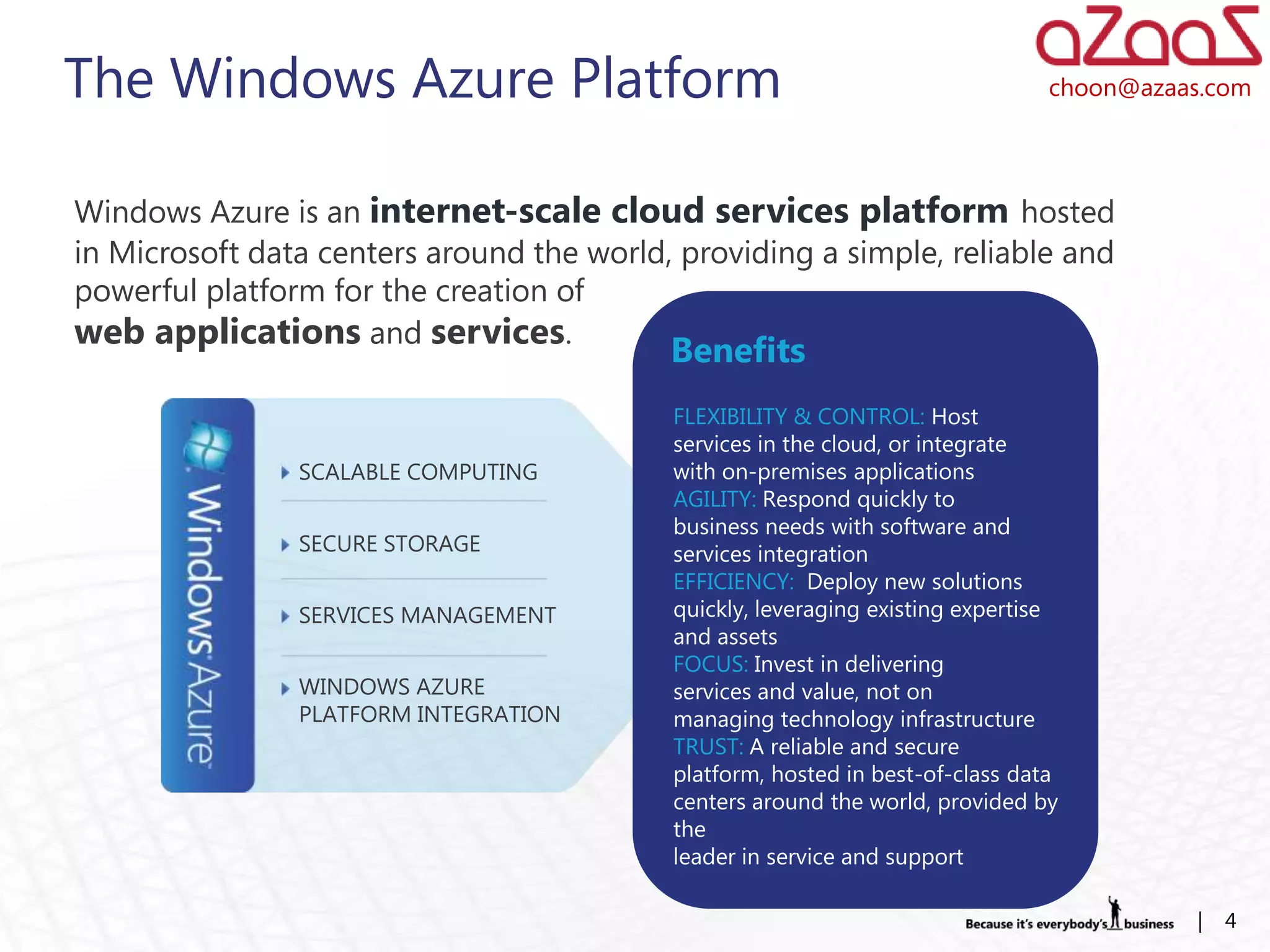
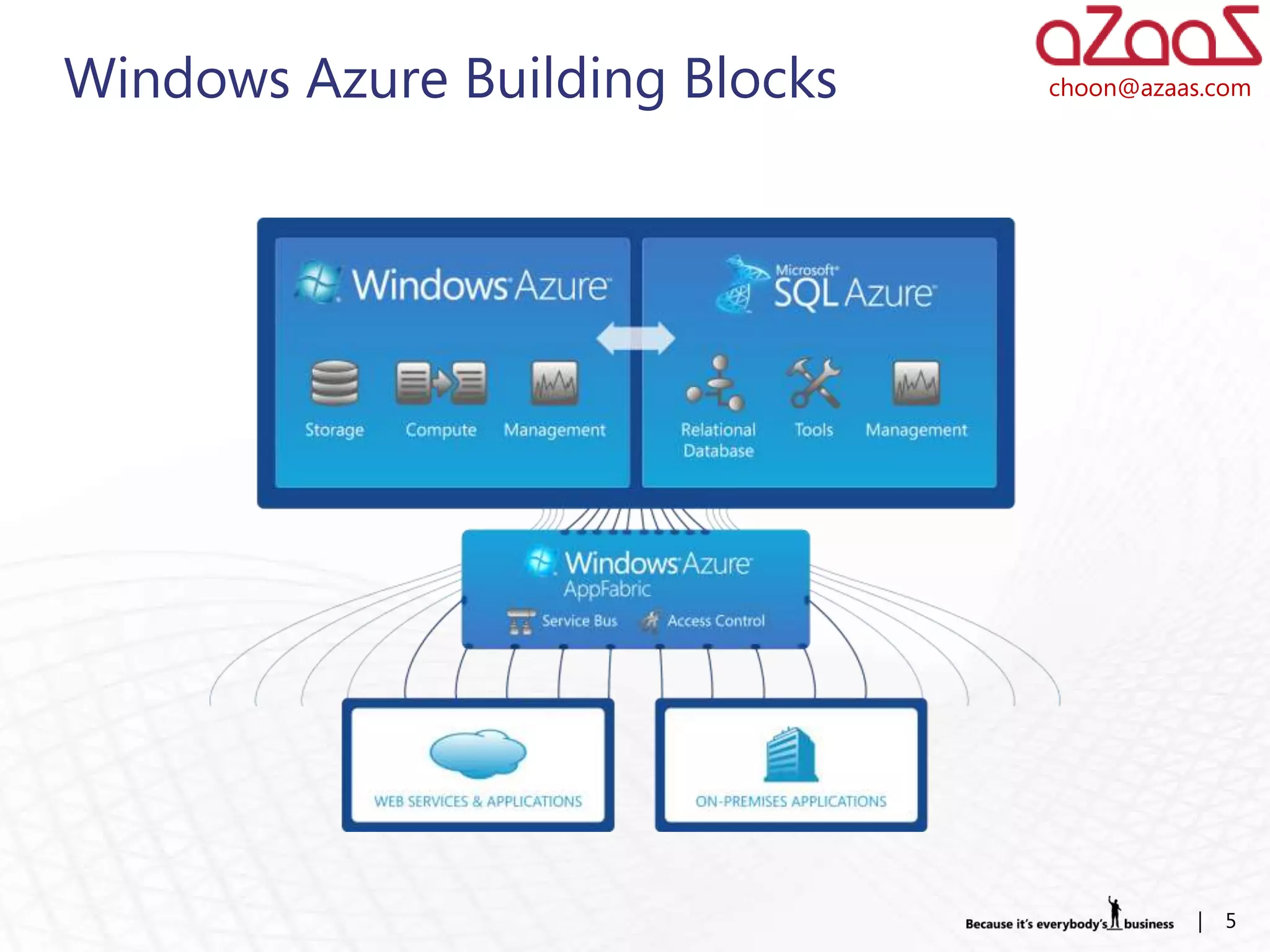
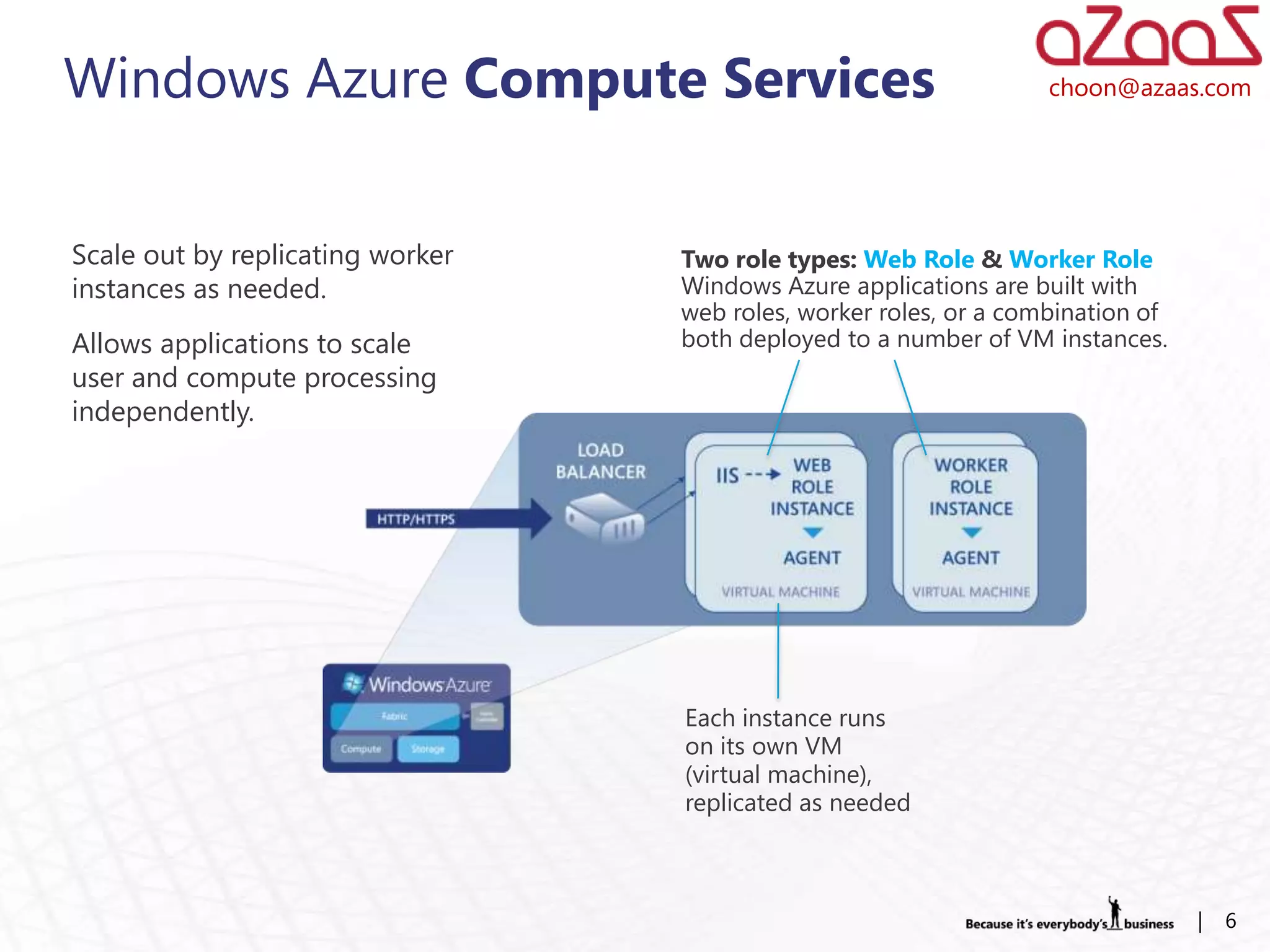
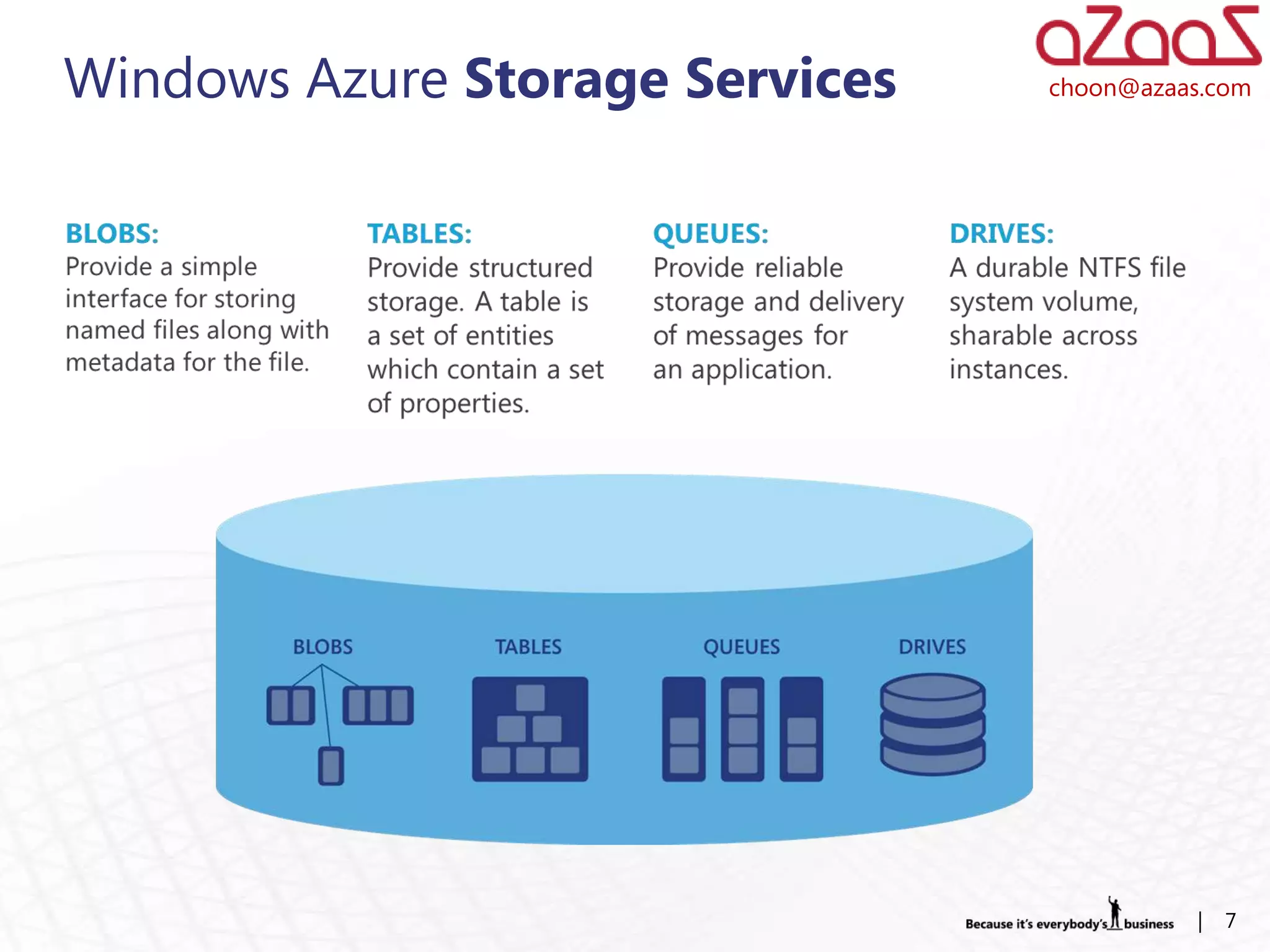
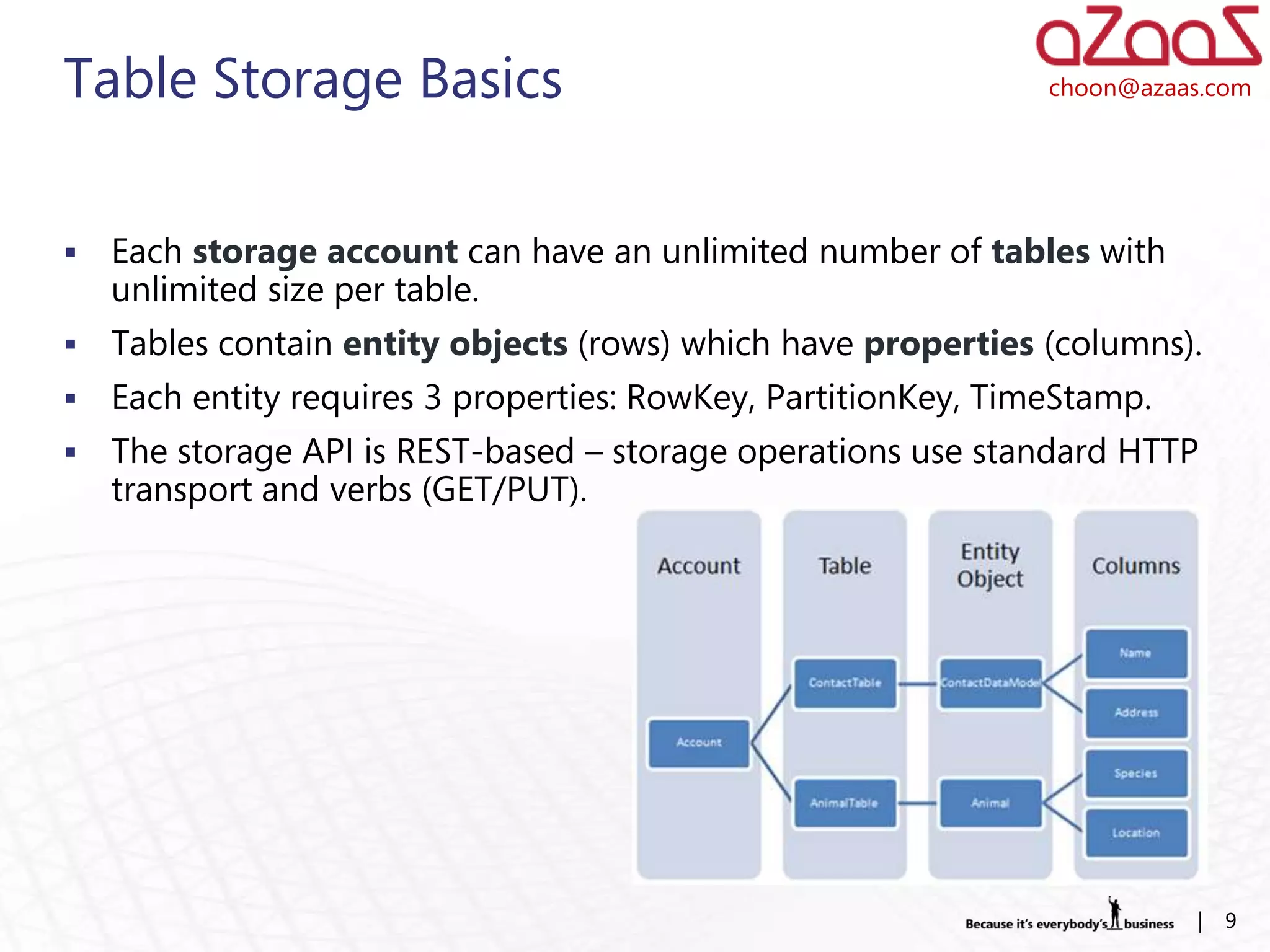
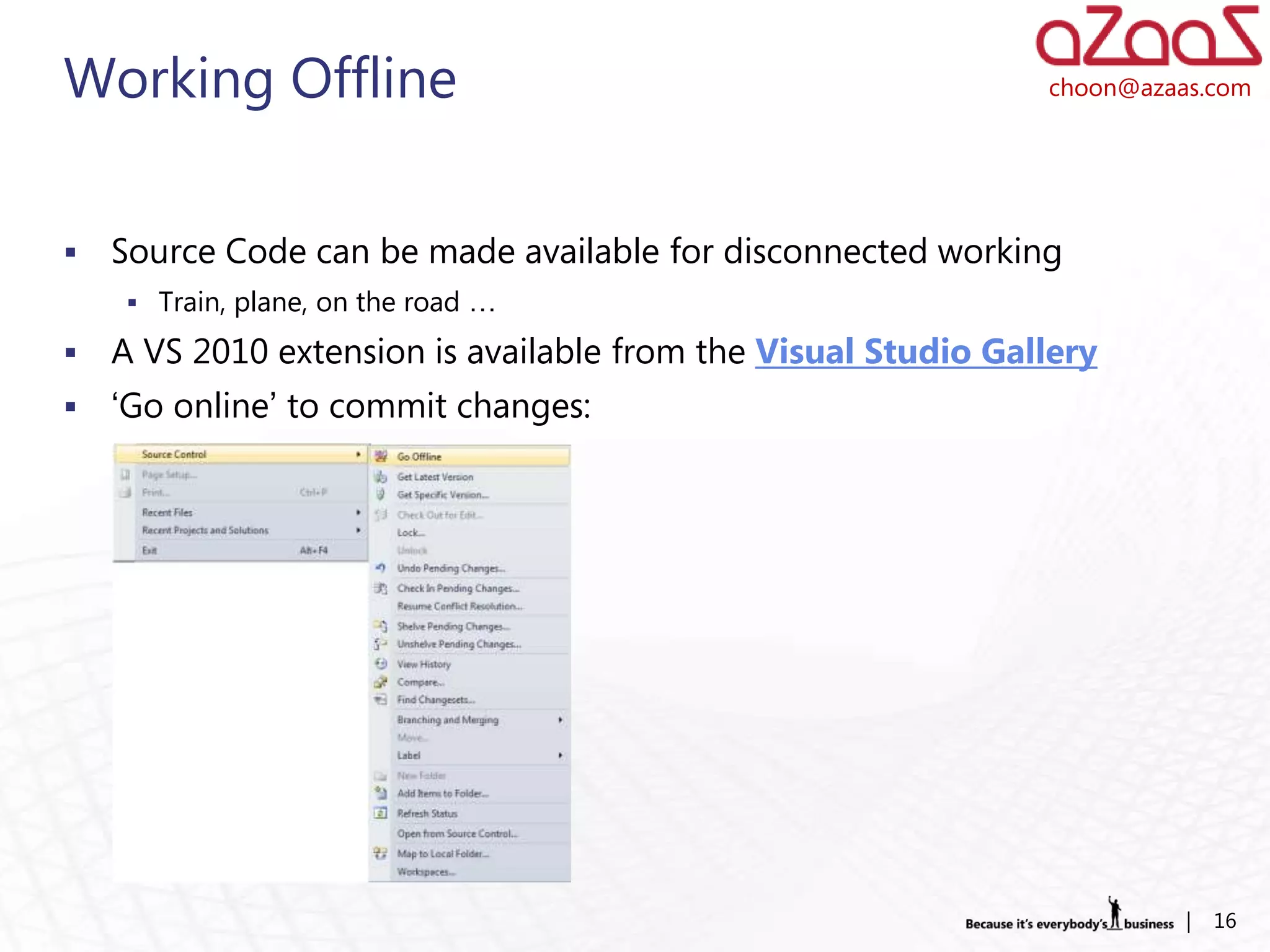
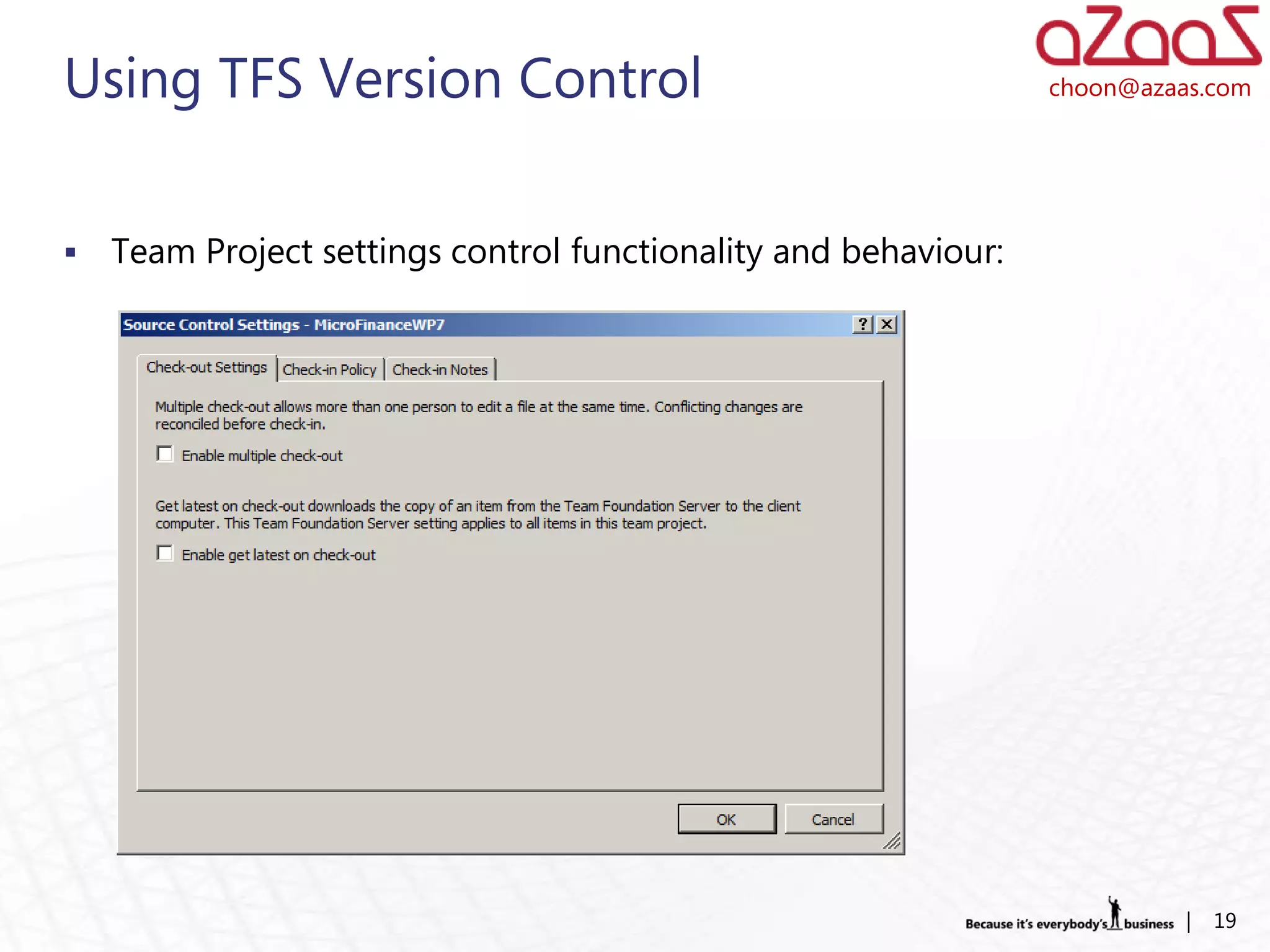
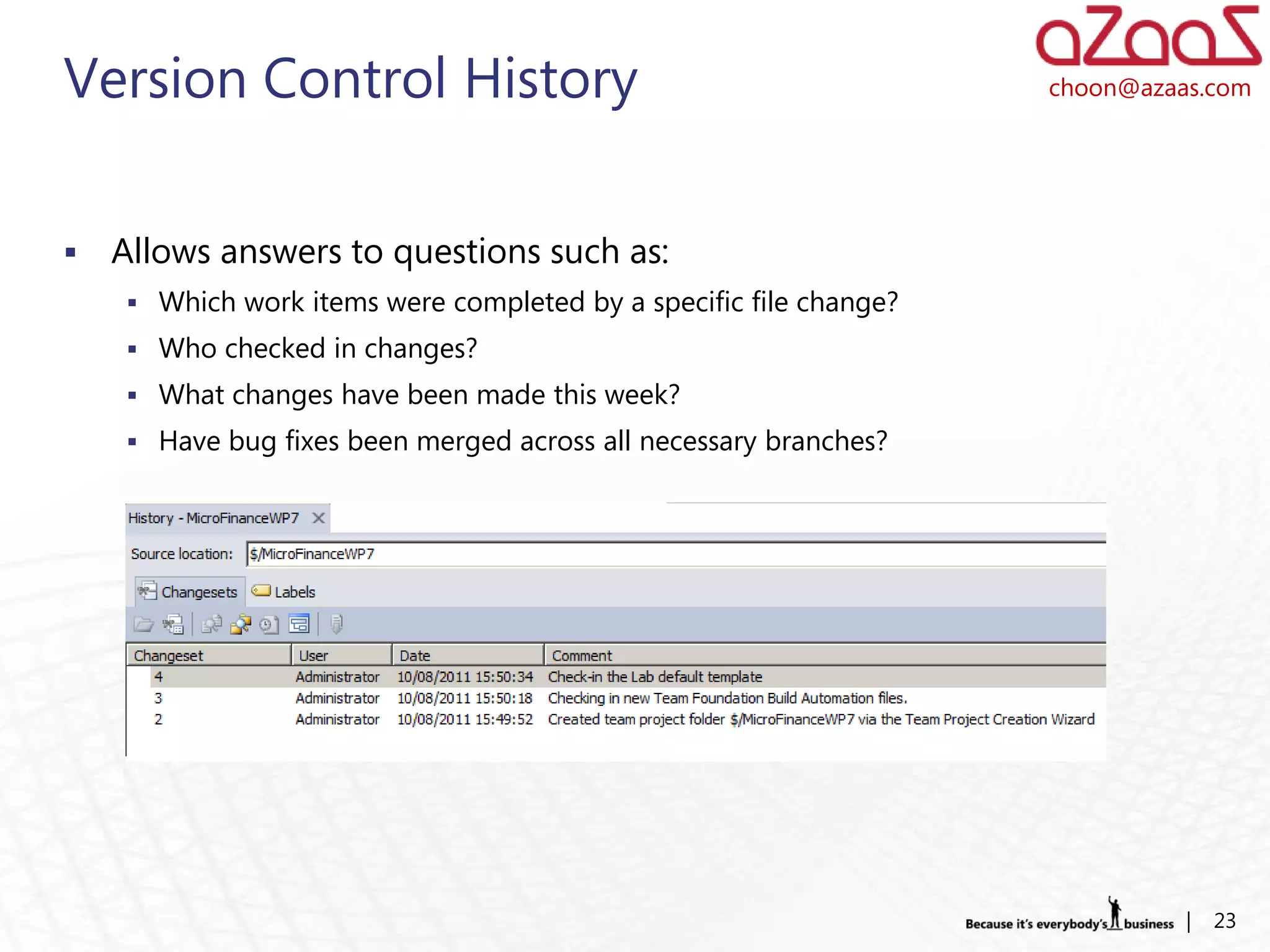
The document discusses how developers can use Visual Studio 2010 and Team Foundation Server (TFS) to work in an Agile environment. It describes how developers can set up their development environment by getting the required source code from TFS, identify and manage their work using work items and queries, work offline by making source code available, and enhance code quality using check-in policies and notes.